Ann Lab Med.
2023 Mar;43(2):167-173. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.2.167.
Performance Evaluation of the DxC 700 AU Chemistry Analyzer in Hemoglobin A1c Measurement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, Osong Health Technology Administration Complex, Cheongju, Korea
- KMID: 2551693
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.2.167
Abstract
- Background
Accurate measurement of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is crucial for a diabetes diagnosis and subsequent patient management. The detection method and presence of variant Hb can interfere with HbA1c measurements. We evaluated the HbA1c-measuring performance of the DxC 700 AU (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA) immunoassay-based device in comparison with another immunoassay device and the reference method.
Methods
A total of 120 normal and 14 variant Hb samples were analyzed using the Cobas c 513 (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and DxC 700 AU analyzers. Variant Hb samples were also analyzed using the reference method, along with 20 normal samples. The accuracy, precision, linearity, and carryover were determined.
Results
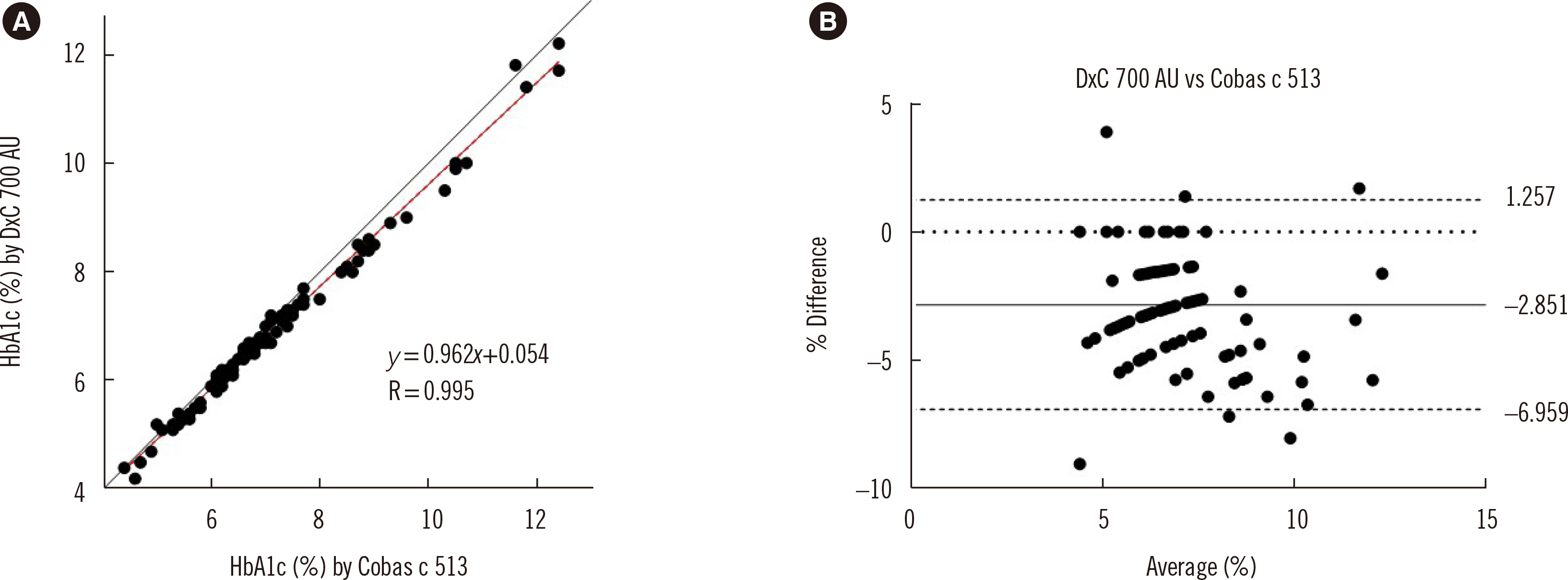
DxC 700 AU results strongly correlated with those of Cobas c 513 and exhibited accuracy in comparison with the reference method. The within-run, between-run, between-day, and total imprecision (%CV) values for the low- and high-concentration control materials were below 2%. The results of DxC 700 AU were linear over a wide HbA1c range (3.39%–18.30%). Although DxC 700 AU performed well in the presence of variant Hb, the HbA1c concentration was underestimated in the presence of fetal Hb. The possibility of interference from a high HbH proportion could not be ruled out.
Conclusions
The overall analytical performance of DxC 700 AU was acceptable. The device is accurate, precise, and linear over a wide HbA1c concentration range. Although DxC 700 AU results highly correlated with those of Cobas c 513, caution should be exercised in cases of high HbF and HbH concentrations.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Finke A, Kobold U, Hoelzel W, Weykamp C, Miedema K, Jeppsson JO. 1998; Preparation of a candidateprimary reference material for the international standardisation of HbA1c determinations. Clin Chem Lab Med. 36:299–308. DOI: 10.1515/CCLM.1998.051. PMID: 9676387.
Article2. Nitin S. 2010; HbA1c and factors other than diabetes mellitus affecting it. Singapore Med J. 51:616–22.3. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2021; 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 44(S1):S73–84. DOI: 10.2337/dc21-S006. PMID: 33298417.4. American Diabetes Association. 2021; 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes - 2021. Diabetes Care. 44(S1):S15–33. DOI: 10.2337/dc21-S002. PMID: 33298413.5. American Diabetes Association. 2014; Standards of medical care in diabetes -2014. Diabetes Care. 37(S1):S14–80. DOI: 10.2337/dc14-S014. PMID: 24357209.6. Gupta S, Jain U, Chauhan N. 2017; Laboratory diagnosis of HbA1c: a review. J Nanomed Res. 5:00120. DOI: 10.15406/jnmr.2017.05.00120.
Article7. Fernández BG, Campuzano JBN, Rocamora DG, Nieto JM, Fernández FAG, Villegas A, et al. Hb Murcia (β118(G19)His>Gln): a new hemoglobin variant found in a Spanish woman. Ann Lab Med. 2021; 41:514–7. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.5.514. PMID: 33824245. PMCID: PMC8041595.
Article8. Lee ST, Kim MS, Choi DY, Kim SK, Ki CS. 2006; Incidence of variant hemoglobin (Hb) and increased fetal Hb concentrations and their effect on Hb A1c measurement in a Korean population. Clin Chem. 52:1445–6. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2006.069617. PMID: 16798979.
Article9. Weykamp CW, Mosca A, Gillery P, Panteghini M. 2011; The analytical goals for hemoglobin A(1c) measurement in IFCC units and National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program Units are different. Clin Chem. 57:1204–6. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2011.162719. PMID: 21571810.
Article10. American Diabetes Association. 2021; Introduction: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 44(S1):S1–2. DOI: 10.2337/dc21-Sint.11. CLSI. 2014. Evaluation of Precision of Quantitative Measurement Procedures; Approved Guideline-Third Edition. CLSI document EP05-A3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:12. CLSI. 2014. Preliminary evaluation of quantitative clinical laboratory measurement procedures: approved guideline. 3rd ed. CLSI EP10-A3-AMD. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:13. Radin MS. 2014; Pitfalls in hemoglobin A1c measurement: when results may be misleading. J Gen Intern Med. 29:388–94. DOI: 10.1007/s11606-013-2595-x. PMID: 24002631. PMCID: PMC3912281.
Article14. Lin CN, Emery TJ, Little RR, Hanson SE, Rohlfing CL, Jaisson S, et al. 2012; Effects of hemoglobin C, D, E, and S traits on measurements of HbA1c by six methods. Clin Chim Acta. 413:819–21. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2011.12.019. PMID: 22244931. PMCID: PMC5068911.
Article15. Little RR, Roberts WL. 2009; A review of variant hemoglobins interfering with hemoglobin A1c measurement. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 3:446–51. DOI: 10.1177/193229680900300307. PMID: 20144281. PMCID: PMC2769887.
Article16. Moassas F, Nweder MS, Murad H. 2019; Hb Knossos (HBB: c.82G > T), β-globin CD 5 (-CT) (HBB: c.17_18delCT) and δ-globin CD 59 (-a) (HBD: c.179 delA) mutations in a Syrian patient with β-thalassemia intermedia. BMC Pediatr. 19:61. DOI: 10.1186/s12887-019-1435-5. PMID: 30777047. PMCID: PMC6378710.17. Rohlfing CL, Connolly SM, England JD, Hanson SE, Moellering CM, Bachelder JR, et al. 2008; The effect of elevated fetal hemoglobin on hemoglobin A1c results: five common hemoglobin A1c methods compared with the IFCC reference method. Am J Clin Pathol. 129:811–4. DOI: 10.1309/YFVTUD0GHJF7D16H. PMID: 18426743.
Article18. Gifford JL, Higgins T, Sadrzadeh SMH. 2019; A high-throughput test for diabetes care: an evaluation of the next generation Roche Cobas c 513 hemoglobin A1C assay. Pract Lab Med. 17:e00147. DOI: 10.1016/j.plabm.2019.e00147. PMID: 31799362. PMCID: PMC6881683.
Article19. Beltran Del Rio M, Tiwari M, Amodu LI, Cagliani J, Rodriguez Rilo HL. 2016; Glycated hemoglobin, plasma glucose, and erythrocyte aging. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 10:1303–7. DOI: 10.1177/1932296816659885. PMID: 27422013. PMCID: PMC5094338.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Performance Evaluation of TOSOH Automated Glycohemoglobin Analyzer HLC-723GHb V A1c 2.2TM
- Performance Evaluation of the ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180
- Performance Evaluation of the ARKRAY ADAMS Bridge System Comprising Glucose GA-1171 and HbA1c HA-8180 Analyzers
- Performance Evaluation of the Roche-Hitachi cobas 8000 c702 Chemistry Autoanalyzer
- Performance Evaluation of the LABGEO PT10 Point-of-care Chemistry Analyzer