Yonsei Med J.
2009 Oct;50(5):601-612. 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.601.
Challenge and Hope in Radiotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Liver Cancer Special Clinic, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jsseong@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1103811
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.601
Abstract
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most critical global health issues. With frequent association of viral liver disease, HCC is highly complex, harboring both cancer and chronic liver disease. The tumor stage and underlying liver function are both major determinants of the treatment selection as well as prognosis in HCC patients, thus allowing no more than a 20% chance for potentially curative therapies. Radiotherapy technology has been evolved remarkably during the past decade, and radiation can be precisely delivered, thereby permitting higher doses to the tumour and reduced doses to surrounding normal tissues. There has been increasing interest in the merits of radiotherapy in HCC over the past few years, as indicated by a Pub Med search. Radiotherapy has been used as the definitive therapy with curative intent in early stage tumours. It has been used also in combination with TACE for intermediate stage tumours. In locally advanced tumours, radiotherapy has been combined with systemic agents. Despite its efficacy, radiotherapy has not yet been incorporated into the standard management guidelines of HCC. The lack of high evidence level data, especially randomized controlled trials, has posed an obstacle in including radiotherapy into the routine treatment schema of HCC. Therefore, well-designed prospective studies are strongly recommended using developing technology for radiotherapy alone or combination therapies. Also, many issues such as the optimal dose-fractionation, intra- or extrahepatic metastasis after radiotherapy, and radiation-induced hepatic dysfunction remain to be solved. In this review, current status of radiotherapy for HCC will be discussed with regard to technical consideration and combination strategy. The limitation and future perspectives will also be discussed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
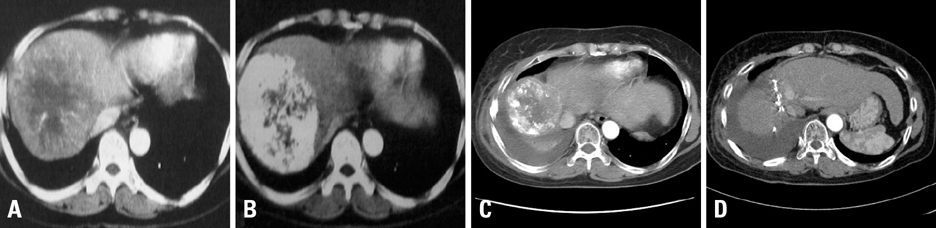
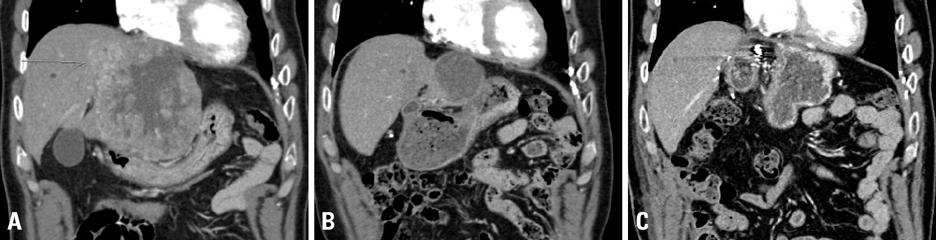
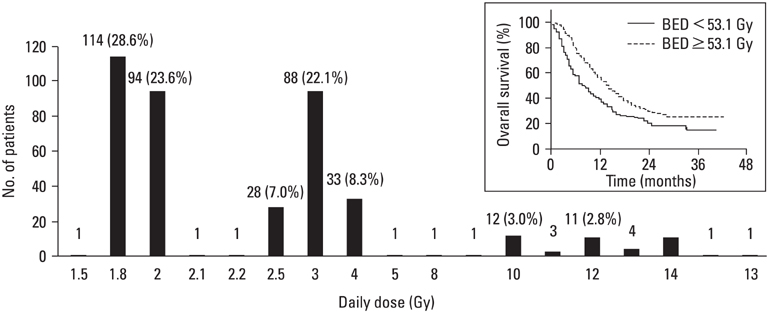
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Solitary Extrahepatic Intraabdominal Metastasis from Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation
Sae Byeol Choi, Hyungi Kim, Sung Hoon Kim, Young Nyun Park, Kyung Sik Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(1):199-203. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.1.199.Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy Shows Long-Term Survival after Conversion from Locally Advanced to Resectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ik Jae Lee, Jun Won Kim, Kwang Hyub Han, Ja Kyung Kim, Kyung Sik Kim, Jin Sub Choi, Young Nyun Park, Jinsil Seong
Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(6):1489-1497. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.6.1489.
Reference
-
1. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005. 55:74–108.
Article2. Joo KR, Bang SJ, Song BC, Youn KH, Joo YH, Yang SH, et al. Hepatitis B viral markers of Korean adults in the late 1990s: survey data of 70,347 health screenees. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999. 33:642–652.3. Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M, Cléries R. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:5 Suppl 1. S5–S16.
Article4. Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM, Beaugrand M, Lencioni R, Burroughs AK, et al. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol. 2001. 35:421–430.
Article5. Bruix J, Sherman M. Practice Guidelines Committee. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005. 42:1208–1236.
Article6. Llovet JM, Real MI, Montana X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J, et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002. 359:1734–1739.
Article7. Yuen MF, Chan AO, Wong BC, Hui CK, Ooi GC, Tso WK, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for inoperable, early stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with Child-Pugh grade A and B; results of a comparative study in 96 Chinese patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. 98:1181–1185.8. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:378–390.
Article9. Thomas M. Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2009. 44:Suppl 19. 136–141.
Article10. Ingold JA, Reed GB, Kaplan HS, Bagshaw MA. Radiation hepatitis. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1965. 93:200–208.11. Lawrence TS, Robertson JM, Anscher MS, Jirtle RL, Ensminger WD, Fajardo LF. Hepatic toxicity resulting from cancer treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995. 31:1237–1248.
Article12. Seong J, Keum KC, Han KH, Lee DY, Lee JT, Chon CY, et al. Combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and local radiotherapy of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999. 43:393–397.
Article13. Seong J, Park HC, Han KH, Lee DY, Lee JT, Chon CY, et al. Local radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients who failed with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000. 47:1331–1335.
Article14. Seong J, Park HC, Han KH, Chon CY, Chu SS, Kim GE, et al. Clinical results of 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic patients. Hepatol Res. 2003. 27:30–35.
Article15. Seong J, Park HC, Han KH, Chon CY. Clinical results and prognostic factors in radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 158 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. 55:329–336.
Article16. Park W, Lim DH, Paik SW, Koh KC, Choi MS, Park CK, et al. Local radiotherapy for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 61:1143–1150.
Article17. Cheng JC, Chuang VP, Cheng SH, Huang AT, Lin YM, Cheng TI, et al. Local radiotherapy with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000. 47:435–442.
Article18. Dawson LA, McGinn CJ, Normolle D, Ten Haken RK, Walker S, Ensminger W, et al. Escalated focal liver radiation and concurrent hepatic artery fluorodeoxyuridine for unresectable intrahepatic malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2000. 18:2210–2218.
Article19. Masuda T, Beppu T, Ishiko T, Horino K, Baba Y, Mizumoto T, et al. Intrahepatic dissemination of hepatocellular carcinoma after local ablation therapy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2008. 15:589–595.
Article20. Matsumoto Y, Fujii H, Matsuda M, Kono H. Multicentric occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnosis and clinical significance. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2001. 8:435–440.
Article21. Cochrane AM, Murray-Lyon IM, Brinkley DM, Williams R. Quadruple chemotherapy versus radiotherapy in treatment of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1977. 40:609–614.
Article22. Friedman MA, Volberding PA, Cassidy MJ, Resser KJ, Wasserman TH, Phillips TL. Therapy for hepatocellular cancer with intrahepatic arterial adriamycin and 5-fluorouracil combined with whole-liver irradiation: a Northern California Oncology Group Study. Cancer Treat Rep. 1979. 63:1885–1888.23. Stillwagon GB, Order SE, Guse C, Klein JL, Leichner PK, Leibel SA, et al. 194 hepatocellular cancers treated by radiation and chemotherapy combinations: toxicity and response: a Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989. 17:1223–1229.
