J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2017 Sep;19(3):217-222. 10.7461/jcen.2017.19.3.217.
Surgical Removal of a Ruptured Radiculomedullary Artery Aneurysm: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. neurosurgeryban@gmail.com
- KMID: 2393506
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.3.217
Abstract
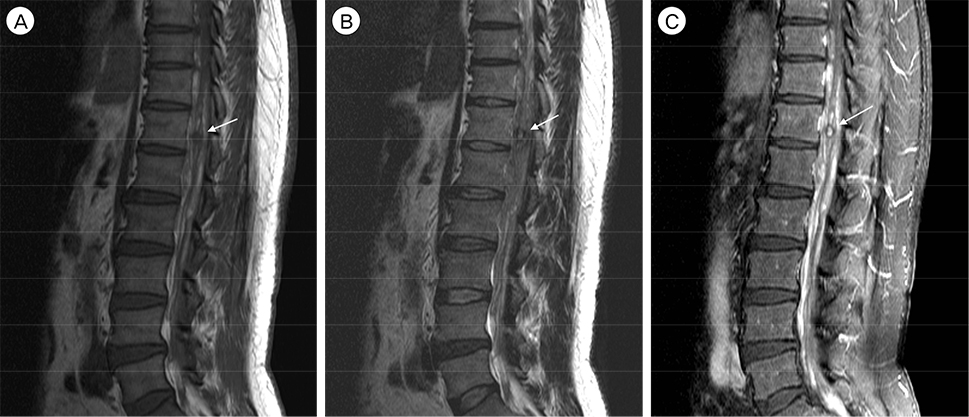
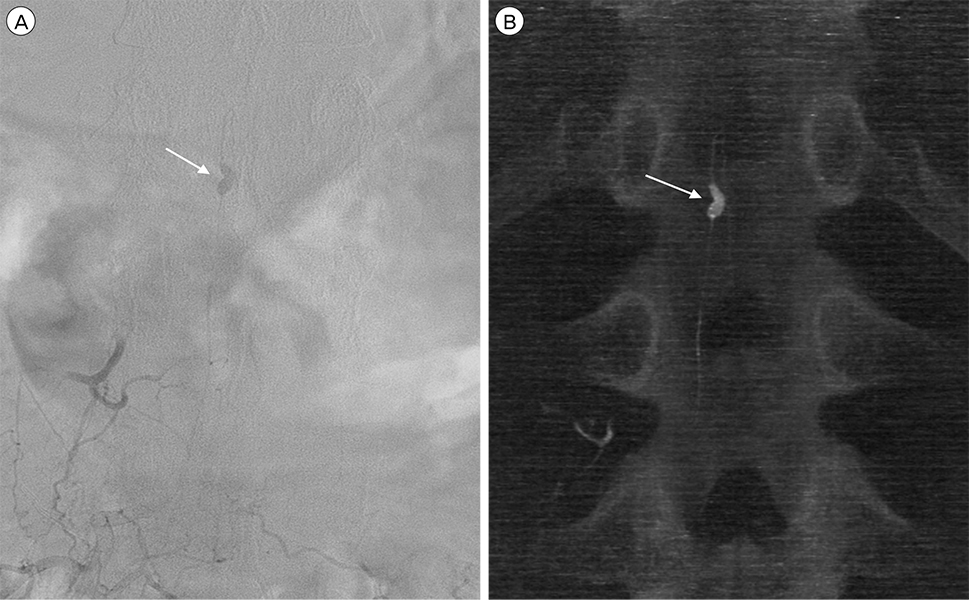
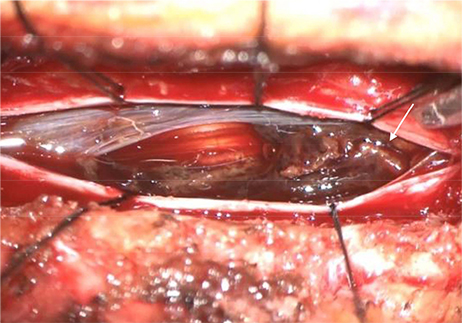
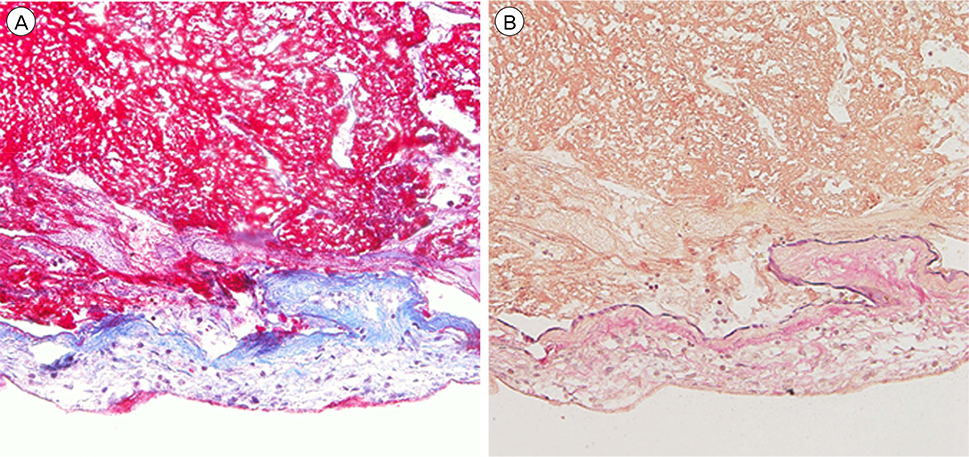
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage due to a solitary spinal aneurysm is extremely rare, and diagnosis and treatment are challenging. We report a rare case of a ruptured radiculomedullary artery aneurysm in a patient with Behçet disease. A 49-year-old man presented with severe lower abdominal and leg pain. Magnetic resonance imaging was performed and an enhanced intradural-extramedullary lesion at the T12 spinal level with subarachnoid hemorrhage was identified. Diagnostic spinal angiography was performed to evaluate the vascular lesion, and a radiculomedullary artery aneurysm at the T12 level was identified. We performed surgical resection of the aneurysm and a good neurological outcome was obtained.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bahar S, Coban O, Gürvit IH, Akman-Demir G, Gökyiğit A. Spontaneous dissection of the extracranial vertebral artery with spinal subarachnoid heaemorrhage in a patient with Behçet's disease. Neuroradiology. 1993; 35(5):352–354.2. Berlis A, Scheufler KM, Schmahl C, Rauer S, Götz F, Schumacher M. Solitary spinal artery aneurysms as a rare source of spinal subarachnoid hemorrhage: potential etiology and treatment strategy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 02. 26(2):405–410.3. Garcia CA, Dulcey S, Dulcey J. Ruptured aneurysm of the spinal artery of Adamkiewicz during pregnancy. Neurology. 1979; 03. 29(3):394–398.
Article4. Gonzalez LF, Zabramski JM, Tabrizi P, Wallace RC, Massand MG, Spetzler RF. Spontaneous spinal subarachnoid hemorrhage secondary to spinal aneurysms: diagnosis and treatemtn paradigm. Neurosurgery. 2005; 12. 57(6):1127–1131. discussion 1127-31.5. Gutierrez Romero D, Batista AL, Gentric JC, Raymond J, Roy D, Weill A. Ruptured isolated spinal artery aneurysms. Report of two cases and review of the literature. Interv Neuroradiol. 2014; 12. 20(6):774–780.
Article6. Iihoshi S, Miyata K, Murakami T, Kaneko T, Koyanagi I. Dissection aneurysm of the radiculomedullary branch of the artery of Adamkiewicz with subarachnoid hmorrhage. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2011; 51(9):649–652.7. Kawamura S, Yoshida T, Nonoyama Y, Yamada M, Suzuki A, Yasui N. Ruptured anterior spinal artery aneurysm: a case report. Surg Neurol. 1999; 06. 51(6):608–612.
Article8. Kim HJ, Choi IS. Dissecting aneurysm of the posterior spinal artery: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2012; 09. 71(3):E749–E756. discussion E756.9. Lavoie P, Raymond J, Roy D, Guilbert F, Weill A. Selective treatment of an anterior spinal artery aneurysm with endosaccular coil therapy. Case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 05. 6(5):460–464.10. Li S. Analysis of 27 cases of large vascular lesions in 161 cases of Behcet's disease: clinical manifestations and treatment outcome. Clin Rheumatol. 2014; 05. 33(5):671–675.
Article11. Massand MG, Wallace RC, Gonzalez LF, Zabramski JM, Spetzler RF. Subarachnoid hemorrhage due to isolated spinal artery aneurysm in four patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 10. 26(9):2415–2419.12. Nakamura H, Kim P, Kanaya H, Kurokawa R, Murata H, Matsuda H. Spinal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by a Mycotic Aneurysm of the Radiculomedullary Artery A Case Report and Review of Literature. NMC Case Rep J. 2015; 03. 2(2):49–52.
Article13. Rengachary SS, Duke DA, Tsai FY, Kragel PJ. Spinal arterial aneurysm: case report. Neurosurgery. 1993; 33(1):125–129. discussion 129-30.14. Son S, Lee SG, Park CW. Solitary ruptured aneurysm of the spinal artery of adamkiewicz with subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013; 07. 54(1):50–53.
Article15. Tsuda K, Ohkura K, Shintani T, Saito T, Shiiya N. Endovascular treatment of a ruptured innominate artery aneurysm in Behcet disease. Ann Vasc Surg. 2016; 05. 33:230.e1–230.e4.
Article16. Vishteh AG, Brown AP, Spetzler RF. Aneurysm of the intradural artery of Adamkiewicz treated with muslin wrapping: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 1997; 01. 40(1):207–209.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Ruptured Aneurysm in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Case Report
- Surgical Treatment of Ruptured Renal Artery Aneurysm: A Report of 2 Cases
- Subdural Hematoma Due to Ruptured Intracerebral Aneurysm
- Ruptured proximal anterior cerebral artery (A1) aneurysm located at an anomalous branching of the fronto-orbital artery--a case report
- Coil Embolization of a Ruptured Anterior Spinal Artery Aneurysm Associated with Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformation