Korean J Gastroenterol.
2023 Aug;82(2):91-95. 10.4166/kjg.2023.057.
Cystic Lymphangioma of Rectum-A Case Report and Review of Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgical Gastroenterology, Seth G S Medical College and KEM Hospital, Mumbai, India
- KMID: 2545333
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.057
Abstract
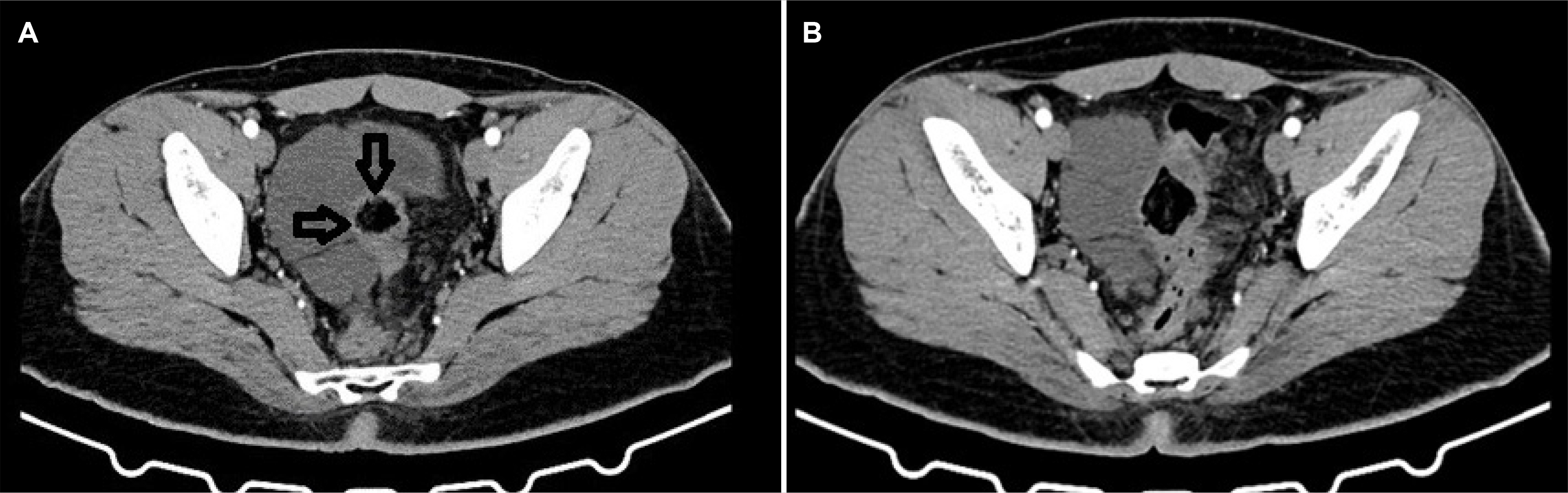
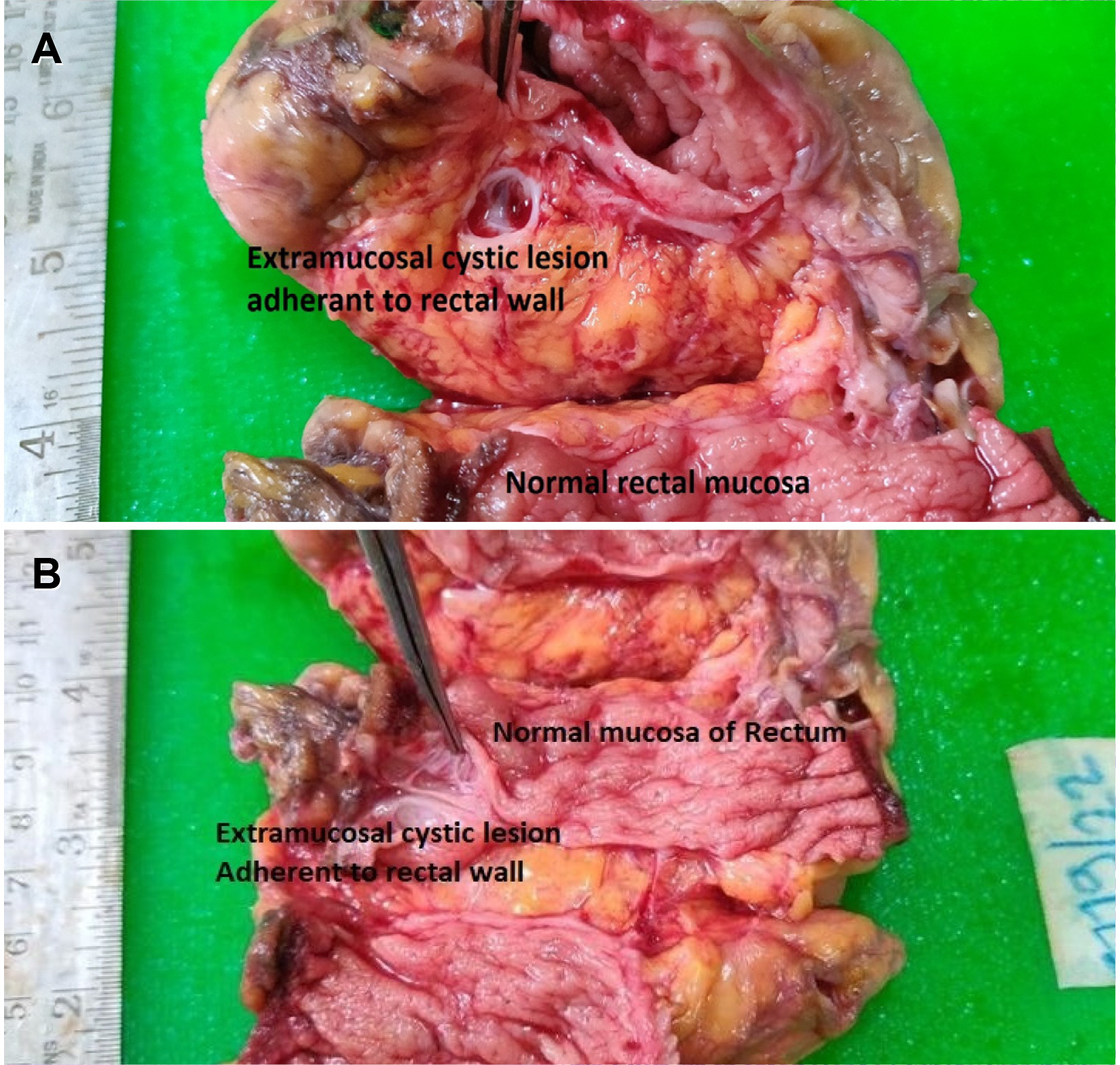
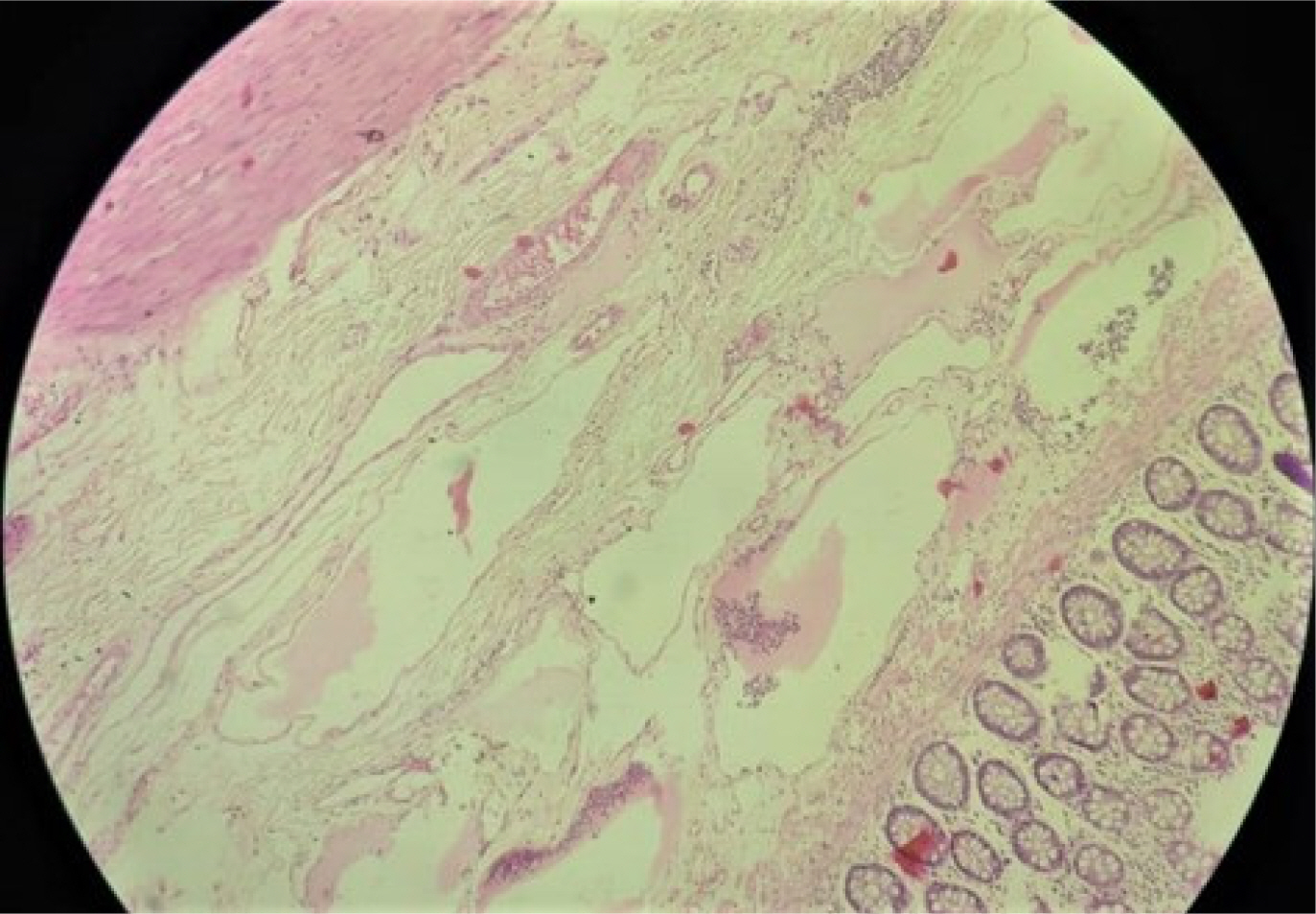
- Colorectal cystic lymphangiomas are rare benign lesions. They are characterized by the presence of either single or multi-cystic spaces lined by endothelium. Though there are multiple case reports of right and transverse colonic lymphangioma; only around 10 cases of lymphangioma of the rectum have been reported. We present a case report of rectal lymphangioma with the relevant literature review.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chisholm AJ, Hillkowits P. 1932; Lymphangioma of the rectum. Am J Surg. 17:281–282. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9610(32)90497-8.
