Clin Endosc.
2023 Nov;56(6):778-789. 10.5946/ce.2022.268.
Significance of rescue hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection in difficult colorectal cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical University, Tokyo, Japan
- 2Endoscopy Center, Tokyo Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
- KMID: 2547900
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.268
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), in which an incision is made around a lesion and snaring is performed after submucosal dissection, has some advantages in colorectal surgery, including shorter procedure time and preventing perforation. However, its value for rescue resection in difficult colorectal ESD cases remains unclear. This study evaluated the utility of rescue hybrid ESD (RH-ESD).
Methods
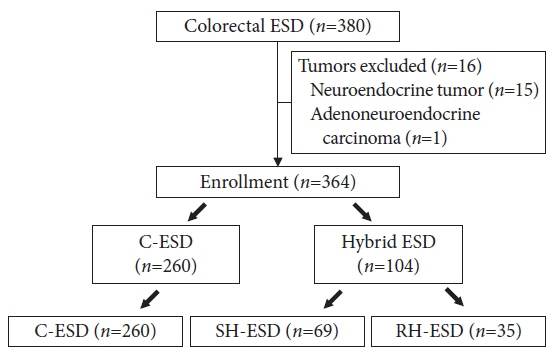
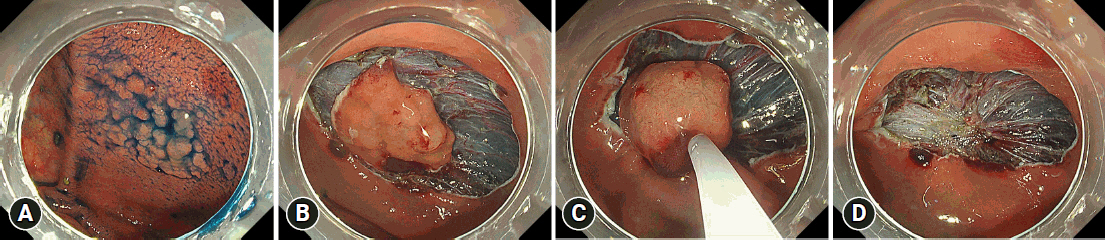
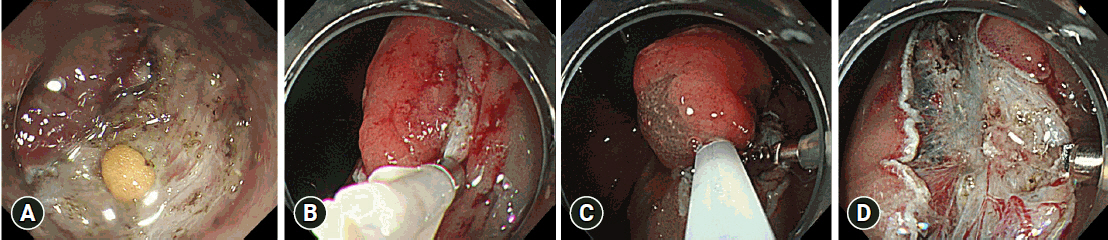
We divided 364 colorectal ESD procedures into the conventional ESD group (C-ESD, n=260), scheduled hybrid ESD group (SH-ESD, n=69), and RH-ESD group (n=35) and compared their clinical outcomes.
Results
Resection time was significantly shorter in the following order: RH-ESD (149 [90–197] minutes) >C-ESD (90 [60–140] minutes) >SH-ESD (52 [29–80] minutes). The en bloc resection rate increased significantly in the following order: RH-ESD (48.6%), SH-ESD (78.3%), and C-ESD (97.7%). An analysis of factors related to piecemeal resection of RH-ESD revealed that the submucosal dissection rate was significantly lower in the piecemeal resection group (25% [20%–30%]) than in the en bloc resection group (40% [20%–60%]).
Conclusions
RH-ESD was ineffective in terms of curative resection because of the low en bloc resection rate, but was useful for avoiding surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Understanding hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection subtleties
João Paulo de Souza Pontual, Alexandre Moraes Bestetti, Diogo Turiani Hourneaux de Moura
Clin Endosc. 2023;56(6):738-740. doi: 10.5946/ce.2023.195.
Reference
-
1. Cao Y, Liao C, Tan A, et al. Meta-analysis of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection for tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:751–757.
Article2. Lian J, Chen S, Zhang Y, et al. A meta-analysis of endoscopic submucosal dissection and EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:763–770.
Article3. Fujiya M, Tanaka K, Dokoshi T, et al. Efficacy and adverse events of EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colon neoplasms: a meta-analysis of studies comparing EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:583–595.
Article4. ASGE Technology Committee, Maple JT, Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:1311–1325.
Article5. Abe N, Gotoda T, Hirasawa T, et al. Multicenter study of the long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in patients 80 years of age or older. Gastric Cancer. 2012; 15:70–75.
Article6. Yamaguchi H, Sato H, Tsukahara K, et al. Co-treatment with endoscopic laryngopharyngeal surgery and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2021; 48:457–463.
Article7. Kim ES, Cho KB, Park KS, et al. Factors predictive of perforation during endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colorectal tumors. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:573–578.
Article8. Yamaguchi H, Fukuzawa M, Kawai T, et al. Predictive factors of postendoscopic submucosal dissection electrocoagulation syndrome and the utility of computed tomography scan after esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Digestion. 2020; 101:579–589.
Article9. Mizushima T, Kato M, Iwanaga I, et al. Technical difficulty according to location, and risk factors for perforation, in endoscopic submucosal dissection of colorectal tumors. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:133–139.
Article10. Tanaka S, Kashida H, Saito Y, et al. JGES guidelines for colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection/endoscopic mucosal resection. Dig Endosc. 2015; 27:417–434.
Article11. Toyonaga T, Man-I M, Morita Y, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) versus simplified/hybrid ESD. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014; 24:191–199.
Article12. Jung Y, Kim JW, Byeon JS, et al. Factors predictive of complete excision of large colorectal neoplasia using hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: a KASID multicenter study. Dig Dis Sci. 2018; 63:2773–2779.
Article13. Oka S, Tanaka S, Saito Y, et al. Local recurrence after endoscopic resection for large colorectal neoplasia: a multicenter prospective study in Japan. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015; 110:697–707.
Article14. Santos JB, Nobre MR, Oliveira CZ, et al. Risk factors for adverse events of colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021; 33(1S Suppl 1):e33–e41.
Article15. Fuccio L, Hassan C, Ponchon T, et al. Clinical outcomes after endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86:74–86.
Article16. Tanaka S, Oka S, Kaneko I, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: possibility of standardization. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:100–107.
Article17. Bae JH, Yang DH, Lee S, et al. Optimized hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors: a randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:584–592.
Article18. Okamoto Y, Oka S, Tanaka S, et al. Indications and outcomes of colorectal hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: a large multicenter 10-year study. Surg Endosc. 2022; 36:1894–1902.
Article19. Terasaki M, Tanaka S, Oka S, et al. Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for laterally spreading tumors larger than 20 mm. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:734–740.
Article20. Byeon JS, Yang DH, Kim KJ, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection with or without snaring for colorectal neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1075–1083.
Article21. Yoshida N, Yagi N, Naito Y. Hybrid ESD techniques for colorectal tumor ESD. Intestine. 2013; 17:51–58.22. Okamoto K, Muguruma N, Kagemoto K, et al. Efficacy of hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) as a rescue treatment in difficult colorectal ESD cases. Dig Endosc. 2017; 29 Suppl 2:45–52.23. Milano RV, Viale E, Bartel MJ, et al. Resection outcomes and recurrence rates of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and hybrid ESD for colorectal tumors in a single Italian center. Surg Endosc. 2018; 32:2328–2339.
Article24. Kang DU, Park JC, Hwang SW, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia with or without the hybrid technique. Colorectal Dis. 2020; 22:2008–2017.
Article25. Wang XY, Chai NL, Zhai YQ, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: an alternative resection modality for large laterally spreading tumors in the cecum? BMC Gastroenterol. 2021; 21:203.
Article26. Papparella LG, Barbaro F, Pecere S, et al. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection techniques of large colorectal lesions: experience of a referral center in Italy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022; 34:375–381.
Article27. Saito Y, Fukuzawa M, Matsuda T, et al. Clinical outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal tumors as determined by curative resection. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:343–352.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Debates on Colorectal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection - Traction for Effective Dissection: Gravity Is Enough
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection in colorectal neoplasia performed with a waterjet system-assisted knife: higher en-bloc resection rate than conventional technique
- A Case of Pneumorrhachis and Pneumoscrotum Following Colon Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Efficacy and Safety of Complete Endoscopic Resection of Colorectal Neoplasia Using a Stepwise Endoscopic Protocol with SOUTEN, a Novel Multifunctional Snare
- History and Development of Accessories for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection