Korean J Radiol.
2011 Apr;12(2):196-202. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.2.196.
Gallbladder Tuberculosis: CT Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China. yurisheng2003@yahoo.com.cn
- 2Department of Radiology, Zhejiang Medical College, Hangzhou 310053, China.
- KMID: 1088564
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.2.196
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We wanted to describe the computed tomography (CT) findings of gallbladder tuberculosis (TB) and to correlate them with pathologic findings.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
There were seven patients (M:F = 3:4; mean age, 46.3 years; age range, 32 to 78 years) in whom gallbladder TB was eventually diagnosed. All of them underwent cross-sectional imaging with CT, a pathologic examination and a retrospective review. CT imaging evaluation was done in each case, including the findings of a mass versus nodule, wall thickening (uniform or irregular) and the enhancement patterns (homogeneous or heterogeneous).
RESULTS
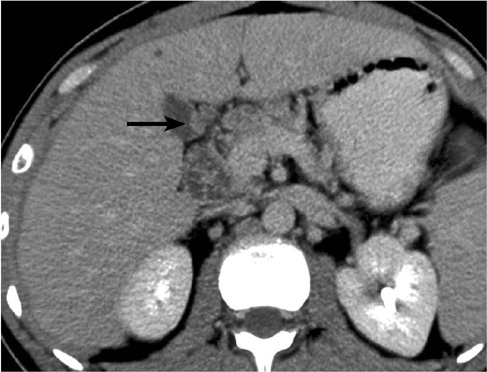
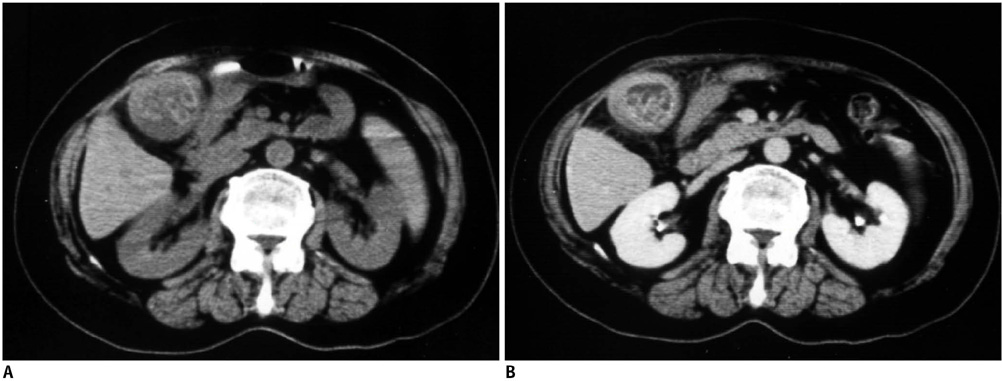
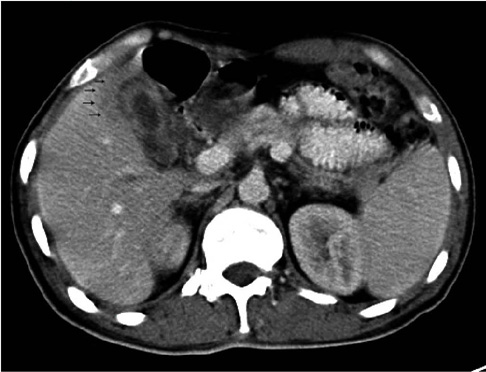
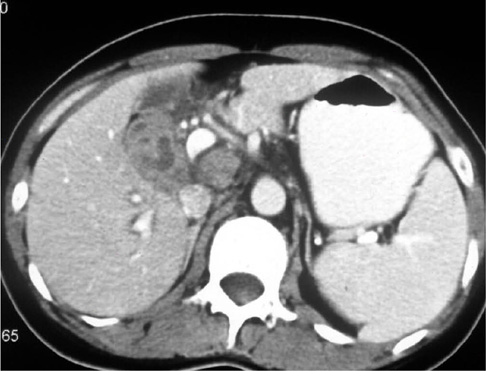
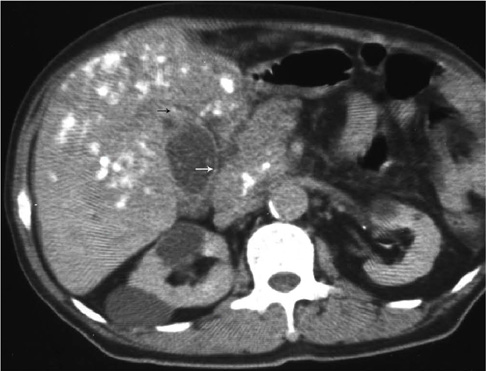
All the cases of gallbladder TB revealed the following three different CT findings: micronodular lesion of the gallbladder wall (n = 1), a thickened wall (n = 4) and a gallbladder mass (n = 2). There were three cases of homogeneous enhancement of the lesions, including homogeneous enhancement with nodular lesion, homogeneous uniform thickness enhancement and homogeneous thickness enhancement in one case each, and these cases pathology showed tuberculous granuloma with a little caseating necrosis in one case and tuberculous granuloma with rich fibrous tissue, but little or no evident caseating necrosis in two cases. Four cases of heterogeneous enhancement of the lesions, including heterogeneous uniform-thickness enhancement in two cases, heterogeneous enhancement with a local mass lesion in one case and heterogeneous enhancement with a mass that replaced the gallbladder in one case; in these cases, pathology showed tuberculous granuloma with marked caseation or liquefaction necrosis in three cases and tuberculous granuloma by fibrous and calcifications accompanied by caseating necrosis in one case. Among the seven cases of gallbladder TB, six cases were accompanied by abdominal extra-gallbladder TB, including abdominal lymph node TB in five cases and hepatic TB in four cases.
CONCLUSION
Gallbladder TB has various CT manifestations, and the enhanced CT findings are well matched with pathological features. An irregularly thickened gallbladder wall or a gallbladder wall mass with multiple-focus necrosis or calcifications accompanied by the typical CT findings of abdominal extra-gallbladder TB should suggest the diagnosis of gallbladder TB.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Gallbladder Tuberculosis Diagnosed by Positive Tuberculosis-Polymerase Chain Reaction
Mi Jin Ryu, Tae Joo Jeon, Ji Young Park, Yena Choi, Seung Suk Baek, Dong Hyun Sinn, Tae Hoon Oh, Jung Yeon Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2014;63(1):51-55. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2014.63.1.51.
Reference
-
1. Chen CH, Yang CC, Yeh YH, Yang JC, Chou DA. Pancreatic tuberculosis with obstructive jaundice--a case report. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999. 94:2534–2536.2. WHO. Tuberculosis control and research strategies for the 1990's. Memorandum from a WHO-meeting. Bull World Health Organ. 1992. 70:17–21.3. Yilmaz T, Sever A, Gur S, Killi RM, Elmas N. CT findings of abdominal tuberculosis in 12 patients. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2002. 26:321–325.4. Yang ZG, Min PQ, Sone S, He ZY, Liao ZY, Zhou XP, et al. Tuberculosis versus lymphomas in the abdominal lymph nodes: evaluation with contrast-enhanced CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 172:619–623.5. Saluja SS, Ray S, Pal S, Kukeraja M, Srivastava DN, Sahni P, et al. Hepatobiliary and pancreatic tuberculosis: a two decade experience. BMC Surg. 2007. 7:10.6. Ramia JM, Muffak K, Fernandez A, Villar J, Garrote D, Ferron JA. Gallbladder tuberculosis: false-positive PET diagnosis of gallbladder cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:6559–6560.7. Abu-Zidan FM, Zayat I. Gallbladder tuberculosis (case report and review of the literature). Hepatogastroenterology. 1999. 46:2804–2806.8. Jain R, Sawhney S, Bhargava D, Berry M. Gallbladder tuberculosis: sonographic appearance. J Clin Ultrasound. 1995. 23:327–329.9. Kumar K, Ayub M, Kumar M, Keswani NK, Shukla HS. Tuberculosis of the gallbladder. HPB Surg. 2000. 11:401–404.10. Duan JG, Liu CL, Chen Y. One case of gallbladder tuberculosis. Chin J Radiol. 1992. 26:379. [Chinese].11. Hahn ST, Park SH, Shin WS, Kim CY, Shinn KS. Gallbladder tuberculosis with perforation and intrahepatic biloma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1995. 20:84–86.12. Rouas L, Mansouri F, Jahid A, Zouaidia F, Saidi H, Nabih N, et al. Gallbladder tuberculosis associated with cholelithiasis. Rev Med Liege. 2003. 58:757–760. [French].13. Strelis AK, Liadunkin IE, Zadorozhnii AI. Diagnosis of disorders of the bile excretory system in patients with tuberculosis in association with chronic opisthorchiasis. Probl Tuberk. 1989. 1:74–75. [Russian].14. D'Agata A, Funto I, Lazzi S, Boncompagni G. Video laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a case of biliary lithiasis associated with gallbladder tuberculosis. Considerations and review of the literature. Minerva Chir. 1997. 52:1103–1108. [Italian].15. Nakajo S, Yamamoto M, Urushihara T, Kajitani T, Tahara E. Diffuse papillomatosis of the gallbladder complicated with tuberculosis. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1988. 38:1473–1480.16. Kim SJ, Lee JM, Lee JY, Choi JY, Kim SH, Han JK, et al. Accuracy of preoperative T-staging of gallbladder carcinoma using MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 190:74–80.17. Banerjee S, Sen S. Tuberculosis of the gall bladder. J Indian Med Assoc. 2003. 101:556–557.18. Ruhl KM, Krones CJ, Hermanns B, Schumpelick V. Tuberculosis of the gall bladder. Chirurg. 2003. 74:478–481. [German].19. Ben RJ, Young T, Lee HS. Hepatobiliary tuberculosis presenting as a gall bladder tumor. Scand J Infect Dis. 1995. 27:415–417.20. Lee YH, Kim SH, Cho MY, Rhoe BS, Kim MS. Actinomycosis of the gallbladder mimicking carcinoma: a case report with US and CT findings. Korean J Radiol. 2007. 8:169–172.21. Henriquez M, Trejo C, Ojeda M, Benavides A. Tuberculosis of the pancreas, an anatomoclinical case. Rev Med Chil. 1992. 120:1153–1157. [Spanish].
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Gallbladder Tuberculosis
- Intramural Hypoattenuated Nodules in Thickened Wall of the Gallbladder: CT Features According to Their Primary Causes
- Ceftriaxone-Associated Biliary Pseuodolithiasis: Sonographic and CT Findings
- A Case of Gallbladder Tuberculosis Diagnosed by Positive Tuberculosis-Polymerase Chain Reaction
- CT findings of traumatic gallblandder perforation