Article2. Matsuda T, Matsutani T, Tsuchiya Y, et al. 2001; A clinical evaluation of lymphangioma of the large intestine: a case presentation of lymphangioma of the descending colon and a review of 279 Japanese cases. J Nippon Med Sch. 68:262–265. DOI: 10.1272/jnms.68.262. PMID: 11404774.
Article3. Sylla P, Deutsch G, Luo J, et al. 2008; Cavernous, arteriovenous, and mixed hemangioma-lymphangioma of the rectosigmoid: rare causes of rectal bleeding--case series and review of the literature. Int J Colorectal Dis. 23:653–658. DOI: 10.1007/s00384-008-0466-4. PMID: 18330577.
Article4. Pandey S, Fan M, Zhu J, Lu X, Chang D, Li X. 2017; Unusual cause of 55 years of rectal bleeding: hemolymphangioma (a case report). Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e6264. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006264. PMID: 28272235. PMCID: PMC5348183.5. Zagaceta Torres W, Ramírez García JF, Chá Vez Rosell MÁN. 2020; [Cystic lymphangioma of the rectum-sigmoid in a public hospital in Lima-Peru: case report]. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 40:64–68. Spanish. DOI: 10.47892/rgp.2020.401.1032. PMID: 32369468.6. Kumar S, Sarkar D, Prasad S, et al. 2012; Large pelvic masses of obscure origin: urologist's perspective. Urol Int. 88:215–224. DOI: 10.1159/000334332. PMID: 22377534.7. Chen G, Cui W, Ji XQ, Du JF. 2013; Diffuse hemolymphangioma of the rectum: a report of a rare case. World J Gastroenterol. 19:1494–1497. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i9.1494. PMID: 23538679. PMCID: PMC3602512.8. Kim KM, Choi KY, Lee A, Kim BK. 2000; Lymphangioma of large intestine: report of ten cases with endoscopic and pathologic correlation. Gastrointest Endosc. 52:255–259. DOI: 10.1067/mge.2000.107710. PMID: 10922105.9. Matsuba Y, Mizuiri H, Murata T, Niimi K. 2003; Adult intussusception due to lymphangioma of the colon. J Gastroenterol. 38:181–185. DOI: 10.1007/s005350300030. PMID: 12640534.10. Chen CF, Chuang CH, Lu CY, Hu C, Kuo TL, Hsieh JS. 2009; Adult intussusception secondary to lymphangioma of the cecum: a case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 25:347–352. DOI: 10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70527-3. PMID: 19561001.