Article24. Park HC, Seong J, Han KH, Chon CY, Moon YM, Suh CO. Dose-response relationship in local radiotherapy for hepatocellulcar carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. 54:150–155.
Article25. Tai A, Erickson B, Khater KA, Li XA. Estimate of radiobiologic parameters from clinical data for biologically based treatment planning for liver irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. 70:900–907.
Article26. Withers HR, Taylor JM. Critical volume model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992. 25:151–152.
Article27. Niemierko A, Goitein M. Modeling of normal tissue response to radiation: the critical volume model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993. 25:135–145.
Article28. Ben-Josef E, Normolle D, Ensminger WD, Walker S, Tatro D, Ten Haken RK, et al. Phase II trial of high-dose conformal radiation therapy with concurrent hepatic artery floxuridine for unresectable intrahepatic malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:8739–8747.29. Seong J, Han KH, Park YN, Nam SH, Kim SH, Keum WS, et al. Lethal hepatic injury by combined treatment of radiation plus chemotherapy in rats with thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. 57:282–288.30. Rubin P, Casarett GW. Clinical radiation pathology. 1968. vol 1. Philadelphia: WB Saunders.31. Emami B, Lyman J, Brown A, Coia L, Goitein M, Munzenrider JE, et al. Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991. 21:109–122.
Article32. Mornex F, Girard N, Beziat C, Kubas A, Khodri M, Trepo C, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of high-dose three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in cirrhotic patients with small-size hepatocellular carcinoma non-eligible for curative therapies--mature results of the French Phase II RTF-1 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 66:1152–1158.
Article33. Lee IJ, Seong J, Shim SJ, Han KH. Radiotherapeutic parameters predictive of liver complications induced by liver tumor radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. 73:154–158.
Article34. Xu ZY, Liang SX, Zhu J, Zhu XD, Zhao JD, Lu HJ, et al. Prediction of radiation-induced liver disease by Lyman normal-tissue complication probability model in three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy for primary liver carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 65:189–195.
Article35. Cheng JC, Wu JK, Lee PC, Liu HS, Jian JJ, Lin YM, et al. Biologic susceptibility of hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy to radiation-induced liver disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 60:1502–1509.
Article36. Dawson LA, Normolle D, Balter JM, McGinn CJ, Lawrence TS, Ten Haken RK. Analysis of radiation-induced liver disease using the Lyman NTCP model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. 53:810–821.
Article37. Dawson LA, Ten Haken RK, Lawrence TS. Partial irradiation of the liver. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2001. 11:240–246.
Article38. Shirato H, Shimizu S, Shimizu T, Nishioka T, Miyasaka K. Real-time tumour-tracking radiotherapy. Lancet. 1999. 353:1331–1332.39. Case RB, Sonke JJ, Moseley DJ, Kim J, Brock KK, Dawson LD. Inter- and intrafraction variability in liver position in non-breath-hold stereotactic body radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. 75:302–308.40. Balter JM, Brock KK, Litzenberg DW, McShan DL, Lawrence TS, Ten Haken R, et al. Daily targeting of intrahepatic tumors for radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. 52:266–271.41. Jiang SB. Radiotherapy of mobile tumors. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2006. 16:239–248.
Article42. Murphy MJ. Tracking moving organs in real time. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004. 14:91–100.43. Dancey JE, Shepherd FA, Paul K, Sniderman KW, Houle S, Gabrys J, et al. Treatment of nonresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with intrahepatic 90Y-microspheres. J Nucl Med. 2000. 41:1673–1681.44. Geschwind JF, Salem R, Carr BI, Soulen MC, Thurston KG, Goin KA, et al. Yttrium-90 microspheres for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:S194–S205.
Article45. Order S, Pajak T, Leibel S, Asbell S, Leichner P, Ettinger D, et al. A randomized prospective trial comparing full dose chemotherapy to 131I antiferritin: an RTOG study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991. 20:953–963.46. Raoul JL, Guyader D, Bretagne JF, Heautot JF, Duvauferrier R, Bourguet P, et al. Prospective randomized trial of chemoembolization versus intra-arterial injection of 131I-labeled-iodized oil in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1997. 26:1156–1161.
Article47. Kim JK, Han KH, Lee JT, Paik YH, Ahn SH, Lee JD, et al. Long-term clinical outcome of phase IIb clinical trial of percutaneous injection with holmium-166/chitosan complex (Milican) for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12:543–548.
Article48. Sohn JH, Choi HJ, Lee JT, Lee JD, Kim JH, Moon YM, et al. Phase II study of transarterial holmium-166-chitosan complex treatment in patients with a single, large hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2009. 76:1–9.
Article49. Ho S, Lau WY, Leung TW, Chan M, Johnson PJ, Li AK. Clinical evaluation of the partition model for estimating radiation doses from yttrium-90 microspheres in the treatment of hepatic cancer. Eur J Nucl Med. 1997. 24:293–298.
Article50. Blomgren H, Lax I, Näslund I, Svanström R. Stereotactic high dose fraction radiation therapy of extracranial tumors using an accelerator. Clinical experience of the first thirty-one patients. Acta Oncol. 1995. 34:861–870.
Article51. Wulf J, Guckenberger M, Haedinger U, Oppitz U, Mueller G, Baier K, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy of primary liver cancer and hepatic metastases. Acta Oncol. 2006. 45:838–847.
Article52. Méndez Romero A, Wunderink W, Hussain SM, De Pooter JA, Heijmen BJ, Nowak PC, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors: a single institution phase i-ii study. Acta Oncol. 2006. 45:831–837.
Article53. Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G, Kim JJ, Cummings B, Knox J, et al. Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:657–664.
Article54. Sakurai M, Okamura J, Kuroda C. Transcatheter chemoembolization effective for treating hepatocellular carcinoma. A histopathologic study. Cancer. 1984. 54:387–392.55. Yu YQ, Xu DB, Zhou XD, Lu JZ, Tang ZY, Mack P. Experience with liver resection after hepatic arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1993. 71:62–65.56. Higuchi T, Kikuchi M, Okazaki M. Hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter hepatic arterial embolization. A histopathologic study of 84 resected cases. Cancer. 1994. 73:2259–2267.
Article57. Baker DG, Krochak RJ. The response of the microvascular system to radiation: a review. Cancer Invest. 1989. 7:287–294.58. Byfield JE, Lynch M, Kulhanian F, Chan PY. Cellular effects of combined adriamycin and x-irradiation in human tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 1977. 19:194–204.
Article59. Nakamura H, Hashimoto T, Oi H, Sawada S. Transcatheter oily chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 1989. 170:783–786.
Article60. Raoul JL, Heresbach D, Bretagne JF, Ferrer DB, Duvauferrier R, Bourguet P, et al. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinomas. A Study of the biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin. Cancer. 1992. 70:585–590.
Article61. Shim SJ, Seong J, Han KH, Chon CY, Suh CO, Lee JT. Local radiotherapy as a complement to incomplete transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2005. 25:1189–1196.62. Yasuda S, Ito H, Yoshikawa M, Shinozaki M, Goto N, Fujimoto H, et al. Radiotherapy for large hepatocellular carcinoma combined with transcatheter arterial embolization and percutaneous ethanol injection therapy. Int J Oncol. 1999. 15:467–473.
Article63. Guo WJ, Yu EX. Evaluation of combined therapy with chemoembolization and irradiation for large hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Radiol. 2000. 73:1091–1097.
Article64. Chia-Hsien Cheng J, Chuang VP, Cheng SH, Lin YM, Cheng TI, Yang PS, et al. Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radiotherapy and/or chemoembolization. Int J Cancer. 2001. 96:243–252.65. Zeng ZC, Tang ZY, Fan J, Zhou J, Qin LX, Ye SL, et al. A comparison of chemoembolization combination with and without radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer J. 2004. 10:307–316.66. Meng MB, Cui YL, Lu Y, She B, Chen Y, Guan YS, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in combination with radiotherapy of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2009. 92:184–194.67. Robertson JM, Lawrence TS, Dworzanin LM, Andrews JC, Walker S, Kessler ML, et al. Treatment of primary hepatobiliary cancers with conformal radiation therapy and regional chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1993. 11:1286–1293.
Article68. Kim JS, Han KH, Lee DY, Seong JS, Youn YH, Cheong JY, et al. Concurrent chemoradiation therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. Korean J Hepatol. 2002. 8:71–79.69. Han KH, Seong J, Kim JK, Ahn SH, Lee do Y, Chon CY. Pilot clinical trial of localized concurrent chemoradiation therapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. Cancer. 2008. 113:995–1003.
Article70. Tandon P, Garcia-Tsao G. Prognostic indicators in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of 72 studies. Liver Int. 2009. 29:502–510.
Article71. Kim JK, Kim MN, Han KH, Seong JS, Lee DY, Lee JT, et al. Prospective large scaled trial of concurrent intraarterial chemoradiation therapy following repeated intraarterial chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. J Hepatol. 2008. 48:S148.72. Hsu WC, Chan SC, Ting LL, Chung NN, Wang PM, Ying KS, et al. Results of three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and thalidomide for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2006. 36:93–99.73. Zeng ZC, Fan J, Tang ZY, Zhou J, Qin LX, Wang JH, et al. A comparison of treatment combinations with and without radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein and/or inferior vena cava tumor thrombus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 61:432–443.
Article74. Nakagawa K, Yamashita H, Shiraishi K, Nakamura N, Tago M, Igaki H, et al. Radiation therapy for portal venous invasion by hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. 11:7237–7241.
Article75. You CR, Jang JW, Kang SH, Bae SH, Choi JY, Yoon SK, et al. [Efficacy of transarterial chemolipiodolization with or without 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for huge HCC with portal vein tumor thrombosis]. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:378–386.
Article76. Kim TH, Kim DY, Park JW, Kim YI, Kim SH, Park HS, et al. Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients for whom transcatheter arterial chemoembolization was ineffective or unsuitable. Am J Clin Oncol. 2006. 29:568–575.
Article77. Kim DY, Park W, Lim DH, Lee JH, Yoo BC, Paik SW, et al. Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for portal vein thrombosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2005. 103:2419–2426.78. Kim JS, Han KH, Lee DY, Seong JS, Youn YH, Cheong JY, et al. [Concurrent chemo-radiation therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis]. Taehan Kan Hakhoe Chi. 2002. 8:71–79.79. Schulz-Ertner D, Tsujii H. Particle radiation therapy using proton and heavier ion beams. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:953–964.80. Kawashima M, Furuse J, Nishio T, Konishi M, Ishii H, Kinoshita T, et al. Phase II study of radiotherapy employing proton beam for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:1839–1846.81. Kato H, Tsujii H, Miyamoto T, Mizoe JE, Kamada T, Tsuji H, et al. Results of the first prospective study of carbon ion radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with liver cirrhosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 59:1468–1476.82. Seong J, Lee IJ, Shim SJ, Lim do H, Kim TH, Kim JH, et al. A multicenter retrospective cohort study of practice patterns and clinical outcome on radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea. Liver Int. 2009. 29:147–152.
Article83. Cheng SH, Lin YM, Chuang VP, Yang PS, Cheng JC, Huang AT, et al. A pilot study of three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999. 14:1025–1033.
Article84. Han KH, Lee JT, Seong J. Treatment of non-resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. 17:Suppl 3. S424–S427.
Article85. Cheng JC, Chou CH, Kuo ML, Hsieh CY. Radiation-enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion with MMP-9 expression through PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. Oncogene. 2006. 25:7009–7018.
Article86. Jiang Y, Xu W, Lu J, He F, Yang X. Invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines: contribution of hepatocyte growth factor, c-met, and transcription factor Ets-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. 286:1123–1130.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differences in radiotherapy application according to regional disease characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Recent developments in radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Novel paradigm in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Anticipating breakthroughs with particle therapy
- Current status of stereotactic body radiotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Treated by Hepatic Artery Injection Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy