Neurointervention.
2024 Mar;19(1):52-56. 10.5469/neuroint.2024.00017.
Fatal Femoral Pseudoaneurysm Rupture after Endovascular Intervention: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2552880
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2024.00017
Abstract
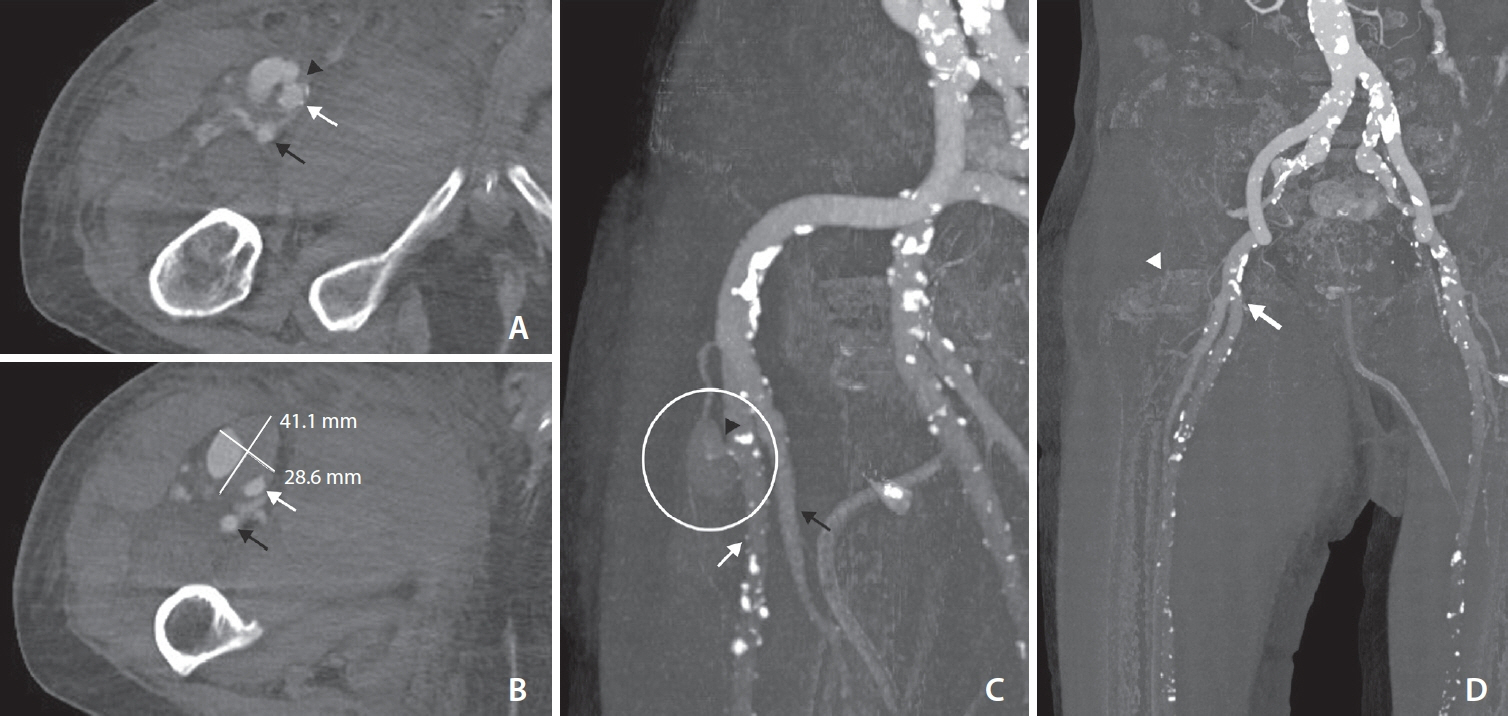
- A rupture of a femoral pseudoaneurysm is an extremely rare complication of endovascular procedures, but its outcome can be life-threatening. In this report, we present a case of a femoral pseudoaneursym rupture in a patient in their early 90s following intra-arterial mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. Despite receiving medical and surgical interventions, the patient subsequently developed multiple organ failure, ultimately resulting in death. This case emphasizes the critical role of appropriate selection of vascular closure technique and careful post-procedural monitoring, particularly in high-risk patients.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ciprian Cacuci A, Krankenberg H, Ingwersen M, Gayed M, Stein SD, Kretzschmar D, et al. Access site complications of peripheral endovascular procedures: a large, prospective registry on predictors and consequences. J Endovasc Ther. 2021; 28:746–754.
Article2. Kopin D, Seth M, Sukul D, Dixon S, Aronow HD, Lee D, et al. Primary and secondary vascular access site complications associated with percutaneous coronary intervention: insights from the BMC2 registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019; 12:2247–2256.
Article3. Tsetis D. Endovascular treatment of complications of femoral arterial access. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33:457–468.
Article4. Rivera PA, Dattilo JB. Pseudoaneurysm. In: Aboubakr S, Abu-Ghosh A, Adibi Sedeh P, Aeby TC, Aeddula NR, Agadi S, et al. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, 2023.5. Morgan R, Belli AM. Current treatment methods for postcatheterization pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:697–710.
Article6. Seon KH, Yoo TH, Jeong SI, Kim SJ, Kim SP. Spontaneous femoral artery pseudoaneurysm rupture in systemic lupus erythematosus patient. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2014; 25:480–483.7. Jalili J, Ebrahiminik H, Zafarani F, Akhavi Milani A. Endovascular treatment of the ruptured pseudoaneurysm of common femoral artery in Behcet’s disease: report of a case with four years of follow-up. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2022; 56:616–621.
Article8. Kulkarni LM, Sirsat SM. Ruptured femoral artery pseudoaneurysm: a life-threatening, iatrogenic catastrophe! Indian J Anaesth. 2016; 60:437–439.
Article9. Patrick JO, Yoo MJ, Larson NP, Bridwell RE. Pulsatile mass: ruptured common femoral artery pseudoaneurysm with active extravasation. Cureus. 2019; 11:e5380.
Article10. Petrou E, Malakos I, Kampanarou S, Doulas N, Voudris V. Life-threatening rupture of a femoral pseudoaneurysm after cardiac catheterization. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2016; 10:201–204.
Article11. Renner J, Pasquier P, Falzone E, Rozwadowski F, Mérat S. Life-threatening rupture of a false aneurysm after femoral arterial catheterization: unexpected delay after a common procedure. Case Rep Vasc Med. 2013; 2013:403507.
Article12. Wiley JM, White CJ, Uretsky BF. Noncoronary complications of coronary intervention. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2002; 57:257–265.
Article13. Sherev DA, Shaw RE, Brent BN. Angiographic predictors of femoral access site complications: implication for planned percutaneous coronary intervention. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2005; 65:196–202.
Article14. Muller DW, Shamir KJ, Ellis SG, Topol EJ. Peripheral vascular complications after conventional and complex percutaneous coronary interventional procedures. Am J Cardiol. 1992; 69:63–68.
Article15. Oweida SW, Roubin GS, Smith RB 3rd, Salam AA. Postcatheterization vascular complications associated with percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. J Vasc Surg. 1990; 12:310–315.
Article16. Graham AN, Wilson CM, Hood JM, Barros D’Sa AA. Risk of rupture of postangiographic femoral false aneurysm. Br J Surg. 1992; 79:1022–1025.
Article17. Noori VJ, Eldrup-Jørgensen J. A systematic review of vascular closure devices for femoral artery puncture sites. J Vasc Surg. 2018; 68:887–899.
Article18. Griese DP, Reents W, Diegeler A, Kerber S, Babin-Ebell J. Simple, effective and safe vascular access site closure with the double-ProGlide preclose technique in 162 patients receiving transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013; 82:E734–E741.
Article19. Lenartova M, Tak T. Iatrogenic pseudoaneurysm of femoral artery: case report and literature review. Clin Med Res. 2003; 1:243–247.
Article20. Lumsden AB, Miller JM, Kosinski AS, Allen RC, Dodson TF, Salam AA, et al. A prospective evaluation of surgically treated groin complications following percutaneous cardiac procedures. Am Surg. 1994; 60:132–137.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Successful Treatment of Huge Pseudoaneurysm Complicated with Endovascular Intervention Using Thrombin Injection
- Bilateral Iliac Endobypass Solution in Iliac Artery Rupture during TEVAR Procedure: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Endovascular treatment of pancreatitis-related gastrointestinal bleeding
- Jejunal Migration of the Stent-Graft Used for Common Hepatic Artery Pseudoaneurysm
- Access site pseudoaneurysms after endovascular intervention for peripheral arterial diseases