Yonsei Med J.
2011 Nov;52(6):1044-1047. 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.6.1044.
Frontal Sinus Lymphoma Presenting As Progressive Multiple Cranial Nerve Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhyoon@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1058831
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2011.52.6.1044
Abstract
- Primary frontal sinus lymphoma is a very uncommon disease. In all the previously reported cases, the presenting symptoms have been due to the tumor mass effect. We present an unusual case report of an immunocompetent patient who presented with facial palsy, and then progressively developed other cranial nerve palsies over several months. He was later diagnosed with diffuse large B cell lymphoma originating from the frontal sinus. The patient underwent chemotherapy, but eventually had to receive autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. He is currently disease-free. The clinical course, diagnostic workup, and therapeutic outcome are described.
MeSH Terms
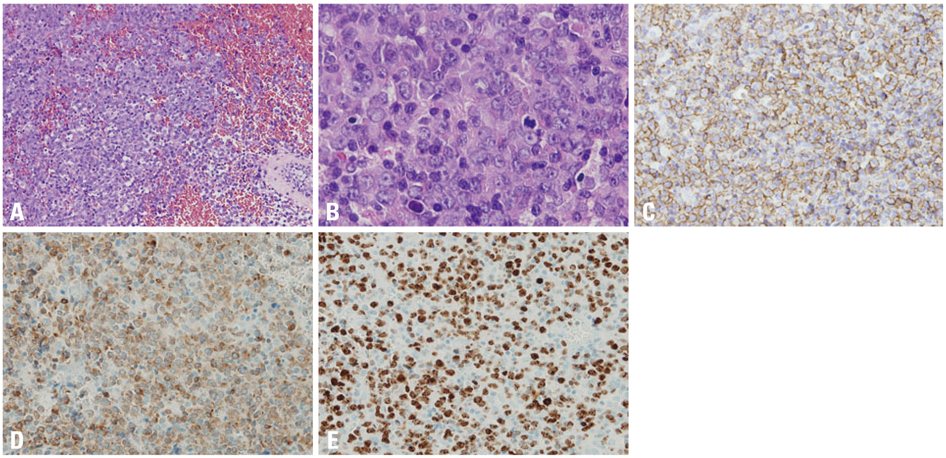
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fellbaum C, Hansmann ML, Lennert K. Malignant lymphomas of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989. 414:399–405.
Article2. Vidal RW, Devaney K, Ferlito A, Rinaldo A, Carbone A. Sinonasal malignant lymphomas: a distinct clinicopathological category. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999. 108:411–419.
Article3. Keane JR. Multiple cranial nerve palsies: analysis of 979 cases. Arch Neurol. 2005. 62:1714–1717.4. Nemet AY, Deckel Y, Kourt G. Orbital invasion of frontal sinus lymphoma. Orbit. 2006. 25:149–151.
Article5. el-Hakim H, Ahsan F, Wills LC. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the frontal sinus: how we diagnosed it. Ear Nose Throat J. 2000. 79:738741–743.
Article6. Neves MC, Lessa MM, Voegels RL, Butugan O. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the frontal sinus: case report and review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J. 2005. 84:47–51.7. Burres SA, Crissman JD, McKenna J, Al-Sarraf M. Lymphoma of the frontal sinus. Case report and review of literature. Arch Otolaryngol. 1984. 110:270–273.8. Chain JR, Kingdom TT. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the frontal sinus presenting as osteomyelitis. Am J Otolaryngol. 2007. 28:42–45.9. Duncavage JA, Campbell BH, Hanson GA, Kun LE, Hansen RM, Toohill RJ, et al. Diagnosis of malignant lymphomas of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and nasopharynx. Laryngoscope. 1983. 93:1276–1280.
Article10. Cooper DL, Ginsberg SS. Brief chemotherapy, involved field radiation therapy, and central nervous system prophylaxis for paranasal sinus lymphoma. Cancer. 1992. 69:2888–2893.
Article11. Spiro JD, Soo KC, Spiro RH. Nonsquamous cell malignant neoplasms of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses. Head Neck. 1995. 17:114–118.
Article12. Hatta C, Ogasawara H, Okita J, Kubota A, Ishida M, Sakagami M. Non-Hodgkin's malignant lymphoma of the sinonasal tract--treatment outcome for 53 patients according to REAL classification. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2001. 28:55–60.
Article13. Shohat I, Berkowicz M, Dori S, Horowitz Z, Wolf M, Taicher S, et al. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the sinonasal tract. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004. 97:328–331.14. Yoon SO, Jeon YK, Paik JH, Kim WY, Kim YA, Kim JE, et al. MYC translocation and an increased copy number predict poor prognosis in adult diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), especially in germinal centre-like B cell (GCB) type. Histopathology. 2008. 53:205–217.
Article15. Niitsu N, Okamoto M, Miura I, Hirano M. Clinical features and prognosis of de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with t (14;18) and 8q24/c-MYC translocations. Leukemia. 2009. 23:777–783.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Head and Neck Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Presenting as Progressive Multiple Cranial Nerve Palsy
- A Case of Neurolymphomatosis Involving Cranial Nerve Diagnosed by PET-CT Imaging
- Isolated Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Caused by Onodi Cell Sinusitis
- The Etiology and Clinical Feature of the Third, Fourth, and Sixth Cranial Nerve Palsy
- Isolated Sphenoid Sinus Mucocele Presenting as Third Nerve Palsy