Korean J Sports Med.
2023 Dec;41(4):241-245. 10.5763/kjsm.2023.41.4.241.
Novel Therapeutic Approach for Tibial Nerve Entrapment in Chronic Heel Pain Diagnosed as Plantar Fasciitis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Borntouch Orthopaedic Clinic, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Family M edicine, Sarang Clinic, Jinju, Korea
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea
- KMID: 2548998
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2023.41.4.241
Abstract
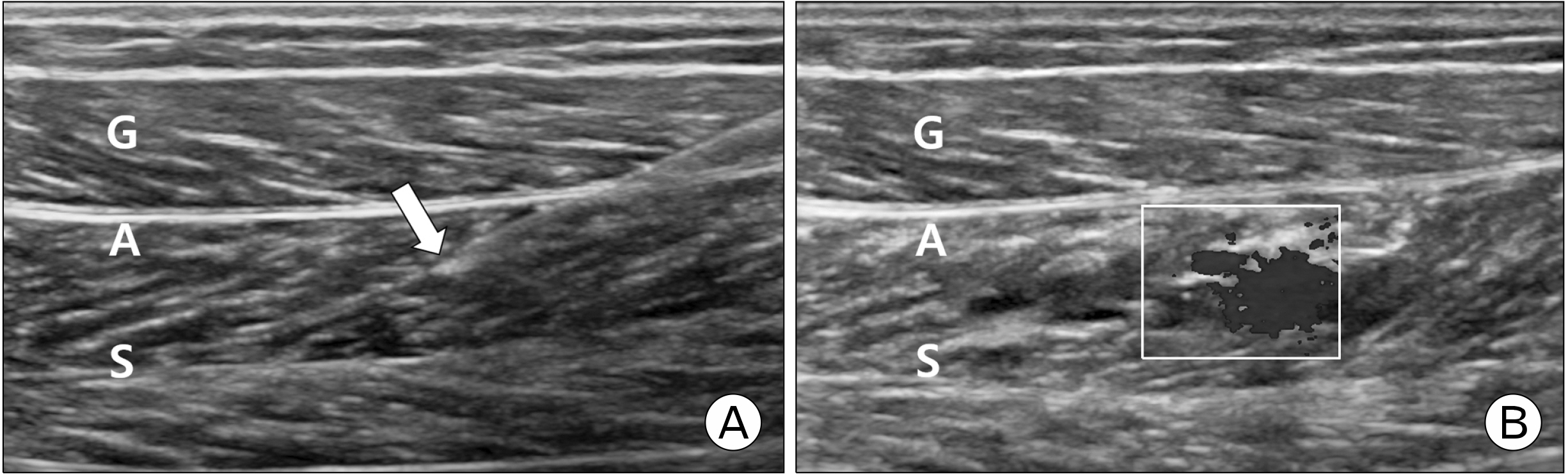
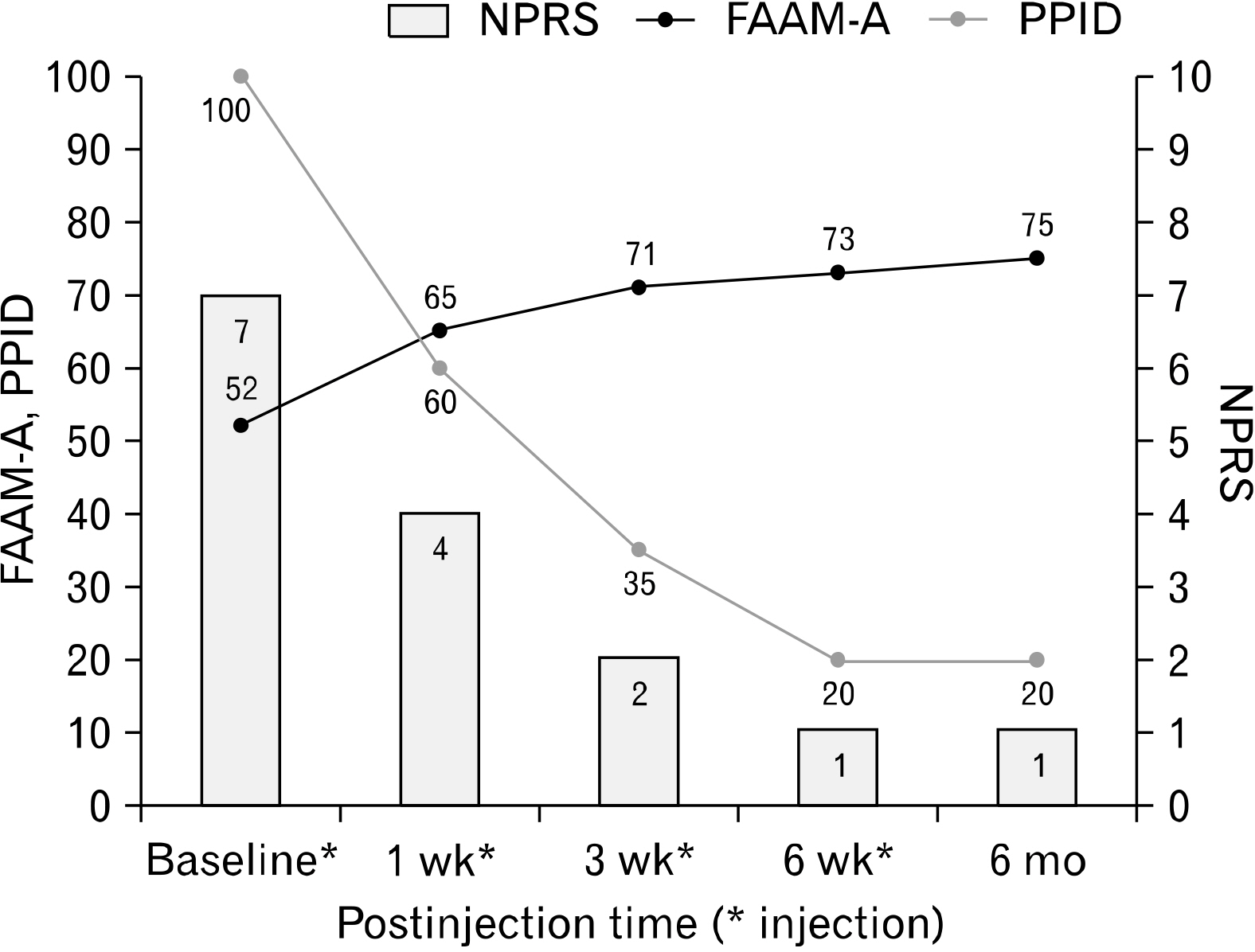
- Plantar heel pain is common in sports medicine and orthopedics; it is usually diagnosed as plantar fasciitis. We report the case of a 43-year-old healthy man with chronic pain over the right heel for 5 years. He was diagnosed with plantar fasciitis and received conservative treatment. Surgery was recommended for the intractable pain, which he refused. He had tenderness in the medial calcaneal tubercle region and midportion of soleus muscle near the tendinous arch. At a tibial nerve entrapment point (NEP) over the tender soleus, 4-mL isotonic saline was injected at presentation and 1, 3, and 6 weeks later. The pain improved significantly. He had no adverse effects or aggravation of symptoms at 6 months later. The injection therapy at NEP of the soleus can be considered in chronic unhealed plantar heel pain, including plantar fasciitis, to release the entrapped tibial nerve.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hill CL, Gill TK, Menz HB, Taylor AW. 2008; Prevalence and correlates of foot pain in a population-based study: the North West Adelaide health study. J Foot Ankle Res. 1:2. DOI: 10.1186/1757-1146-1-2. PMID: 18822153. PMCID: PMC2547889.
Article2. Nahin RL. 2018; Prevalence and pharmaceutical treatment of plantar fasciitis in United States adults. J Pain. 19:885–96. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2018.03.003. PMID: 29597082. PMCID: PMC6066406.
Article3. Arslan A, Koca TT, Utkan A, Sevimli R, Akel İ. 2016; Treatment of chronic plantar heel pain with radiofrequency neural ablation of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve and medial calcaneal nerve branches. J Foot Ankle Surg. 55:767–71. DOI: 10.1053/j.jfas.2016.03.009. PMID: 27073185.4. Tapadia M, Mozaffar T, Gupta R. 2010; Compressive neuropathies of the upper extremity: update on pathophysiology, classification, and electrodiagnostic findings. J Hand Surg Am. 35:668–77. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.01.007. PMID: 20223605. PMCID: PMC4715364.
Article5. Pomeroy G, Wilton J, Anthony S. 2015; Entrapment neuropathy about the foot and ankle: an update. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 23:58–66. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-23-01-58. PMID: 25538131.6. Alshami AM, Souvlis T, Coppieters MW. 2008; A review of plantar heel pain of neural origin: differential diagnosis and management. Man Ther. 13:103–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.math.2007.01.014. PMID: 17400020.
Article7. Seong JW. Principle and insights into pain. Vol. 1:Koonja Press;2015.8. Lee S, Oh CJ, Seong JW. 2016; Sympathetic nerve entrapment point injection as an antireflux procedure for refractory laryngopharyngeal reflux: a first case report of innovative autonomic regulation. Innov Clin Neurosci. 13:32–6.9. Han SE, Lin CS, Boland RA, Kiernan MC. 2011; Nerve compression, membrane excitability, and symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 44:402–9. DOI: 10.1002/mus.22078. PMID: 21996801.
Article10. Seong JW, Kwon DR. 2020; A proposal for a new headache classification system for general practitioners. Med Hypotheses. 143:110103. DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110103. PMID: 32721801.
Article11. Lareau CR, Sawyer GA, Wang JH, DiGiovanni CW. 2014; Plantar and medial heel pain: diagnosis and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 22:372–80. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-22-06-372. PMID: 24860133.12. De Maeseneer M, Madani H, Lenchik L, et al. 2015; Normal anatomy and compression areas of nerves of the foot and ankle: US and MR imaging with anatomic correlation. Radiographics. 35:1469–82. DOI: 10.1148/rg.2015150028. PMID: 26284303.
Article13. Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yaşar E, Yazicioğlu K. 2013; Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 41:2609–16. DOI: 10.1177/0363546513496542. PMID: 23893418.
Article14. Staud R, Weyl EE, Bartley E, Price DD, Robinson ME. 2014; Analgesic and anti-hyperalgesic effects of muscle injections with lidocaine or saline in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Eur J Pain. 18:803–12. DOI: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00422.x. PMID: 24193993. PMCID: PMC4010579.
Article15. Wolf JM, Ozer K, Scott F, Gordon MJ, Williams AE. 2011; Comparison of autologous blood, corticosteroid, and saline injection in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter study. J Hand Surg Am. 36:1269–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2011.05.014. PMID: 21705157.
Article16. Yelland MJ, Glasziou PP, Bogduk N, Schluter PJ, McKernon M. 2004; Prolotherapy injections, saline injections, and exercises for chronic low-back pain: a randomized trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 29:9–16. DOI: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000105529.07222.5B. PMID: 14699269.
Article17. Renan-Ordine R, Alburquerque-Sendín F, de Souza DP, Cleland JA, Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C. 2011; Effectiveness of myofascial trigger point manual therapy combined with a self-stretching protocol for the management of plantar heel pain: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 41:43–50. DOI: 10.2519/jospt.2011.3504. PMID: 21285525.
Article18. Sweeting D, Parish B, Hooper L, Chester R. 2011; The effectiveness of manual stretching in the treatment of plantar heel pain: a systematic review. J Foot Ankle Res. 4:19. DOI: 10.1186/1757-1146-4-19. PMID: 21703003. PMCID: PMC3150253.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Subcalcaneal Bursitis Developed after Execessive Walking Exercise
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis
- Correlation between Internet Search Query Data and the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Data for Seasonality of Plantar Fasciitis
- Clinical Characteristics of the Causes of Plantar Heel Pain
- Outcome of Nonoperative Treatment for Proximal Plantar Fasciitis: Comparative Analysis According to Plantar Fascia Thickness