Article11. Ly MMG, De Robles MS, Mckenzie C, Young CJ. 2019; Colonic lymphangioma presenting with intermittent pain and intussusception. J Surg Case Rep. 2019:rjy336. DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjy336. PMID: 30651966. PMCID: PMC6329364.
Article12. Kim DI, Seo HI, Kim JH, Kim HS, Jo HJ. 2011; Adult intussusception due to cecal lymphangioma: A case report. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 27:99–101. DOI: 10.3393/jksc.2011.27.2.99. PMID: 21602970. PMCID: PMC3092083.
Article13. Kim TO, Lee JH, Kim GH, et al. 2006; Adult intussusception caused by cystic lymphangioma of the colon: a rare case report. World J Gastroenterol. 12:2130–2132. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i13.2130. PMID: 16610070. PMCID: PMC4087698.
Article14. Kunimura T, Inagaki T, Hayashi R, Katou H, Iwaku K, Morohoshi T. 2005; A case of multiple colonic lymphangiomas causing intussusception. J Gastroenterol. 40:316–318. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-004-1544-1. PMID: 15830294.
Article15. Sugiura H, Katoh H, Inomata H, Maeda Y, Saitoh M, Tanabe T. 1990; A case of bleeding lymphangioma of the large intestine. J Surg Hokkaido. 35:123–126.16. Zilko PJ, Laurence BH, Sheiner H, Pollard J. 1975; Cystic lymphangiomyoma of the colon causing protein-losing enteropathy. Am J Dig Dis. 20:1076–1080. DOI: 10.1007/BF01071198. PMID: 1200000.
Article17. Morozumi K, Omoto T, Miyazaki H, et al. 1999; Two cases of lymphangioma of the colon accompanied with colon cancer. Gastroenterol Endosc. 41:1323–1329.18. Young TH, Ho AS, Tang HS, Hsu CT, Lee HS, Chao YC. 1996; Cystic lymphangioma of the transverse colon: report of a case and review of the literature. Abdom Imaging. 21:415–417. DOI: 10.1007/s002619900094. PMID: 8832861.
Article19. Bhutani MS, Annangi S, Koduru P, Aggarwal A, Suzuki R. 2016; Diagnosis of cystic lymphangioma of the colon by endoscopic ultrasound: Biopsy is not needed! Endosc Ultrasound. 5:335–338. DOI: 10.4103/2303-9027.191668. PMID: 27803907. PMCID: PMC5070292.
Article20. Zhuo CH, Shi DB, Ying MG, et al. 2014; Laparoscopic segmental colectomy for colonic lymphangiomas: a definitive, minimally invasive surgical option. World J Gastroenterol. 20:8745–8750. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8745. PMID: 25024636. PMCID: PMC4093731.
Article21. Wegner G. 1877; Uber lymphangiome. Arch Klin Chir. 20:641–707.22. Wiegand S, Eivazi B, Barth PJ, et al. 2008; Pathogenesis of lymphangiomas. Virchows Arch. 453:1–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00428-008-0611-z. PMID: 18500536.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Retroperitoneal cystic lymphangioma in an aged man: report of a case and review of the literature
- Cystic Lymphangioma Involving the Mesentery and the Retroperitoneum: A Case Report
- Cystic lymphangioma of the pancreas: a case report
- A Case of Cystic Lymphangioma of the Scrotum and Retroperitoneum
- Sonographic Finding of Scrotal Cystic Lymphangioma with Hemorrhage Caused by Percutaneous Needle Aspiration: A Case Report