Korean J Ophthalmol.
2005 Dec;19(4):302-304. 10.3341/kjo.2005.19.4.302.
A Case of Complete Ophthalmoplegia in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pochun CHA University College of Medicine, Pundang CHA Hospital, Sungnam, Korea. eye@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 754444
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2005.19.4.302
Abstract
- PURPOSE
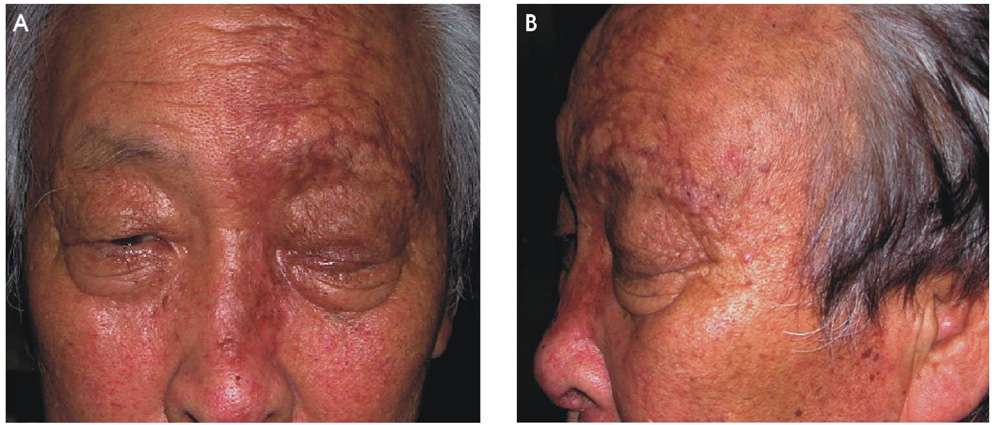
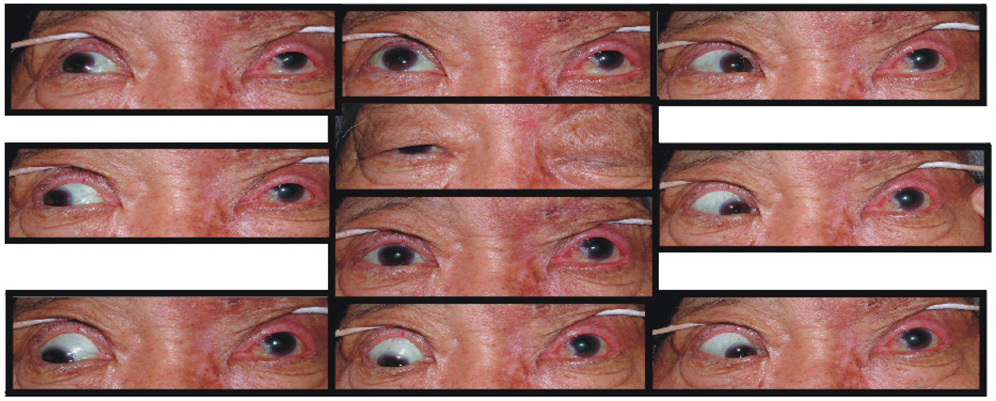
To report a case with complete ophthalmoplegia after herpes zoster ophthalmicus. METHODS: A 70-year-old male patient visited a clinic because of vesicular eruptions over the left side of his face with severe pain. Drooping and severe swelling of the left eyelid were present, along with keratitis and uveitis. While the lid swelling and uveitis were improving, external ophthalmoplegia and exophthalmos were discovered. Intramuscular injections of dexamethasone 5 mg were given for 10 days, followed by oral administration of prednisolone at a dosage of 15 mg for two weeks and 10 mg for two weeks. RESULTS: The patient was fully recovered from the complete ophthalmoplegia and exophthalmos six months after the onset of the cutaneous lesion. CONCLUSIONS: Complete ophthalmoplegia is a rare ophthalmic complication of herpes zoster infection. Therefore, an evaluation of extraocular muscle and lid function should be performed during the examination of herpes zoster patients in order to screen for ophthalmoplegia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus Complicated by Hyphema, Glaucoma and External Ophthalmoplegia
Shin Hae Park, Wung Jae Kim, Suk Woo Yang, Man Soo Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007;48(11):1573-1578. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2007.48.11.1573.Ocular Manifestations of Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
Yoo-Ri Chung, Yoon-Hee Chang, Dae Hee Kim, Hong Seok Yang
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010;51(2):164-168. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2010.51.2.164.
Reference
-
1. Marsh RJ, Dulley B, Kelly V. External ocular motor alsies in ophthalmic zoster: a review. Br J Ophthalmol. 1977. 61:677–682.2. Edgerton AE. Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus; report of cases and review of literlature. Arch Ophthalmol. 1945. 34:40–62.3. Womack LW, Liesegang TJ. Complication of herpes zoster ophthalmicus. Arch ophthalmol. 1983. 101:42–45.4. Hahn ES, Jung YC, Chang K. A case of herpes zoster ophthalmicus complicated by abducens palsy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1989. 30:447–453.5. Lee HR, Cho BC. A clinical study of herpes zoster ophthalmicus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1988. 29:387–391.6. Goldsmith MO. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus with VIth nerve palsy. Can J Ophahalmol. 1968. 3:279–283.7. Chang-Godinich A, Lee AG, Brazis PW, et al. Complete Ophthalmoplegia After Zoster Ophthalmicus. J Neuroophthalmol. 1997. 17:262–265.8. Pandey PK. Extraocular Muscle and Facial Paresis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2001. 38:363–366.9. Archambault P, Wise JS, Rosen J. Herpes Zoster Ophthalmoplegia, Report of Six Cases. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1988. 8:185–191.10. Copes S, Jones AT. Hemiplegia complicating ophthalmic zoster. Lancet. 1954. 2:898–899.11. Appelbaum E, Kreps SI, Sunshine A. A zoster enecephalomyelitis. Am J Med. 1914-1915. 7:513–514.12. Marsh RJ. Current management of ophthalmic herpes zoster. Tran Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1976. 96:334–337.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ophthalmoplegia in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
- Ophthalmoplegia in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
- A Case of Ophthalmoplegia Caused by Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
- A Case of Isolated Iridoplegia in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
- Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus Complicated by Hyphema, Glaucoma and External Ophthalmoplegia