Yonsei Med J.
2010 May;51(3):475-477. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.475.
Subarachnoid and Intraventricular Hemorrhage due to Ruptured Aneurysm after Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology & Pain Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ysshin@yuhs.ac
- 2Anesthesia & Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1075008
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.475
Abstract
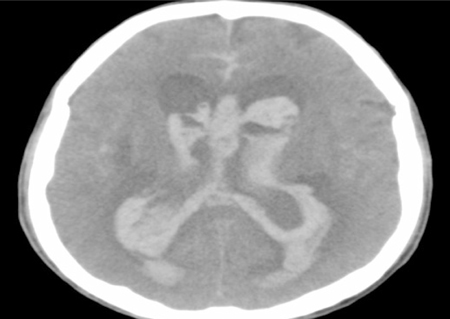
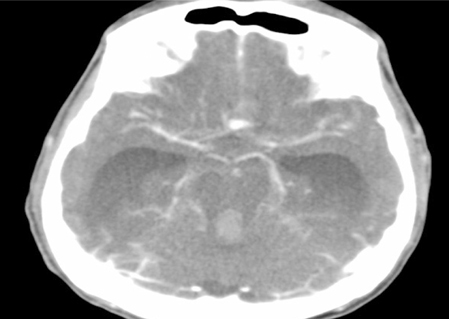
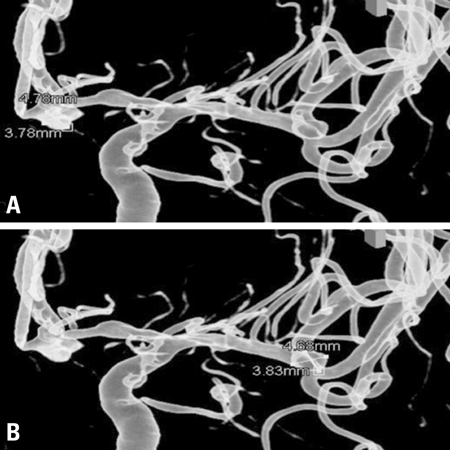
- A patient received combined spinal-epidural anesthesia for a scheduled total knee arthroplasty. After an injection of spinal anesthetic and ephedrine due to a decrease in blood pressure, the patient developed a severe headache. The patient did not respond to verbal command at the completion of the operation. A brain CT scan revealed massive subarachnoid and intraventricular hemorrhages, and a CT angiogram showed a ruptured aneurysm. Severe headaches should not be overlooked in an uncontrolled hypertensive patient during spinal anesthesia because it may imply an intracranial and intraventricular hemorrhage due to the rupture of a hidden aneurysm.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. van Gijn J, Rinkel GJ. Subarachnoid haemorrhage: diagnosis, causes and management. Brain. 2001. 124:249–278.
Article2. van Gijn J, Kerr RS, Rinkel GJ. Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 2007. 369:306–318.
Article3. Pulsinelli WA. Bennett JC, Plum F, editors. Cerebrovascular diseases, aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cecil's textbook of medicine. 1996. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;2073–2076.4. Wijdicks EF, Kallmes DF, Manno EM, Fulgham JR, Piepgras DG. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: neurointensive care and aneurysm repair. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005. 80:550–559.
Article5. Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, Vincent AJ, Hofman A, Krestin GP, et al. Incidental findings on brain MRI in the general population. N Engl J Med. 2007. 357:1821–1828.
Article6. El Khaldi M, Pernter P, Ferro F, Alfieri A, Decaminada N, Naibo L, et al. Detection of cerebral aneurysms in nontraumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage: role of multislice CT angiography in 130 consecutive patients. Radiol Med. 2007. 112:123–137.
Article7. Eggert SM, Eggers KA. Subarachnoid haemorrhage following spinal anaesthesia in an obstetric patient. Br J Anaesth. 2001. 86:442–444.
Article8. Sherer DM, Onyeije CI, Yun E. Pneumocephalus following inadvertent intrathecal puncture during epidural anesthesia: a case report and review of the literature. J Matern Fetal Med. 1999. 8:138–140.
Article9. Böttiger BW, Diezel G. [Acute intracranial subarachnoid hemorrhage following repeated spinal anesthesia]. Anaesthesist. 1992. 41:152–157.10. Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:Suppl 1. S5–S20.11. Banerji MA, Lebovitz HE. Insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant variants in NIDDM. Diabetes. 1989. 38:784–792.
Article12. Priebe HJ. Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage and the anaesthetist. Br J Anaesth. 2007. 99:102–118.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Embolization Therapy for a Ruptured Spinal Artery Aneurysm Associated with Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformation and Presenting with Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Intraventricular Hemorrhage due to Aneurysm of the Distal Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery: Case Report
- A Ruptured Aneurysm in the Branch of the Anterior Spinal Artery
- Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysm in a 45-day-old Infant
- Surgical Removal of a Ruptured Radiculomedullary Artery Aneurysm: A Case Report