Cancer Res Treat.
2023 Jul;55(3):1031-1047. 10.4143/crt.2022.1658.
Efficacy of Salvage Treatments in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Including Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology-Oncology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Health Sciences and Technology, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences and Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2544183
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2022.1658
Abstract
- Purpose
We intend to evaluate the efficacy of salvage treatments for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (R/R DLBCL) through meta-analysis.
Materials and Methods
R/R DLBCL trials were divided into two groups based on eligibility for autologous stem-cell transplantation (ASCT), and meta-analysis of each group was performed. Random effects models were used to estimate the 1-year progression-free survival (PFS) rate, and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was used as reference treatment.
Results
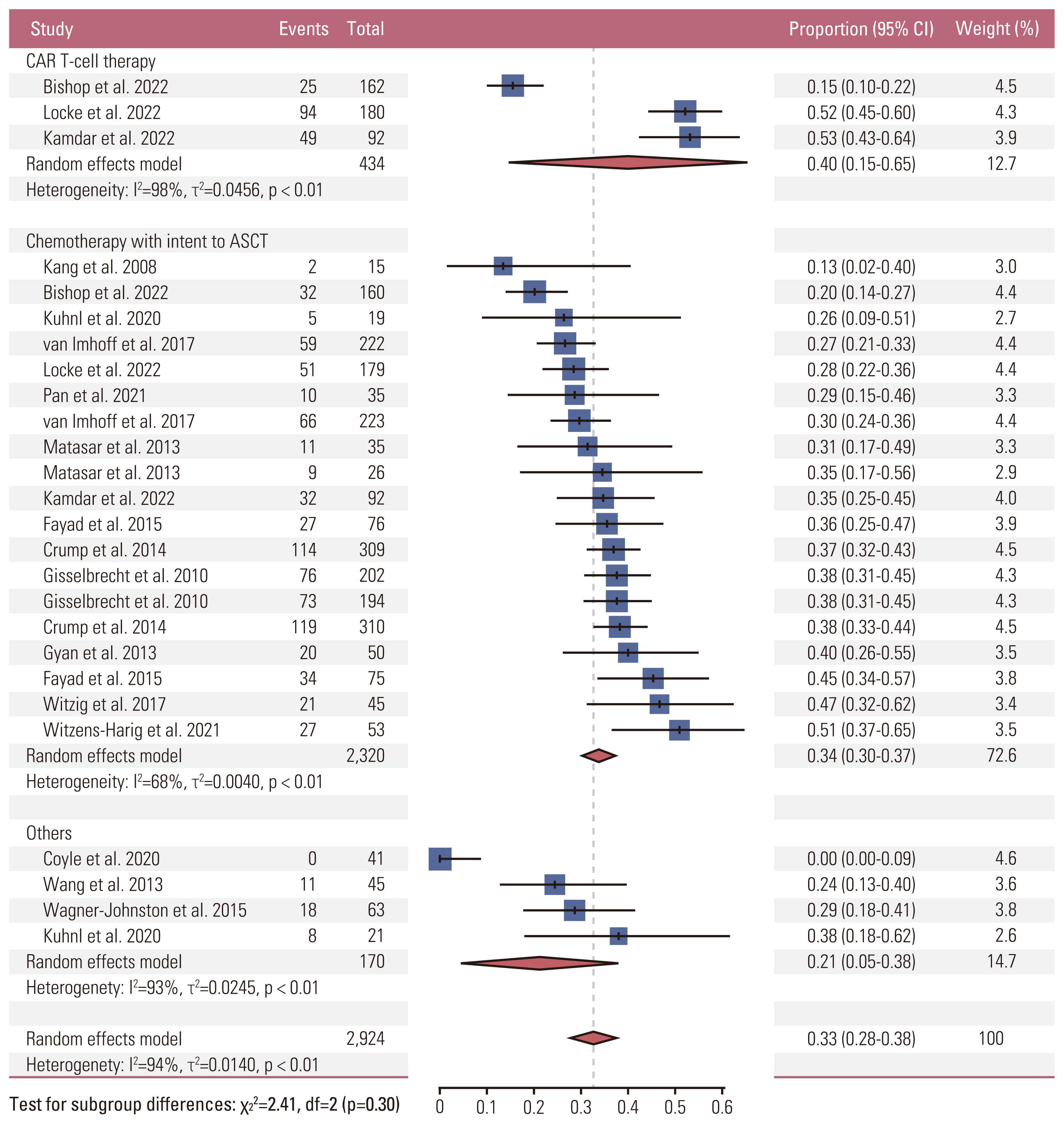
Twenty-six ASCT-eligible cohorts from 17 studies comprising 2,924 patients and 59 ASCT-ineligible cohorts from 53 studies comprising 3,617 patients were included in the pooled analysis. In the ASCT-eligible group, the pooled 1-year PFS rate was 0.40 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.15 to 0.65) for the CAR T-cell group and 0.34 (95% CI, 0.30 to 0.37) for the group with chemotherapy followed by ASCT intention. The two treatments were not significantly different in meta-regression analysis. In the ASCT-ineligible group, the pooled 1-year PFS was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.35 to 0.46) for CAR T-cell, and the highest primary outcome was 0.47 (95% CI, 0.37 to 0.57) for the tafasitamab group. CAR T-cell therapy showed significantly better outcomes than chemotherapy and therapies based on ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and selinexor. However, loncastuximab, polatuzumab plus bendamustine and rituximab, and the tafasitamab group showed no different efficacy than CAR T-cell therapy after adjusting for median number of previous lines of treatment.
Conclusion
Although several regimens were crudely grouped for classification, CAR T-cell therapy did not outperform chemotherapy followed by ASCT in the second-line setting or several recently developed agents in the ASCT-ineligible setting.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Teras LR, DeSantis CE, Cerhan JR, Morton LM, Jemal A, Flowers CR. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016; 66:443–59.
Article2. Sehn LH, Salles G. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:842–58.
Article3. Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood. 2010; 116:2040–5.
Article4. Gisselbrecht C, Glass B, Mounier N, Singh Gill D, Linch DC, Trneny M, et al. Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:4184–90.
Article5. Schuster SJ, Svoboda J, Chong EA, Nasta SD, Mato AR, Anak O, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells in refractory B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:2545–54.
Article6. Locke FL, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Perales MA, Kersten MJ, Oluwole OO, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022; 386:640–54.
Article7. Kamdar M, Solomon SR, Arnason J, Johnston PB, Glass B, Bachanova V, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): results from an interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022; 399:2294–308.8. Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-cell therapy in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:2531–44.
Article9. Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK, Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:45–56.
Article10. Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020; 396:839–52.
Article11. Bishop MR, Dickinson M, Purtill D, Barba P, Santoro A, Hamad N, et al. Second-line tisagenlecleucel or standard care in aggressive B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022; 386:629–39.
Article12. Roschewski M, Longo DL, Wilson WH. CAR T-cell therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: who, when, and how? N Engl J Med. 2022; 386:692–6.
Article13. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines: B-cell lymphomas V5.2022 [Internet]. Plymouth Meeting, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network;2022. [cited 2022 Aug 7]. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physcian_gls/pdf/b-cell.pdf.14. Sehn LH, Herrera AF, Flowers CR, Kamdar MK, McMillan A, Hertzberg M, et al. Polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38:155–65.
Article15. Kalakonda N, Maerevoet M, Cavallo F, Follows G, Goy A, Vermaat JS, et al. Selinexor in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (SADAL): a single-arm, multinational, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020; 7:e511–22.
Article16. Salles G, Duell J, Gonzalez Barca E, Tournilhac O, Jurczak W, Liberati AM, et al. Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (L-MIND): a multicentre, prospective, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020; 21:978–88.
Article17. Caimi PF, Ai W, Alderuccio JP, Ardeshna KM, Hamadani M, Hess B, et al. Loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (LOTIS-2): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021; 22:790–800.
Article18. Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 2000; 283:2008–12.
Article19. Kang HJ, Kim WS, Suh C, Park YH, Kim BS, Yuh YJ, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin and dexamethasone (ICD) combination chemotherapy for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma previously treated with rituximab plus CHOP. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008; 62:299–304.
