Cancer Res Treat.
2023 Oct;55(4):1171-1180. 10.4143/crt.2022.1581.
Sublobar Resection versus Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Clinical Stage I Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Study Using Data from the Korean Nationwide Lung Cancer Registry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2547791
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2022.1581
Abstract
- Purpose
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) had been increasingly recognized as a favorable alternative to surgical resection in patients with high risk for surgery. This study compared survival outcomes between sublobar resection (SLR) and SBRT for clinical stage I non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Materials and Methods
Data were obtained from the Korean Association of Lung Cancer Registry, a sampled nationwide database. This study retrospectively reviewed 382 patients with clinical stage I NSCLC who underwent curative SLR or SBRT from 2014 to 2016.
Results
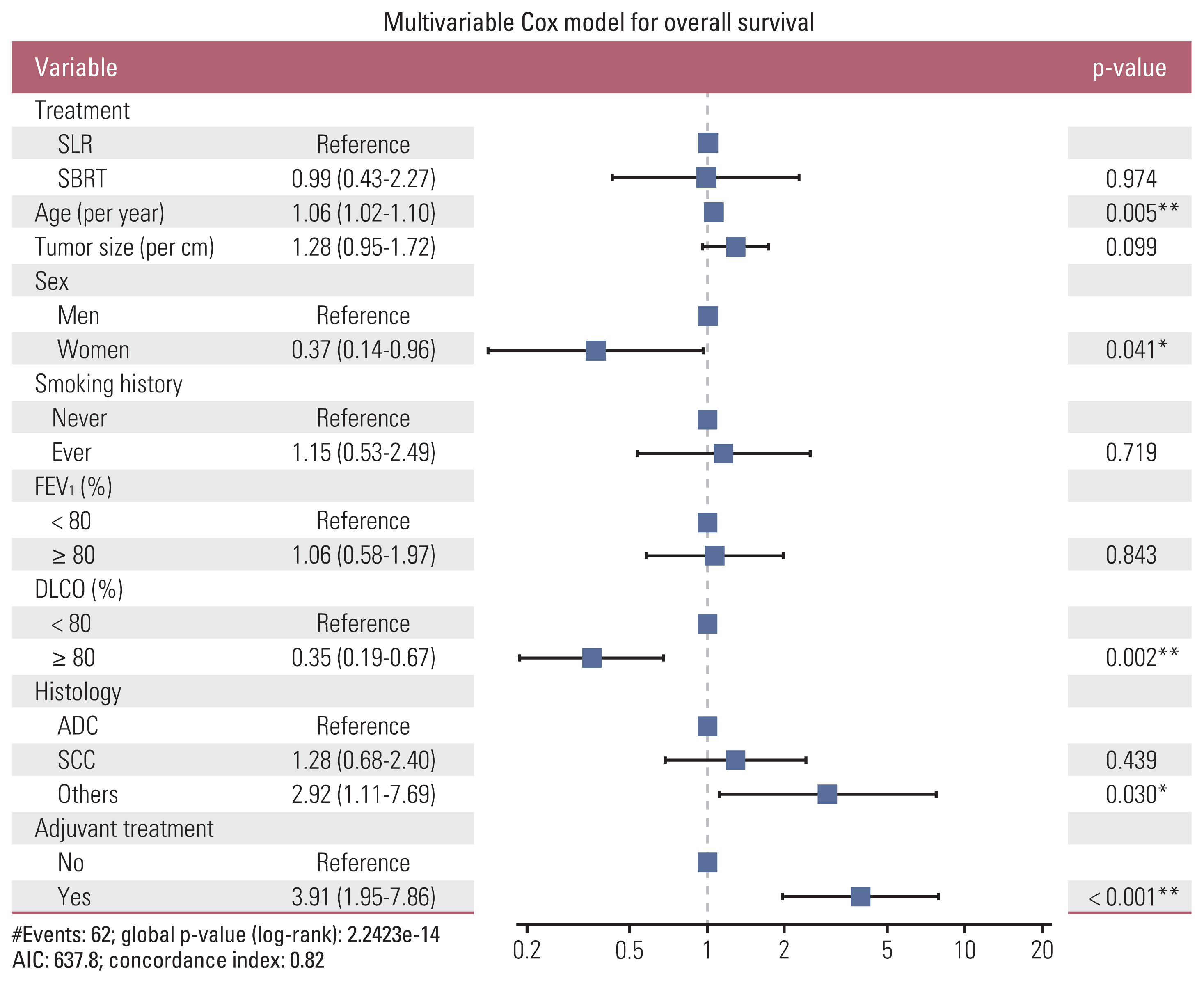
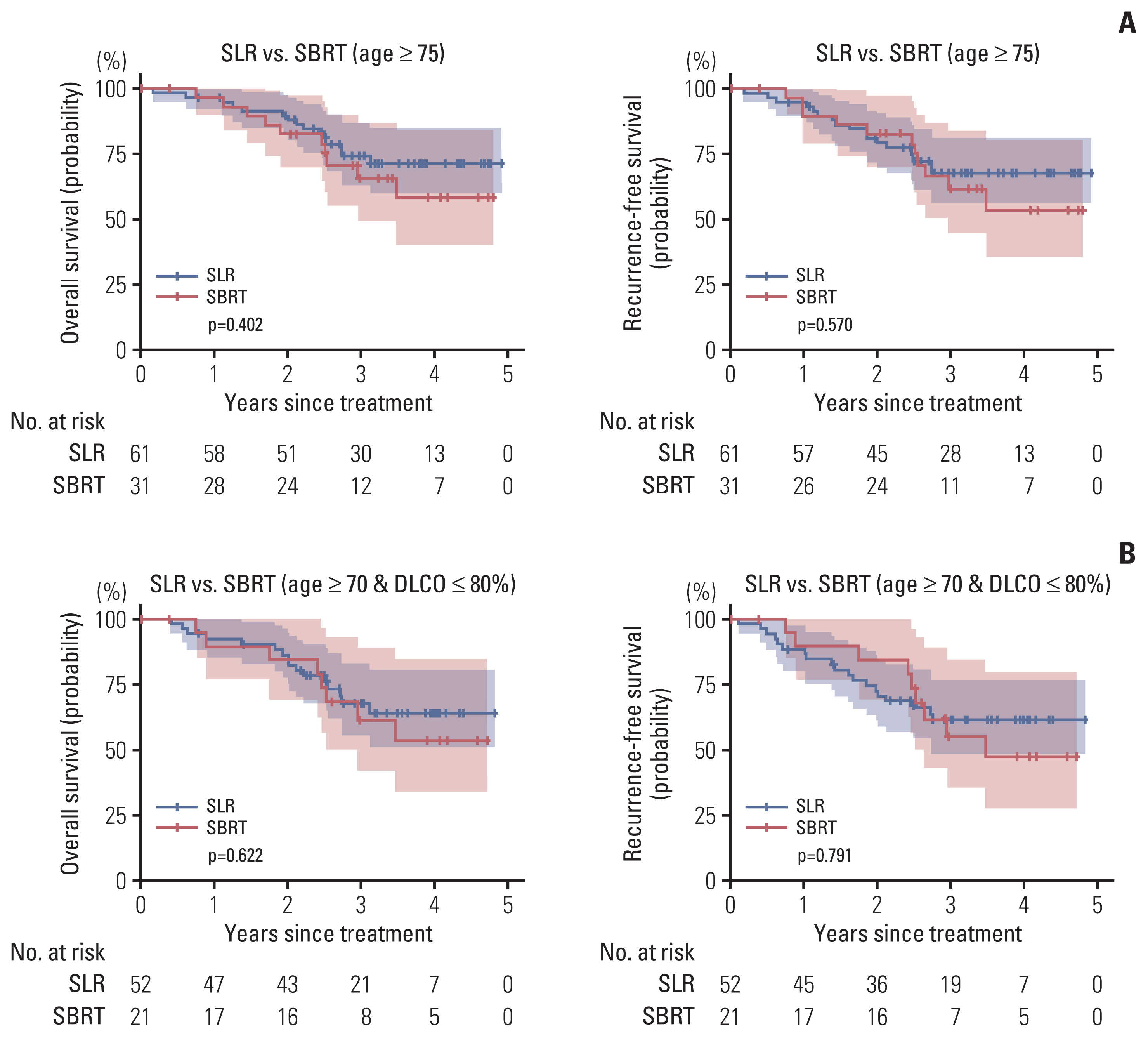
Of the patients, 43 and 339 underwent SBRT and SLR, respectively. Patients in the SBRT group were older and had worse pulmonary function. The 3-year overall survival (OS) rate was significantly better in the SLR group compared with the SBRT group (86.6% vs. 57%, log-rank p < 0.001). However, after adjusting for age, sex, tumor size, pulmonary function, histology, smoking history, and adjuvant therapy, treatment modality was not an independent prognostic factor for survival (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.43 to 2.77; p=0.974). We performed subgroup analysis in the following high-risk populations: patients who were older than 75 years; patients who were older than 70 years and had diffusing capacity of lung for carbon monoxide ≤ 80%. In each subgroup, there were no differences in OS and recurrence-free survival between patients who underwent SLR and those who received SBRT.
