Korean J Lab Med.
2011 Jan;31(1):30-36. 10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.1.30.
Distribution of Virulence Genes in spa Types of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients in Intensive Care Units
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. euichong@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 1096657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.1.30
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Various virulence factors and superantigens are encoded by mobile genetic elements. The relationship between clonal background and virulence factors differs in different geographic regions. We compared the distribution and relationship of spa types and virulence genes among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains isolated from a tertiary hospital in 2000-01 and 2007-08.
METHODS
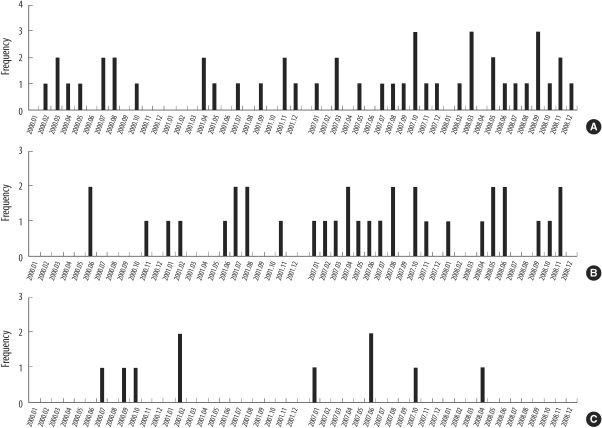
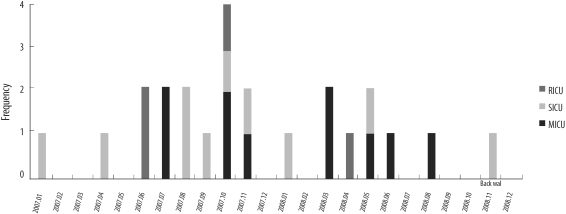
In 2000-01 and 2007-08, 94 MRSA strains were collected from 3 intensive care units at a Korean tertiary hospital. We performed spa typing and multiplex PCR for 19 superantigen genes.
RESULTS
Relatively frequent spa types were t037 (40.5%), t002, t601, and t2138 in 2000-01, and t2460 (43.9%), t002, t037, t601, t324, and t2139 in 2007-08. We identified 4 novel spa types, 2 of which were designated as t5076 and t5079. Superantigen profiles were closely linked to spa types. For example, sea, sek, and seq superantigen genes were mainly detected in t037 strains.
CONCLUSIONS
Major spa types differed depending on study periods, and the distribution of superantigen genes correlated with spa type.
MeSH Terms
-
Bacterial Typing Techniques
DNA, Bacterial/chemistry
Genotype
Humans
Intensive Care Units/statistics & numerical data
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus/genetics/*isolation & purification/pathogenicity
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Staphylococcal Infections/microbiology
Superantigens/genetics
Virulence/genetics
Virulence Factors/*genetics
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holtfreter S, Grumann D, Schmudde M, Nguyen HT, Eichler P, Strommenger B, et al. Clonal distribution of superantigen genes in clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:2669–2680. PMID: 17537946.2. Diep BA, Carleton HA, Chang RF, Sensabaugh GF, Perdreau-Remington F. Roles of 34 virulence genes in the evolution of hospital- and community-associated strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 2006; 193:1495–1503. PMID: 16652276.3. Niemeyer DM, Pucci MJ, Thanassi JA, Sharma VK, Archer GL. Role of mecA transcriptional regulation in the phenotypic expression of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1996; 178:5464–5471. PMID: 8808937.4. Koreen L, Ramaswamy SV, Graviss EA, Naidich S, Musser JM, Kreiswirth BN. spa typing method for discriminating among Staphylococcus aureus isolates: implications for use of a single marker to detect genetic micro- and macrovariation. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:792–799. PMID: 14766855.5. Frénay HM, Bunschoten AE, Schouls LM, van Leeuwen WJ, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, Verhoef J, et al. Molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on the basis of protein A gene polymorphism. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1996; 15:60–64. PMID: 8641305.6. Lindsay JA, Moore CE, Day NP, Peacock SJ, Witney AA, Stabler RA, et al. Microarrays reveal that each of the ten dominant lineages of Staphylococcus aureus has a unique combination of surface-associated and regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 2006; 188:669–676. PMID: 16385056.7. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Twelfth informational supplement, M100-S12. 2002. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards.8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Nineteenth informational supplement, M100-S19. 2009. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.9. Mehrotra M, Wang G, Johnson WM. Multiplex PCR for detection of genes for Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin 1, and methicillin resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38:1032–1035. PMID: 10698991.10. Hwang SY, Kim SH, Jang EJ, Kwon NH, Park YK, Koo HC, et al. Novel multiplex PCR for the detection of the Staphylococcus aureus superantigen and its application to raw meat isolates in Korea. Int J Food Microbiol. 2007; 117:99–105. PMID: 17439826.11. Aires de Sousa M, Conceição T, Simas C, de Lencastre H. Comparison of genetic backgrounds of methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Portuguese hospitals and the community. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:5150–5157. PMID: 16207977.12. Witte W, Strommenger B, Cuny C, Heuck D, Nuebel U. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus containing the Panton-Valentine leucocidin gene in Germany in 2005 and 2006. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007; 60:1258–1263. PMID: 17934203.13. Varshney AK, Mediavilla JR, Robiou N, Guh A, Wang X, Gialanella P, et al. Diverse enterotoxin gene profiles among clonal complexes of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from the Bronx, New York. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009; 75:6839–6849. PMID: 19749060.14. Jarraud S, Peyrat MA, Lim A, Tristan A, Bes M, Mougel C, et al. egc, a highly prevalent operon of enterotoxin gene, forms a putative nursery of superantigens in Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 2001; 166:669–677. PMID: 11123352.15. Hu DL, Omoe K, Inoue F, Kasai T, Yasujima M, Shinagawa K, et al. Comparative prevalence of superantigenic toxin genes in meticillin-resistant and meticillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Med Microbiol. 2008; 57:1106–1112. PMID: 18719180.16. Peck KR, Baek JY, Song JH, Ko KS. Comparison of genotypes and enterotoxin genes between Staphylococcus aureus isolates from blood and nasal colonizers in a Korean hospital. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:585–591. PMID: 19654937.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection in Neonates
- Multilocus Sequence Typing of Clonal Changes of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Intensive Care Unit Patients: 1996 versus 2004
- Genetic Variability of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Strains Isolated from Burns Patients
- A case of multiple furunculosis caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococcs aureus