Korean J Ophthalmol.
2007 Sep;21(3):146-150. 10.3341/kjo.2007.21.3.146.
Evaluation of the Efficacy of Vitrectomy for Persistent Diabetic Macular Edema and Associated Factors Predicting Outcome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Hangil Eye Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. jiani4@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1099029
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2007.21.3.146
Abstract
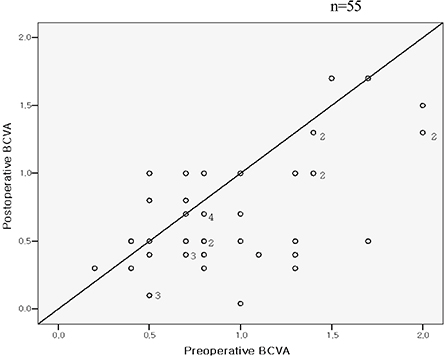
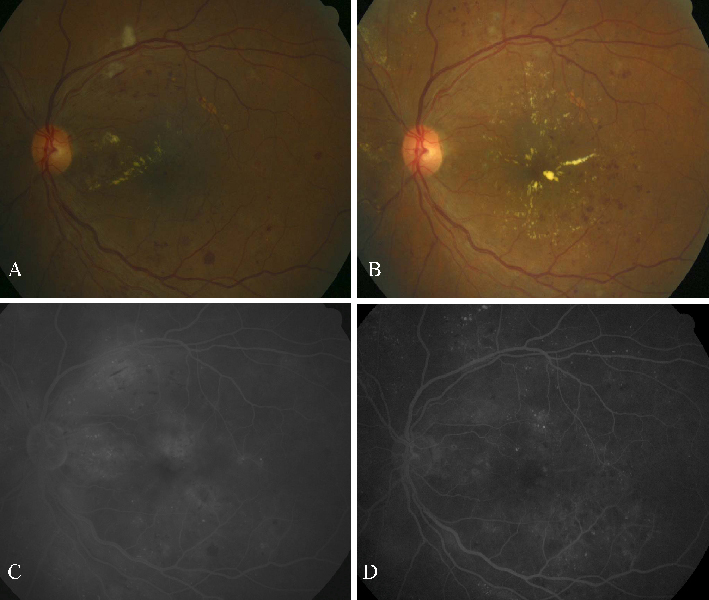
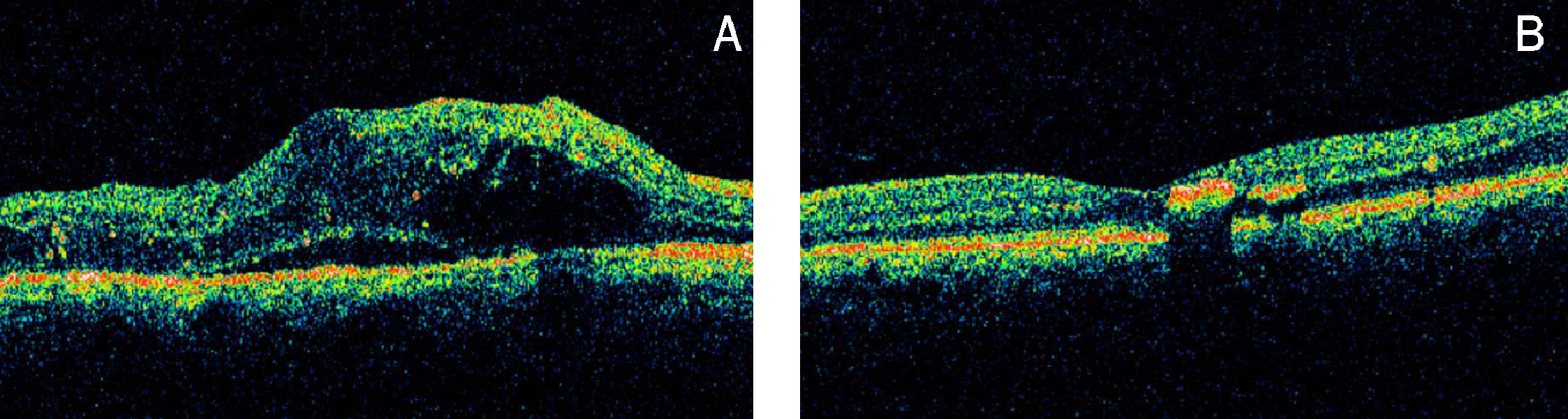
- PURPOSE: To evaluate the efficacy of vitrectomy for persistent diabetic macular edema after laser photocoagulation or intravitreal triamcinolone injections and to determine the demographic and ocular factors that influence functional and anatomical outcomes. METHODS: We retrospectively evaluated 55 eyes (51 patients) that had persistent diffuse macular edema after laser photocoagulation or intravitreal triamcinolone injections. We compared preoperative and postoperative best corrected visual acuity and macular thickness by Optical Coherence Tomography and investigated factors including patient's age, presence of vitreomacular traction, grade of diabetic retinopathy, and intraoperative internal limiting membrane removal that may influence the surgical results. RESULTS: The mean preoperative BCVA (log MAR) was 0.91+/-0.40 (0.8-1.2). The BCVA improved to 0.72+/-0.39 (0.3-1.2). The mean preoperative macular thickness was 440+/-130 (202-805) micrometer and the mean macular thickness decreased to 306+/-97 (136-580) micrometer postoperatively. The eyes showed statistically significant improvement in BCVA and central macular thickness (p<0.001). Preoperative better BCVA was associated with an improved postoperative visual acuity. (p=0.04). No other covariates were found to be statistically significant factors for prognosis of postoperative BCVA. CONCLUSIONS: In eyes with persistent diabetic macular edema after laser or IVTA injections, vitrectomy was effective for decreasing macular thickness and improvement of vision. The visual improvement after vitrectomy was associated with the preoperative better BCVA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stefaniotou MI, Aspiotis MV, Kalogeropoulos CD. Vitrectomy results for diffuse DME with and without ILM removal. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2004. 14:137–143.2. Dillinger P, Mester U. Vitrectomy with removal of the internal limiting membrane in chronic diabetic macular oedema. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2004. 242:630–637.3. Kralinger MT, Pedri M, Kralinger F, et al. Long-term outcome after vitrectomy for diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmologica. 2006. 220:147–152.4. Jahn CE, Topfner von Schutz K, Richter J, et al. Improvement of visual acuity in eyes with diabetic macular edema after treatment with pars plana vitrectomy. Ophthalmologica. 2004. 218:378–384.5. Stolba U, Binder S, Gruber D, et al. Vitrectomy for persistent diffuse diabetic macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005. 140:295–301.6. Tachi N, Ogino N. Vitrectomy for diffuse macular edema in cases of diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996. 122:258–260.7. Shah S, Patel M, Thomas D, et al. Factors predicting outcome of vitrectomy for diabetic macular oedema: results of a prospective study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006. 90:33–36.8. Klein R, Klein B, Moss S, et al. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy. IV. Diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 1984. 91:1464–1474.9. Klein R, Klein B, Moss S. Visual impairment in diabetes. Ophthalmology. 1984. 91:1–8.10. The Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Photocoagulation for diabetic macular edema. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study report no 1. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985. 103:1796–1806.11. Massin , Audren F, Haouchine B, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for diabetic diffuse macular edema. Preliminary results of a prospective controlled trial. Ophthalmology. 2004. 111:218–224.12. Jonas JB, Kreissig I, Sofker A, Degenring RF. Intravitreal injection of triamcinolone for diffuse diabetic macular edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003. 121:57–61.13. Martidis A, Duker JS, Greenberg PB, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for refractory diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2002. 109:920–927.14. Lewis H, Abrams GW, Blumenkranz MS, Campo RV. Vitrectomy for diabetic macular traction edema associated with posterior hyaloidal traction. Ophthalmology. 1992. 99:753–759.15. Gandorfer A, Messmer EM, Ulbig MW, Kampik A. Resolution of diabetic macular edema after surgical removal of the posterior hyaloid and the inner limiting membrane. Retina. 2000. 20:126–133.16. Bahadir M, Ertan A, Mertoglu O. Visual acuity comparison of vitrectomy with and without internal limiting membrane removal in the treatment of diabetic macular edema. Int Ophthalmol. 2005. 26:3–8.17. Avci R, Kaderli B, Avci B, et al. Pars plana vitrectomy and removal of the internal limiting membrane in the treatment of chronic macular oedema. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2004. 242:845–852.18. Kamura Y, Sato Y, Isomae T, Shimada H. Effects of internal limiting membrane peeling in vitrectomy on diabetic cystoid macular edema patients. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2005. 49:297–300.19. Ikagawa H, Yoneda M, Iwaki M, et al. Chemical toxicity of indocyanine green damages retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. 46:2531–2539.20. Yamamoto T, Hitani K, Sato Y, et al. Pars plana vitrectomy with and without peeling of the inner limiting membrane for diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmologica. 2005. 219:206–213.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Efficiency of Vitrectomy for Diabetic Macular Edema
- A Multimodal Approach to Diabetic Macular Edema
- Clinical Analysis of Combined Vitrectomy and Phacoemulsification with Intraocular Lens Implantation for Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
- Analysis of Vitrectomy Results in Diabetic Macular Edema using Optical Coherence Tomography
- Risk Factors for Diffuse Diabetic Macular Edema as Classified by Optical Coherence Tomography