Article20. Fayad L, Ansell SM, Advani R, Coiffier B, Stuart R, Bartlett NL, et al. Dacetuzumab plus rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide as salvage therapy for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma relapsing after rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisolone: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015; 56:2569–78.
Article21. Crump M, Kuruvilla J, Couban S, MacDonald DA, Kukreti V, Kouroukis CT, et al. Randomized comparison of gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin versus dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin chemotherapy before autologous stem-cell transplantation for relapsed and refractory aggressive lymphomas: NCIC-CTG LY.12. J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:3490–6.
Article22. van Imhoff GW, McMillan A, Matasar MJ, Radford J, Ardeshna KM, Kuliczkowski K, et al. Ofatumumab versus rituximab salvage chemoimmunotherapy in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: the ORCHARRD study. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:544–51.23. Gyan E, Damotte D, Courby S, Senecal D, Quittet P, Schmidt-Tanguy A, et al. High response rate and acceptable toxicity of a combination of rituximab, vinorelbine, ifosfamide, mito-xantrone and prednisone for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in first relapse: results of the R-NIMP GOELAMS study. Br J Haematol. 2013; 162:240–9.24. Matasar MJ, Czuczman MS, Rodriguez MA, Fennessy M, Shea TC, Spitzer G, et al. Ofatumumab in combination with ICE or DHAP chemotherapy in relapsed or refractory intermediate grade B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2013; 122:499–506.25. Kuhnl A, Peckitt C, Patel B, Ardeshna KM, Macheta MP, Radford J, et al. R-GEM-Lenalidomide versus R-GEM-P as second-line treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results of the UK NRCI phase II randomised LEGEND trial. Ann Hematol. 2020; 99:105–12.
Article26. Witzig TE, Johnston PB, LaPlant BR, Kurtin PJ, Pederson LD, Moore DF Jr, et al. Long-term follow-up of chemoimmunotherapy with rituximab, oxaliplatin, cytosine arabinoside, dexamethasone (ROAD) in patients with relapsed CD20+ B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: results of a study of the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center Research Consortium (MCCRC) MC-0485 now known as academic and community cancer research united (ACCRU). Am J Hematol. 2017; 92:1004–10.
Article27. Pan J, Ghimire S, Alpdogan SO, Chapman A, Carabasi M, DiMeglio M, et al. Phase I/II study of bendamustine in combination with ofatumumab, carboplatin, etoposide (BOCE) for relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2021; 62:590–7.
Article28. Witzens-Harig M, Viardot A, Keller U, Wosniok J, Deuster O, Klemmer J, et al. The mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus added to rituximab combined with dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatinum (R-DHAP) for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL: results from the phase-II STORM trial. Hemasphere. 2021; 5:e636.29. Wang M, Fowler N, Wagner-Bartak N, Feng L, Romaguera J, Neelapu SS, et al. Oral lenalidomide with rituximab in relapsed or refractory diffuse large cell, follicular and transformed lymphoma: a phase II clinical trial. Leukemia. 2013; 27:1902–9.
Article30. Wagner-Johnston ND, Goy A, Rodriguez MA, Ehmann WC, Hamlin PA, Radford J, et al. A phase 2 study of inotuzumab ozogamicin and rituximab, followed by autologous stem cell transplant in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015; 56:2863–9.31. Coyle L, Morley NJ, Rambaldi A, Mason KD, Verhoef G, Furness CL, et al. Open-label, phase 2 study of blinatumomab as second salvage therapy in adults with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020; 61:2103–12.32. Sang W, Shi M, Yang J, Cao J, Xu L, Yan D, et al. Phase II trial of co-administration of CD19- and CD20-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cells for relapsed and refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Med. 2020; 9:5827–38.
Article33. Lopez A, Gutierrez A, Palacios A, Blancas I, Navarrete M, Morey M, et al. GEMOX-R regimen is a highly effective salvage regimen in patients with refractory/relapsing diffuse large-cell lymphoma: a phase II study. Eur J Haematol. 2008; 80:127–32.
Article34. Czuczman MS, Trneny M, Davies A, Rule S, Linton KM, Wagner-Johnston N, et al. A phase 2/3 multicenter, randomized, open-lbel study to compare the efficacy and safety of lenalidomide versus investigator’s choice in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017; 23:4127–37.35. Ohmachi K, Niitsu N, Uchida T, Kim SJ, Ando K, Takahashi N, et al. Multicenter phase II study of bendamustine plus rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:2103–9.
Article36. Vacirca JL, Acs PI, Tabbara IA, Rosen PJ, Lee P, Lynam E. Bendamustine combined with rituximab for patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2014; 93:403–9.
Article37. Dang NH, Ogura M, Castaigne S, Fayad LE, Jerkeman M, Radford J, et al. Randomized, phase 3 trial of inotuzumab ozogamicin plus rituximab versus chemotherapy plus rituximab for relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2018; 182:583–6.
Article38. Murayama K, Kiguchi T, Izutsu K, Kameoka Y, Hidaka M, Kato H, et al. Bendamustine plus rituximab in Japanese patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2022; 101:979–89.39. Pettengell R, Sebban C, Zinzani PL, Derigs HG, Kravchenko S, Singer JW, et al. Monotherapy with pixantrone in histologically confirmed relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: post-hoc analyses from a phase III trial. Br J Haematol. 2016; 174:692–9.40. Joshi M, Taper J, Forsyth C, Rowlings P, Campbell P, Crispin P, et al. Outpatient rituximab, ifosfamide, etoposide (R-IE) in patients older than 60 years with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who are not candidates for stem cell transplantation. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020; 61:91–7.
Article41. Pettengell R, Dlugosz-Danecka M, Andorsky D, Belada D, Georgiev P, Quick D, et al. Pixantrone plus rituximab versus gemcitabine plus rituximab in patients with relapsed aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma not eligible for stem cell transplantation: a phase 3, randomized, multicentre trial (PIX306). Br J Haematol. 2020; 188:240–8.
Article42. Lugtenburg PJ, Zijlstra JM, Doorduijn JK, Bohmer LH, Hoogendoorn M, Berenschot HW, et al. Rituximab-PECC induction followed by (90) Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan consolidation in relapsed or refractory DLBCL patients who are ineligible for or have failed ASCT: results from a phase II HOVON study. Br J Haematol. 2019; 187:347–55.
Article43. Hu J, Wang X, Chen F, Ding M, Dong M, Yang W, et al. Combination of decitabine and a modified regimen of cisplatin, cytarabine and dexamethasone: a potential salvage regimen for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after second-line treatment failure. Front Oncol. 2021; 11:687374.
Article44. Wilson WH, Phillips T, Popplewell L, de Vos S, Chhabra S, Kimball AS, et al. Phase 1b/2 study of ibrutinib and lenalidomide with dose-adjusted EPOCH-R in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2021; 62:2094–106.
Article45. Hess G, Huttmann A, Witzens-Harig M, Dreyling MH, Keller U, Marks R, et al. A phase II trial to evaluate the combination of pixantrone and obinutuzumab for patients with relapsed aggressive lymphoma: final results of the prospective, multicentre GOAL trial. Br J Haematol. 2022; 198:482–91.46. Palazon-Carrion N, Martin Garcia-Sancho A, Nogales-Fer-nandez E, Jimenez-Cortegana C, Carnicero-Gonzalez F, Rios-Herranz E, et al. Lenalidomide plus R-GDP (R2-GDP) in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: final results of the R2-GDP-GOTEL trial and immune biomarker subanalysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2022; 28:3658–68.47. Herrera AF, Goy A, Mehta A, Ramchandren R, Pagel JM, Svoboda J, et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with durvalumab in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 2020; 95:18–27.
Article48. Younes A, Brody J, Carpio C, Lopez-Guillermo A, Ben-Yehuda D, Ferhanoglu B, et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a phase 1/2a study. Lancet Haematol. 2019; 6:e67–78.
Article49. Graf SA, Cassaday RD, Morris K, Voutsinas JM, Wu QV, Behnia S, et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy in relapsed or refractory, transformed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021; 21:176–81.
Article50. Zinzani PL, Pellegrini C, Gandolfi L, Stefoni V, Quirini F, Derenzini E, et al. Combination of lenalidomide and rituximab in elderly patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a phase 2 trial. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011; 11:462–6.
Article51. Houot R, Cartron G, Bijou F, de Guibert S, Salles GA, Fruchart C, et al. Obinutuzumab plus Lenalidomide (GALEN) for the treatment of relapse/refractory aggressive lymphoma: a phase II LYSA study. Leukemia. 2019; 33:776–80.
Article52. Major A, Kline J, Karrison TG, Fishkin PA, Kimball AS, Petrich AM, et al. Phase I/II clinical trial of temsirolimus and lenalidomide in patients with relapsed and refractory lymphomas. Haematologica. 2022; 107:1608–18.
Article53. Terui Y, Rai S, Izutsu K, Yamaguchi M, Takizawa J, Kuroda J, et al. A phase 2 study of polatuzumab vedotin+bendamustine +rituximab in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2021; 112:2845–54.
Article54. Sehn LH, Hertzberg M, Opat S, Herrera AF, Assouline S, Flowers CR, et al. Polatuzumab vedotin plus bendamustine and rituximab in relapsed/refractory DLBCL: survival update and new extension cohort data. Blood Adv. 2022; 6:533–43.
Article55. Morschhauser F, Flinn IW, Advani R, Sehn LH, Diefenbach C, Kolibaba K, et al. Polatuzumab vedotin or pinatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma: final results from a phase 2 randomised study (ROMULUS). Lancet Haematol. 2019; 6:e254–65.
Article56. Jurczak W, Zinzani PL, Gaidano G, Goy A, Provencio M, Nagy Z, et al. Phase IIa study of the CD19 antibody MOR208 in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2018; 29:1266–72.
Article57. Morschhauser F, Illidge T, Huglo D, Martinelli G, Paganelli G, Zinzani PL, et al. Efficacy and safety of yttrium-90 ibritumomab tiuxetan in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not appropriate for autologous stem-cell transplantation. Blood. 2007; 110:54–8.58. Arnason JE, Luptakova K, Rosenblatt J, Tzachanis D, Avigan D, Zwicker JI, et al. Yttrium-90 ibritumomab tiuxetan followed by rituximab maintenance as treatment for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma are not candidates for autologous stem cell transplant. Acta Haematol. 2015; 133:347–53.59. Smith SM, van Besien K, Karrison T, Dancey J, McLaughlin P, Younes A, et al. Temsirolimus has activity in non-mantle cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma subtypes: the University of Chicago phase II consortium. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:4740–6.
Article60. Coiffier B, Radford J, Bosly A, Martinelli G, Verhoef G, Barca G, et al. A multicentre, phase II trial of ofatumumab monotherapy in relapsed/progressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2013; 163:334–42.
Article61. Barnes JA, Jacobsen E, Feng Y, Freedman A, Hochberg EP, LaCasce AS, et al. Everolimus in combination with rituximab induces complete responses in heavily pretreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2013; 98:615–9.
Article62. de Vos S, Forero-Torres A, Ansell SM, Kahl B, Cheson BD, Bartlett NL, et al. A phase II study of dacetuzumab (SGN-40) in patients with relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and correlative analyses of patient-specific factors. J Hematol Oncol. 2014; 7:44.
Article63. Papadopoulos KP, Lopez-Jimenez J, Smith SE, Steinberg J, Keating A, Sasse C, et al. A multicenter phase II study of sepantronium bromide (YM155) plus rituximab in patients with relapsed aggressive B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016; 57:1848–55.64. Puvvada SD, Li H, Rimsza LM, Bernstein SH, Fisher RI, LeBlanc M, et al. A phase II study of belinostat (PXD101) in relapsed and refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas: SWOG S0520. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016; 57:2359–69.
Article65. Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, de Guibert S, Dupuis J, Ribrag V, Bouabdallah R, et al. A phase II, single-arm, multicentre study of coltuximab ravtansine (SAR3419) and rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2016; 173:722–30.
Article66. Assouline SE, Nielsen TH, Yu S, Alcaide M, Chong L, MacDonald D, et al. Phase 2 study of panobinostat with or without rituximab in relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2016; 128:185–94.
Article67. Batlevi CL, Crump M, Andreadis C, Rizzieri D, Assouline SE, Fox S, et al. A phase 2 study of mocetinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in relapsed or refractory lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2017; 178:434–41.
Article68. Younes A, Salles G, Martinelli G, Bociek RG, Barrigon DC, Barca EG, et al. Pan-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition with buparlisib in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Haematologica. 2017; 102:2104–12.69. Ribrag V, Kim WS, Bouabdallah R, Lim ST, Coiffier B, Illes A, et al. Safety and efficacy of abexinostat, a pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor, in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results of a phase II study. Haematologica. 2017; 102:903–9.
Article70. Trneny M, Verhoef G, Dyer MJ, Ben Yehuda D, Patti C, Canales M, et al. A phase II multicenter study of the anti-CD19 antibody drug conjugate coltuximab ravtansine (SAR3419) in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma previously treated with rituximab-based immunotherapy. Haematologica. 2018; 103:1351–8.
Article71. Burke JM, Shustov A, Essell J, Patel-Donnelly D, Yang J, Chen R, et al. An open-label, phase II trial of entospletinib (GS-9973), a selective spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018; 18:e327–31.72. Barnes JA, Redd R, Fisher DC, Hochberg EP, Takvorian T, Neuberg D, et al. Panobinostat in combination with rituximab in heavily pretreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results of a phase II study. Hematol Oncol. 2018; 36:633–7.
Article73. Zaja F, Salvi F, Rossi M, Sabattini E, Evangelista A, Ciccone G, et al. Single-agent panobinostat for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: clinical outcome and correlation with genomic data: a phase 2 study of the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018; 59:2904–10.
Article74. Galanina N, Smith SM, Liao C, Petrich A, Libao B, Gartenhaus R, et al. University of Chicago phase II consortium trial of selumetinib (MEKi) demonstrates low tolerability and efficacy in relapsed DLBCL. Br J Haematol. 2018; 181:264–7.
Article75. Ansell SM, Minnema MC, Johnson P, Timmerman JM, Armand P, Shipp MA, et al. Nivolumab for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients ineligible for or having failed autologous transplantation: a single-arm, phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:481–9.
Article76. Lenz G, Hawkes E, Verhoef G, Haioun C, Thye Lim S, Seog Heo D, et al. Single-agent activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition with copanlisib in patients with molecularly defined relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2020; 34:2184–97.
Article77. Mussetti A, Sureda A. Second-line CAR T cells for lymphomas. Lancet. 2022; 399:2247–9.
Article78. Shargian L, Raanani P, Yeshurun M, Gafter-Gvili A, Gurion R. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is superior to standard of care as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Haematol. 2022; 198:838–46.
Article79. Shadman M, Pasquini M, Ahn KW, Chen Y, Turtle CJ, Hematti P, et al. Autologous transplant vs chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for relapsed DLBCL in partial remission. Blood. 2022; 139:1330–9.
Article80. Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Reagan PM, Miklos DB, et al. Comparison of 2-year outcomes with CAR T cells (ZUMA-1) vs salvage chemotherapy in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2021; 5:4149–55.81. Maziarz RT, Zhang J, Yang H, Chai X, Yuan C, Schwarz E, et al. Indirect comparison of tisagenlecleucel and historical treatments for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022; 6:2536–47.
Article82. Nowakowski GS, Yoon DH, Mondello P, Joffe E, Fleury I, Peters A, et al. Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide versus pola-BR, R2, and CAR T: comparing outcomes from RE-MIND2, an observational, retrospective cohort study in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2021; 138(Supp 1):183.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- Current Challenges in Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Therapy in Patients With B-cell Lymphoid Malignancies
- Delayed Terminal Ileal Perforation in a Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma Patient with Rapid Remission Following Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy
- Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T Cell Therapy
- Comparison of Efficacy of Pembrolizumab between Epstein-Barr Virus‒Positive and ‒Negative Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas