Cancer Res Treat.
2025 Apr;57(2):590-596. 10.4143/crt.2024.531.
Nivolumab in Relapsed or Refractory Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: Multicenter, Retrospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University, Seongnam, Korea
- 4Center for Hematologic Malignancies, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
- 5Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2566875
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2024.531
Abstract
- Purpose
Given that 40%-50% of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) tissues exhibit aberrancy on 9p24.1, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) may work for the disease.
Materials and Methods
To define the role of ICIs in PCNSL, we carried out a nationwide retrospect analysis for 22 patients who had been treated with nivolumab monotherapy for relapsed or refractory PCNSL.
Results
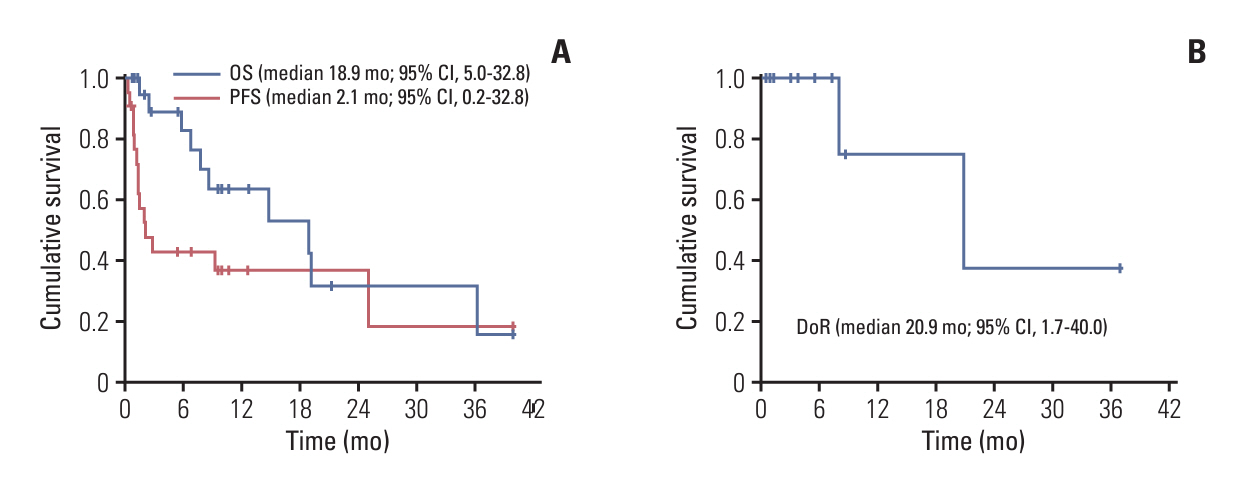
The median age at diagnosis was 66, and male: female ratio was 1:1. Patients received nivolumab after a median of 3 lines (range, 2 to 6) of therapy and at the median age of 67 years (range, 37 to 82 years). Eleven patients (50%) were refractory to the last treatment prior to nivolumab. With a median follow-up duration of 22.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 13.1 to 31.5), nine patients (41%) had an objective response (6 complete responses, 3 partial responses), and the median duration of response was 20.9 months (95% CI, 1.7 to 40.0). The median progression-free survival and overall survival were 2.1 months (95% CI, 0.2 to 4.0) and 18.9 months (95% CI, 5.0 to 32.8), respectively. Nivolumab was generally well-tolerated as no patients required dose reduction and only two patients required delay of treatment.
Conclusion
Our study suggests that nivolumab can be a reasonable option with the durable response for RR PCNSL.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC Press;2017.2. Ferreri AJ, Cwynarski K, Pulczynski E, Ponzoni M, Deckert M, Politi LS, et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix regimen) in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: results of the first randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 (IELSG32) phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2016; 3:e217–27.
Article3. Bromberg JE, Issa S, Bakunina K, Minnema MC, Seute T, Durian M, et al. Rituximab in patients with primary CNS lymphoma (HOVON 105/ALLG NHL 24): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 intergroup study. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:216–28.
Article4. Enting RH, Demopoulos A, DeAngelis LM, Abrey LE. Salvage therapy for primary CNS lymphoma with a combination of rituximab and temozolomide. Neurology. 2004; 63:901–3.
Article5. Severson EA, Haberberger J, Hemmerich A, Huang RS, Edgerly C, Schiavone K, et al. Genomic profiling reveals differences in primary central nervous system lymphoma and large B-cell lymphoma, with subtyping suggesting sensitivity to BTK inhibition. Oncologist. 2023; 28:e26–35.
Article6. Chapuy B, Roemer MG, Stewart C, Tan Y, Abo RP, Zhang L, et al. Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood. 2016; 127:869–81.
Article7. Green MR, Monti S, Rodig SJ, Juszczynski P, Currie T, O’Donnell E, et al. Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2010; 116:3268–77.
Article8. Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:311–9.
Article9. Herrera AF, LeBlanc ML, Castellino SM, Li H, Rutherford SC, Evens AM, et al. SWOG S1826, a randomized study of nivolumab(N)-AVD versus brentuximab vedotin(BV)-AVD in advanced stage (AS) classic Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). J Clin Oncol. 2023; 41(17 Suppl):LBA4.
Article10. Zinzani PL, Thieblemont C, Melnichenko V, Bouabdallah K, Walewski J, Majlis A, et al. Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: final analysis of KEYNOTE-170. Blood. 2023; 142:141–5.
Article11. Nayak L, Iwamoto FM, LaCasce A, Mukundan S, Roemer MG, Chapuy B, et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system and testicular lymphoma. Blood. 2017; 129:3071–3.
Article12. Gavrilenko AN, Volkov NP, Shmidt DI, Polushin AY, Kondakova E, Lepik KV, et al. Nivolumab in primary CNS lymphoma and primary testicular lymphoma with CNS involvement: single center experience. Blood. 2020; 136(Suppl 1):4.
Article13. Abrey LE, Batchelor TT, Ferreri AJ, Gospodarowicz M, Pulczynski EJ, Zucca E, et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize baseline evaluation and response criteria for primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:5034–43.
Article14. Ferreri AJ, Blay JY, Reni M, Pasini F, Spina M, Ambrosetti A, et al. Prognostic scoring system for primary CNS lymphomas: the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:266–72.
Article15. Radke J, Ishaque N, Koll R, Gu Z, Schumann E, Sieverling L, et al. The genomic and transcriptional landscape of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Nat Commun. 2022; 13:2558.
Article16. Ou A, Sumrall A, Phuphanich S, Spetzler D, Gatalica Z, Xiu J, et al. Primary CNS lymphoma commonly expresses immune response biomarkers. Neurooncol Adv. 2020; 2:vdaa018.
Article17. Monabati A, Nematollahi P, Dehghanian A, Safaei A, Sadeghipour A, Movahedinia S, et al. Immune checkpoint molecules in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2020; 11:491–8.
Article18. Cho I, Lee H, Yoon SE, Ryu KJ, Ko YH, Kim WS, et al. Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer. 2020; 20:120.
Article19. Takashima Y, Kawaguchi A, Sato R, Yoshida K, Hayano A, Homma J, et al. Differential expression of individual transcript variants of PD-1 and PD-L2 genes on Th-1/Th-2 status is guaranteed for prognosis prediction in PCNSL. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:10004.
Article20. Minderman M, Amir A, Kraan W, Schilder-Tol EJ, Oud M, Scheepstra CG, et al. Immune evasion in primary testicular and central nervous system lymphomas: HLA loss rather than 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 alterations. Blood. 2021; 138:1194–7.21. Nayyar N, White MD, Gill CM, Lastrapes M, Bertalan M, Kaplan A, et al. MYD88 L265P mutation and CDKN2A loss are early mutational events in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood Adv. 2019; 3:375–83.
Article22. Roemer MG, Advani RH, Ligon AH, Natkunam Y, Redd RA, Homer H, et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 genetic alterations define classical Hodgkin lymphoma and predict outcome. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:2690–7.
Article23. Zinzani PL, Santoro A, Gritti G, Brice P, Barr PM, Kuruvilla J, et al. Nivolumab combined with brentuximab vedotin for relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: efficacy and safety from the phase II CheckMate 436 study. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:3081–9.
Article24. Kaulen LD, Gumbinger C, Hinz F, Kessler T, Winkler F, Bendszus M, et al. Intraventricular immune checkpoint inhibition with nivolumab in relapsed primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurooncol Adv. 2022; 4:vdac051.
Article25. Ambady P, Szidonya L, Firkins J, James J, Johansson K, White T, et al. Combination immunotherapy as a non-chemotherapy alternative for refractory or recurrent CNS lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019; 60:515–8.
Article26. Sagiv-Barfi I, Kohrt HE, Czerwinski DK, Ng PP, Chang BY, Levy R. Therapeutic antitumor immunity by checkpoint blockade is enhanced by ibrutinib, an inhibitor of both BTK and ITK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015; 112:E966–72.
Article27. Feng L, Gao X, Jiao Z, Wang Z, Min F. BTK inhibitor combined with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of CD20-negative primary central nervous system lymphoma: a case report. Oncol Lett. 2023; 25:48.
Article28. Westin J, Nair R, Fayad L, Iyer SP, Malpica L, Neelapu SS, et al. Nivolumab and ibrutinib for treatment of patients with refractory or relapsed central nervous system lymphoma. Blood. 2023; 142(Suppl 1):1721.
Article29. Ghesquieres H, Chevrier M, Laadhari M, Chinot O, Choquet S, Molucon-Chabrot C, et al. Lenalidomide in combination with intravenous rituximab (REVRI) in relapsed/refractory primary CNS lymphoma or primary intraocular lymphoma: a multicenter prospective ‘proof of concept’ phase II study of the French Oculo-Cerebral lymphoma (LOC) Network and the Lymphoma Study Association (LYSA). Ann Oncol. 2019; 30:621–8.
Article30. Bagal B, Sarma R, Dey S, Nayak L, Bonda A, Goda J, et al. Lenalidomide following whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma ineligible for intensive systemic therapy. Br J Haematol. 2023; 201:150–3.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Mimicking Behcet's Disease
- Two Cases of Treatment with Intrathecal Rituximab for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma
- Experience of Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma with Central Nervous System Involvement at Diagnosis
- Primary Non-Hodgkin ''s Lymphoma Involving the Third Ventricle: A Case Report
- Recent advances in the management of primary central nervous system lymphoma