Conclusion
In our study, there were no significant differences in terms of survival or recurrence between SBRT and SLR in medically compromised stage I NSCLC patients. Our findings suggest that SBRT could be considered as a potential treatment option for selected patients.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Senan S, Paul MA, Lagerwaard FJ. Treatment of early-stage lung cancer detected by screening: surgery or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy? Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14:e270–4.2. Lagerwaard FJ, Verstegen NE, Haasbeek CJ, Slotman BJ, Paul MA, Smit EF, et al. Outcomes of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy in patients with potentially operable stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 83:348–53.3. Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Shibata T, Onishi H, Kokubo M, Karasawa K, et al. Prospective trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for both operable and inoperable T1N0M0 non-small cell lung cancer: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG0403. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015; 93:989–96.4. Timmerman RD, Paulus R, Pass HI, Gore EM, Edelman MJ, Galvin J, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for operable early-stage lung cancer: findings from the NRG oncology RTOG 0618 trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018; 4:1263–6.5. Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, Gomi K, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 81:1352–8.6. Matsuo Y, Chen F, Hamaji M, Kawaguchi A, Ueki N, Nagata Y, et al. Comparison of long-term survival outcomes between stereotactic body radiotherapy and sublobar resection for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer in patients at high risk for lobectomy: a propensity score matching analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2014; 50:2932–8.7. Varlotto J, Fakiris A, Flickinger J, Medford-Davis L, Liss A, Shelkey J, et al. Matched-pair and propensity score comparisons of outcomes of patients with clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer treated with resection or stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer. 2013; 119:2683–91.8. Chang JY, Senan S, Paul MA, Mehran RJ, Louie AV, Balter P, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:630–7.9. Crabtree TD, Denlinger CE, Meyers BF, El Naqa I, Zoole J, Krupnick AS, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy versus surgical resection for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 140:377–86.10. Paul S, Lee PC, Mao J, Isaacs AJ, Sedrakyan A. Long term survival with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) versus thoracoscopic sublobar lung resection in elderly people: national population based study with propensity matched comparative analysis. BMJ. 2016; 354:i3570.11. Grills IS, Mangona VS, Welsh R, Chmielewski G, McInerney E, Martin S, et al. Outcomes after stereotactic lung radiotherapy or wedge resection for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:928–35.12. Wu J, Bai HX, Chan L, Su C, Zhang PJ, Yang L, et al. Sublobar resection compared with stereotactic body radiation therapy and ablation for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: a National Cancer Database study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020; 160:1350–7.13. Wang HH, Zhang CZ, Zhang BL, Chen J, Zeng XL, Deng L, et al. Sublobar resection is associated with improved outcomes over radiotherapy in the management of high-risk elderly patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:6033–42.14. Poullis M. Treatment outcomes in stage I lung cancer: a comparison of surgery and stereotactic body radiation therapy. J Thorac Oncol. 2016; 11:e64–5.15. Tandberg DJ, Tong BC, Ackerson BG, Kelsey CR. Surgery versus stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a comprehensive review. Cancer. 2018; 124:667–78.16. Choi CM, Kim HC, Jung CY, Cho DG, Jeon JH, Lee JE, et al. Report of the Korean Association of Lung Cancer Registry (KALC-R), 2014. Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 51:1400–10.17. Hong S, Won YJ, Lee JJ, Jung KW, Kong HJ, Im JS, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2018. Cancer Res Treat. 2021; 53:301–15.18. Korea Central Cancer Registry, National Cancer Center. Annual report of cancer statistics in Korea in 2016. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2018.19. Black K. Business statistics for contemporary decision making. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons;2004.20. Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer;2010.21. Brunelli A, Charloux A, Bolliger CT, Rocco G, Sculier JP, Varela G, et al. ERS/ESTS clinical guidelines on fitness for radical therapy in lung cancer patients (surgery and chemo-radiotherapy). Eur Respir J. 2009; 34:17–41.22. Moreno AC, Fellman B, Hobbs BP, Liao Z, Gomez DR, Chen A, et al. Biologically effective dose in stereotactic body radiotherapy and survival for patients with early-stage NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2020; 15:101–9.23. Ginsberg RJ, Rubinstein LV. Randomized trial of lobectomy versus limited resection for T1 N0 non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer Study Group. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995; 60:615–22.24. Port JL, Parashar B, Osakwe N, Nasar A, Lee PC, Paul S, et al. A propensity-matched analysis of wedge resection and stereotactic body radiotherapy for early stage lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014; 98:1152–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Radiation Therapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Focused on Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy in Stage I
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- Lobectomy versus Sublobar Resection in Non-Lepidic Small-Sized Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Stereotactic radiotherapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer
- Outcomes of Completion Lobectomy for Locoregional Recurrence after Sublobar Resection in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer