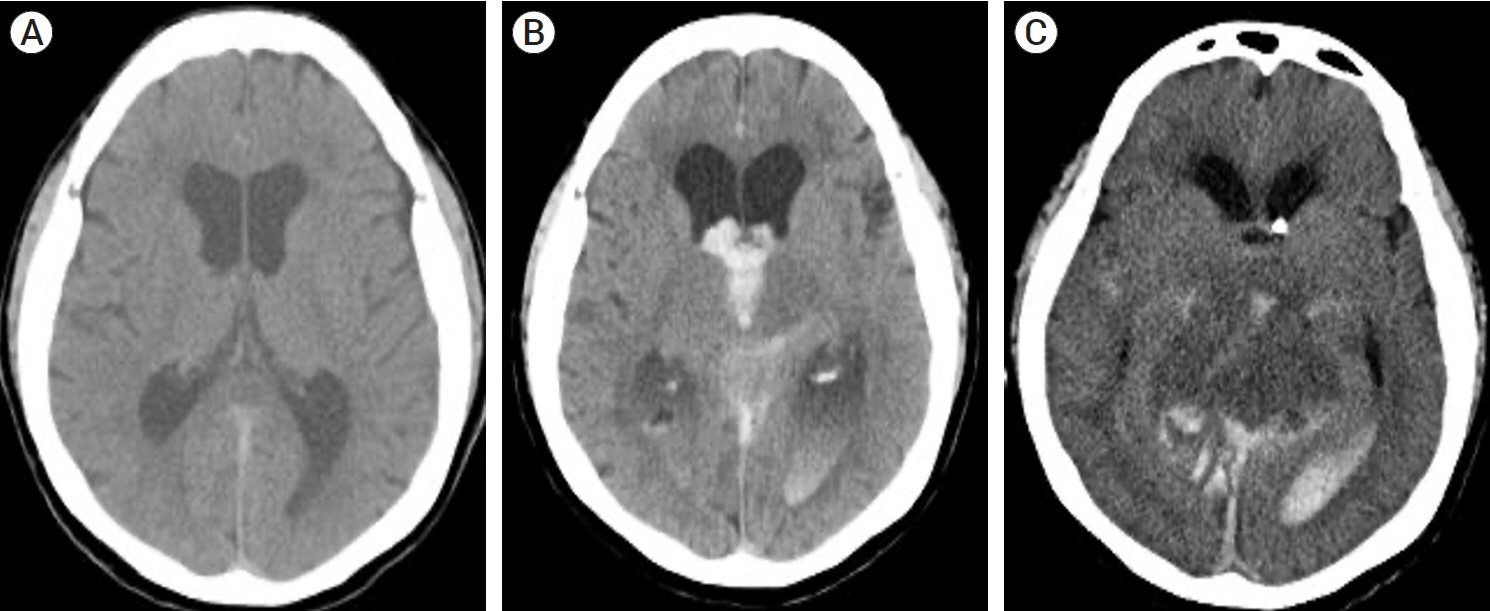
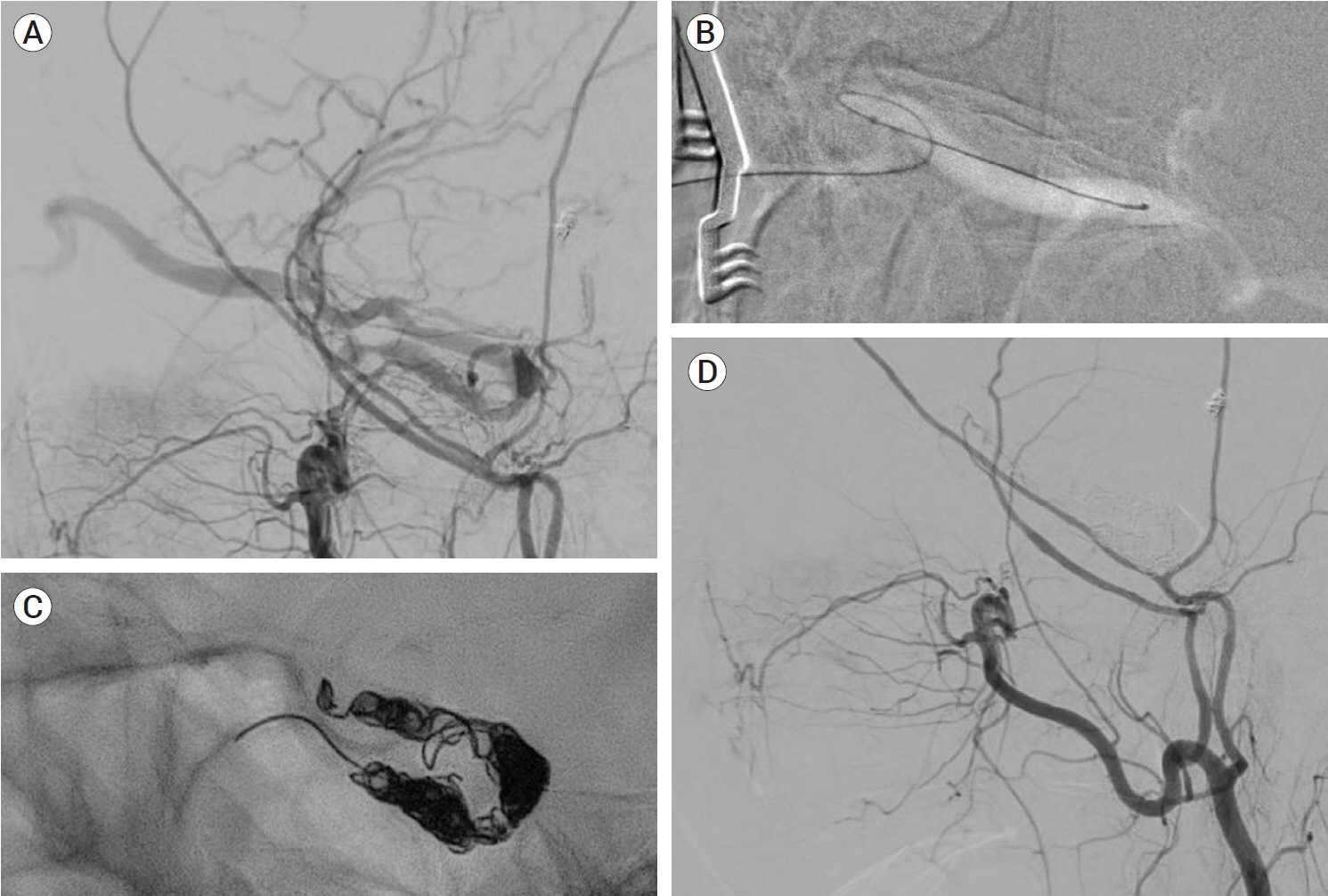
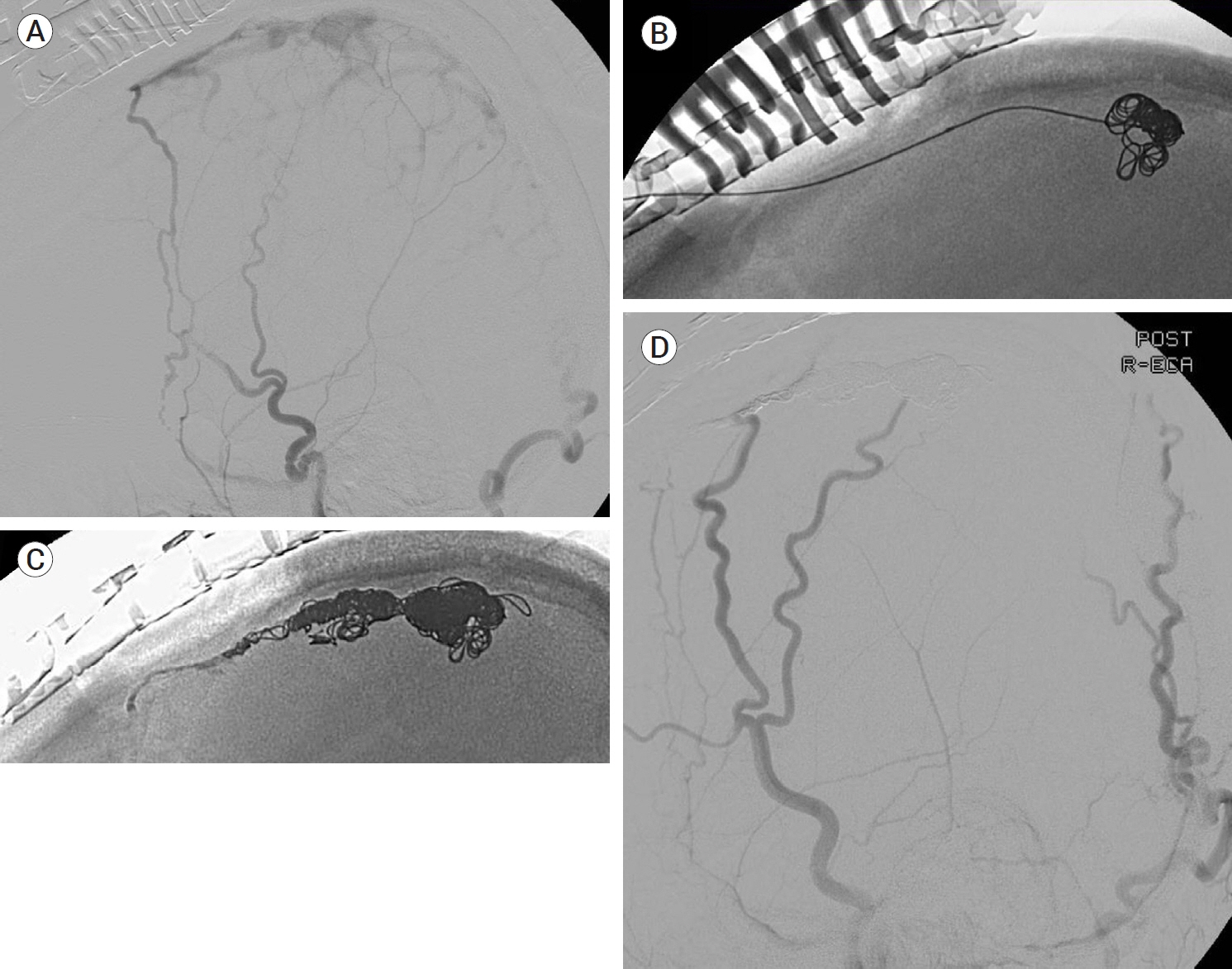
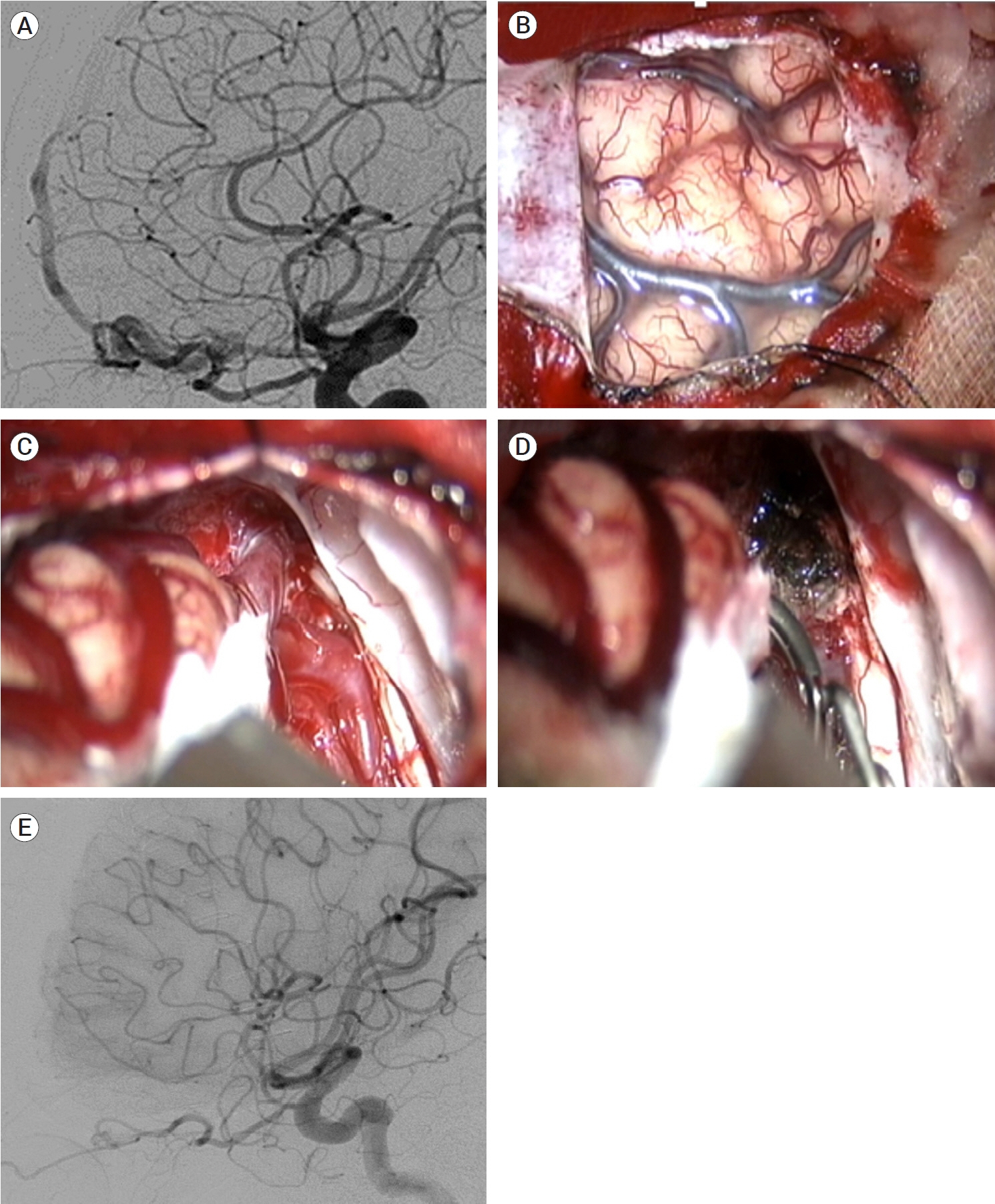
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2023 Jun;25(2):117-131. 10.7461/jcen.2023.E2022.10.006.
Role of surgery in management of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2543508
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2023.E2022.10.006
Abstract
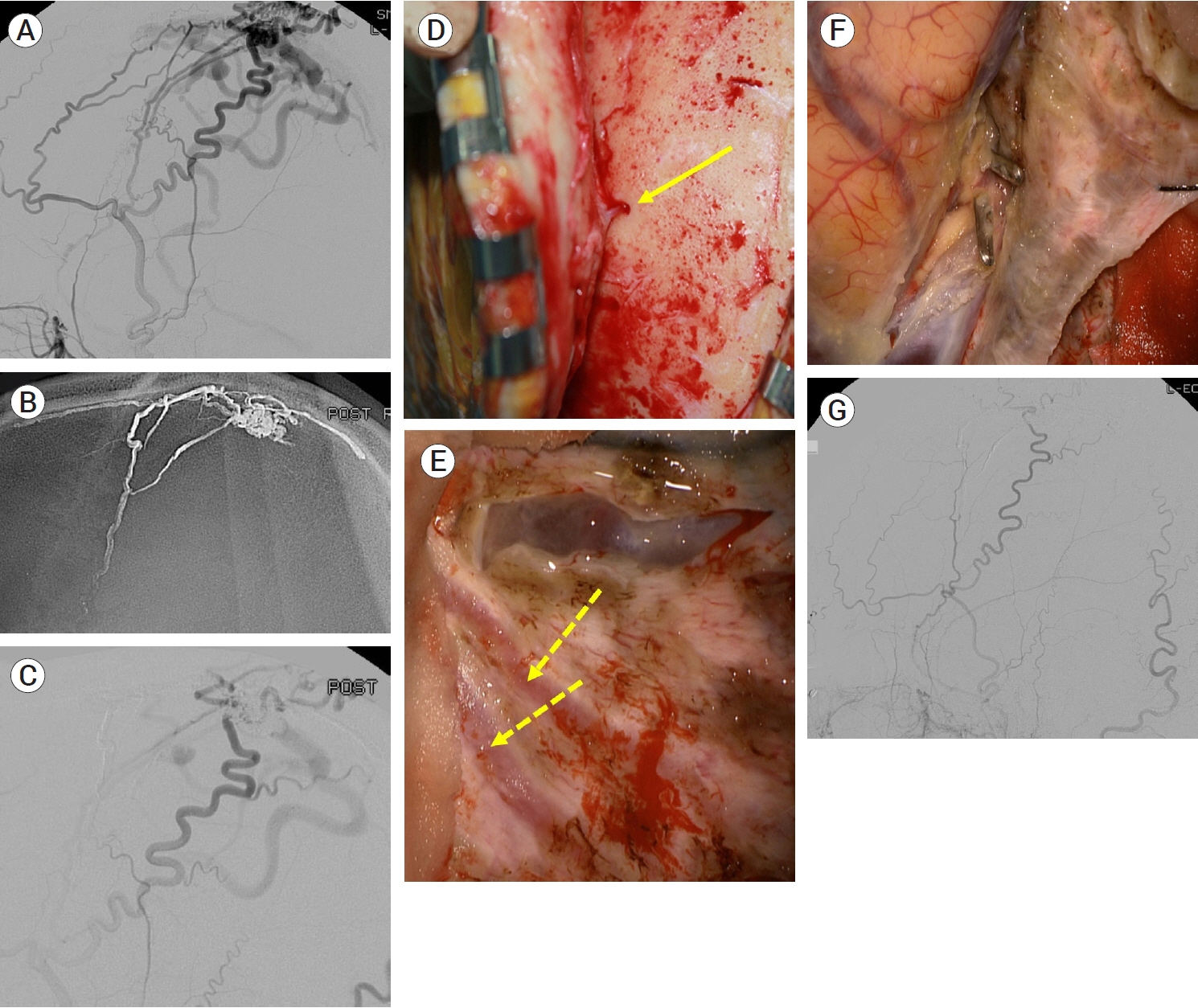
- Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVF) are abnormal connections between intracranial arterial and venous systems within the dural layers. Intracranial DAVFs are rare but can occur wherever dural components exist. The pathogenesis of DAVFs is controversial. Venous hypertension is considered as a main cause of clinical symptoms which are subclassified into asymptomatic, benign and aggressive manifestations. To date, several classification schemes have been proposed to stratify the natural course and risks of DAVFs. Currently, endovascular therapy is the main treatment modality. Moreover, the use of radiosurgery and radiotherapy has been limited. Open surgery is also selectively performed as a main treatment modality for specific types of DAVFs and an adjunctive modality for the endovascular approach. Herein, we present a review of the general perspectives of intracranial DAVFs with an emphasis on the role of surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Al-Shahi R, Bhattacharya JJ, Currie DG, Papanastassiou V, Ritchie V, Roberts RC, et al. Prospective, population-based detection of intracranial vascular malformations in adults: the Scottish Intracranial Vascular Malformation Study (SIVMS). Stroke. 2003; May. 34(5):1163–9.2. Baek HG, Park SH, Park KS, Kang DH, Hwang JH, Hwang SK. Stereotactic radiosurgery for dural arteriovenous fistulas involving the transverse-sigmoid sinus: a single center experience and review of the literatures. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2019; Jul. 62(4):458–66.3. Barrow DL, Spector RH, Braun IF, Landman JA, Tindall SC, Tindall GT. Classification and treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg. 1985; Feb. 62(2):248–56.4. Beer-Furlan A, Joshi KC, Dasenbrock HH, Chen M. Endovascular management of complex superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula. Neurosurg Focus. 2019; Apr. 46(- Suppl_2):V11.
Article5. Bhatia KD, Lee H, Kortman H, Klostranec J, Guest W, Wälchli T, et al. Endovascular management of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: transarterial approach. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2022; Mar. 43(3):324–31.
Article6. Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA. A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg. 1995; Feb. 82(2):166–79.7. Brown RD, Wiebers DO, Nichols DA. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: angiographic predictors of intracranial hemorrhage and clinical outcome in nonsurgical patients. J Neurosurg. 1994; Oct. 81(4):531–8.8. Brown RD, Wiebers DO, Torner JC, O’Fallon WM. Incidence and prevalence of intracranial vascular malformations in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1965 to 1992. Neurology. 1996; Apr. 46(4):949–52.9. Chaudhary N, Lownie SP, Bussière M, Pelz DM, Nicolle D. Transcortical venous approach for direct embolization of a cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2012; Jun. 70(2 Suppl Operative):343–8.10. Chen CJ, Lee CC, Ding D, Starke RM, Chivukula S, Yen CP, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: a systematic review. J Neurosurg. 2015; Feb. 122(2):353–62.11. Cho WS, Han JH, Kang HS, Kim JE, Kwon OK, Oh CW, et al. Treatment outcomes of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas of the transverse and sigmoid sinuses from a single institute in Asia. J Clin Neurosci. 2013; Jul. 20(7):1007–12.12. Chung SJ, Kim JS, Kim JC, Lee SK, Kwon SU, Lee MC, et al. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: analysis of 60 patients. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2002; 13(2):79–88.13. Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, et al. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology. 1995; Mar. 194(3):671–80.14. Cognard C, Januel AC, Silva NA, Tall P. Endovascular treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with cortical venous drainage: new management using onyx. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; Feb. 29(2):235–41.
Article15. Cohen SD, Goins JL, Butler SG, Morris PP, Browne JD. Dural arteriovenous fistula: diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Laryngoscope. 2009; Feb. 119(2):293–7.16. De Keukeleire K, Vanlangenhove P, Kalala Okito JP, Hallaert G, Van Roost D, Defreyne L. Transarterial embolization with ONYX for treatment of intracranial non-cavernous dural arteriovenous fistula with or without cortical venous reflux. J Neurointerv Surg. 2011; Sep. 3(3):224–8.17. Deniwar MA, Kwon B, Song Y, Park JC, Lee DH. Use of a rigid-tipped microguidewire for the endovascular treatment of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas with an occluded inferior petrosal sinus. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2022; Sep. 65(5):688–96.
Article18. Détraz L, Orlov K, Berestov V, Borodetsky V, Rouchaud A, de Abreu Mattos LG, et al. Posterior fossa dural arteriovenous fistulas with subarachnoid venous drainage: outcomes of endovascular treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019; Aug. 40(8):1363–8.
Article19. Dijk JMC, terBrugge KG, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC. Clinical course of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with long-term persistent cortical venous reflux. Stroke. 2002; May. 33(5):1233–6.
Article20. Ding D, Starke RM, Crowley RW, Liu KC. Interhemispheric approach for endoscopic ligation of an anterior cranial fossa dural arteriovenous fistula. J Clin Neurosci. 2015; Dec. 22(12):1969–72.
Article21. Djindjian R, Merland JJ. Normal super-selective arteriography of the external carotid artery, in Super-Selective Arteriography of the External Carotid Artery. Berlin, Heidelberg, Springer;1978. p. 1–123.22. Ernst R, Bulas R, Tomsick T, van Loveren H, Aziz KA. Three cases of dural arteriovenous fistula of the anterior condylar vein within the hypoglossal canal. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; Nov-Dec. 20(10):2016–20.23. Gandhi D, Chen J, Pearl M, Huang J, Gemmete JJ, Kathuria S. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: classification, imaging findings, and treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; Jun. 33(6):1007–13.24. Gross BA, Albuquerque FC, McDougall CG, Jankowitz BT, Jadhav AP, Jovin TG, et al. A multi-institutional analysis of the untreated course of cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg. 2018; Nov. 129(5):1114–9.
Article25. Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Goto K, Norman D, Newton TH. Dural fistulas involving the transverse and sigmoid sinuses: results of treatment in 28 patients. Radiology. 1987; May. 163(2):443–7.
Article26. Hellstern V, Aguilar-Pérez M, Schob S, Bhogal P, AlMatter M, Kurucz P, et al. Endovascular treatment of dural arteriovenous fistulas of the anterior or posterior condylar vein: a cadaveric and clinical study and literature review. Clin Neuroradiol. 2019; Jun. 29(2):341–9.
Article27. Hoh BL, Choudhri TF, Connolly ES, Solomon RA. Surgical management of high-grade intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: leptomeningeal venous disruption without nidus excision. Neurosurgery. 1998; Apr. 42(4):796–804; discussion 804-5.
Article28. Hou K, Li G, Luan T, Xu K, Yu J. Endovascular treatment of the cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: current status and considerations. Int J Med Sci. 2020; May. 17(8):1121–30.
Article29. Houser OW, Baker HL, Rhoton AL, Okazaki H. Intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations. Radiology. 1972; Oct. 105(1):55–64.
Article30. Houser OW, Campbell JK, Campbell RJ, Sundt TM. Arteriovenous malformation affecting the transverse dural venous sinus--an acquired lesion. Mayo Clin Proc. 1979; Oct. 54(10):651–61.31. Ito J, Imamura H, Kobayashi K, Tsuchida T, Sato S. Dural arteriovenous malformations of the base of the anterior cranial fossa. Neuroradiology. 1983; 24(3):149–54.
Article32. Iwama T, Hashimoto N, Takagi Y, Tanaka M, Yamamoto S, Nishi S, et al. Hemodynamic and metabolic disturbances in patients with intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: positron emission tomography evaluation before and after treatment. J Neurosurg. 1997; May. 86(5):806–11.
Article33. Jang JH, Cho WS, Kang HS, Kim JE. Surgical obliteration of anterior cranial fossa dural arteriovenous fistulas via unilateral high frontal craniotomy. World Neurosurg. 2019; Oct. 130:89–94.
Article34. Jia ZY, Song YS, Sheen JJ, Kim JG, Lee DH, Suh DC. Cannulation of occluded inferior petrosal sinuses for the transvenous embolization of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas: usefulness of a frontier-wire probing technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018; Dec. 39(12):2301–6.
Article35. Kalsi P, Padmanabhan R, Prasad KSM, Mukerji N. Treatment of low flow, indirect cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas with external manual carotid compression - the UK experience. Br J Neurosurg. 2020; Dec. 34(6):701–3.
Article36. Kim MS, Oh CW, Han DH, Kwon OK, Jung HW, Han MH. Intraosseous dural arteriovenous fistula of the skull base associated with hearing loss. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2002; May. 96(5):952–5.37. Kiyosue H, Hori Y, Okahara M, Tanoue S, Sagara Y, Matsumoto S, et al. Treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: current strategies based on location and hemodynamics, and alternative techniques of transcatheter embolization. Radiographics. 2004; Nov-Dec. 24(6):1637–53.
Article38. Kiyosue H, Tanoue S, Okahara M, Hori Y, Kashiwagi J, Sagara Y, et al. Angioarchitecture of transverse-sigmoid sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation of shunted pouches by multiplanar reformatted images of rotational angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; Aug. 34(8):1612–20.
Article39. Klisch J, Huppertz HJ, Spetzger U, Hetzel A, Seeger W, Schumacher M. Transvenous treatment of carotid cavernous and dural arteriovenous fistulae: results for 31 patients and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2003; Oct. 53(4):836–56.
Article40. Kojima T, Miyachi S, Sahara Y, Nakai K, Okamoto T, Hattori K, et al. The relationship between venous hypertension and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor: hemodynamic and immunohistochemical examinations in a rat venous hypertension model. Surg Neurol. 2007; Sep. 68(3):277–84.
Article41. Kuroda S, Furukawa K, Shiga T, Ushikoshi S, Katoh C, Aoki T, et al. Pretreatment and posttreatment evaluation of hemodynamic and metabolic parameters in intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae with cortical venous reflux. Neurosurgery. 2004; Mar. 54(3):585–91; discussion 591.
Article42. Kuwayama N. Epidemiologic survey of dural arteriovenous fistulas in japan: clinical frequency and present status of treatment. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2016; 123:185–8.
Article43. Lalwani AK, Dowd CF, Halbach VV. Grading venous restrictive disease in patients with dural arteriovenous fistulas of the transverse/sigmoid sinus. J Neurosurg. 1993; Jul. 79(1):11–5.
Article44. Lasjaunias P, Chiu M, ter Brugge K, Tolia A, Hurth M, Bernstein M. Neurological manifestations of intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg. 1986; May. 64(5):724–30.
Article45. Lawton MT, Chun J, Wilson CB, Halbach VV. Ethmoidal dural arteriovenous fistulae: an assessment of surgical and endovascular management. Neurosurgery. 1999; Oct. 45(4):805–10.
Article46. Lee SH, Cho WS, Kang HS, Kim JE, Cho YD, Yoo DH, et al. Newly occurring cranial nerve palsy after endovascular treatment of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019; Nov. 11(11):1168–72.
Article47. Leone G, Renieri L, Enriquez-Marulanda A, Dmytriw AA, Nappini S, Laiso A, et al. Carotid cavernous fistulas and dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus: validation of a new classification according to venous drainage. World Neurosurg. 2019; Aug. 128:e621–31.
Article48. Li Q, Zhang Q, Huang QH, Fang YB, Zhang ZL, Xu Y, et al. A pivotal role of the vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway in the formation of venous hypertension-induced dural arteriovenous fistulas. Mol Med Rep. 2014; May. 9(5):1551–8.
Article49. Lv X, Li Y, Liu A, Lv M, Jiang C, Wu Z. Endovascular embolization of dural arteriovenous fistulas of the anterior cranial fossa: three case reports. Neurol Res. 2008; Oct. 30(8):852–9.
Article50. McConnell KA, Tjoumakaris SI, Allen J, Shapiro M, Bescke T, Jabbour PM, et al. Neuroendovascular management of dural arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2009; Oct. 20(4):431–9.
Article51. Meneghelli P, Pasqualin A, Lanterna LA, Bernucci C, Spinelli R, Dorelli G, et al. Surgical treatment of anterior cranial fossa dural arterio-venous fistulas (DAVFs): a two-centre experience. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2017; May. 159(5):823–30.
Article52. Mielke D, Mayfrank L, Psychogios MN, Rohde V. The anterior interhemispheric approach: a safe and effective approach to anterior skull base lesions. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2014; Apr. 156(4):689–96.53. Mossa-Basha M, Chen J, Gandhi D. Imaging of cerebral arteriovenous malformations and dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2012; Jan. 23(1):27–42.
Article54. Nam TK, Byun JS, Choi HH, Chung MS, Lee EJ. Feasibility and effectiveness of direct puncture and Onyx embolization for transverse sinus dural arteriovenous fistula. Yonsei Med J. 2019; Nov. 60(11):1112–5.
Article55. Narayanan S. Endovascular management of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurol Clin. 2010; Nov. 28(4):899–911.
Article56. Narvid J, Do HM, Blevins NH, Fischbein NJ. CT angiography as a screening tool for dural arteriovenous fistula in patients with pulsatile tinnitus: feasibility and test characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; Mar. 32(3):446–53.
Article57. Natarajan SK, Ghodke B, Kim LJ, Hallam DK, Britz GW, Sekhar LN. Multimodality treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas in the Onyx era: a single center experience. World Neurosurg. 2010; Apr. 73(4):365–79.
Article58. O’Connor KP, Bohnstedt BN. Left anterior cranial fossa dural arteriovenous fistula ligation using a supra-orbital (eyebrow) craniotomy. Neurosurg Focus. 2019; Apr. 46(Suppl_2):V3.
Article59. Oh JS, Yoon SM, Shim JJ, Bae HG. Transcranial direct middle meningeal artery puncture for the onyx embolization of dural arteriovenous fistula involving the superior sagittal sinus. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015; Jan. 57(1):54–7.
Article60. Olteanu-Nerbe V, Uhl E, Steiger HJ, Yousry T, Reulen HJ. Dural arteriovenous fistulas including the transverse and sigmoid sinuses: results of treatment in 30 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1997; 139(4):307–18.
Article61. Pekkola J, Kangasniemi M. Posterior fossa dural arteriovenous fistulas: diagnosis and follow-up with time-resolved imaging of contrast kinetics (TRICKS) at 1.5T. Acta Radiol. 2011; May. 52(4):442–7.
Article62. Phan K, Xu J, Leung V, Teng I, Sheik-Ali S, Maharaj M, et al. Orbital approaches for treatment of carotid cavernous fistulas: a systematic review. World Neurosurg. 2016; Dec. 96:243–51.
Article63. Pollock BE, Nichols DA, Garrity JA, Gorman DA, Stafford SL. Stereotactic radiosurgery and particulate embolization for cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulae. Neurosurgery. 1999; Sep. 45(3):459–66. discussion 466-7.
Article64. Polster SP, Carrión-Penagos J, Christorfordis G, Awad IA. Dural arteriovenous malforations. in Stroke. Elsevier;2022. p. 1016–1027.e2.65. Reinges MH, Thron A, Mull M, Huffmann BC, Gilsbach JM. Dural arteriovenous fistulae at the foramen magnum. J Neurol. 2001; Mar. 248(3):197–203.
Article66. Reynolds MR, Lanzino G, Zipfel GJ. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae. Stroke. 2017; May. 48(5):1424–31.
Article67. Rhim JK, Cho YD, Park JJ, Jeon JP, Kang HS, Kim JE, et al. Endovascular treatment of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula with ipsilateral inferior petrosal sinus occlusion: a single-center experience. Neurosurgery. 2015; Aug. 77(2):192–9.68. Rhim JK, Cho YD, Yoo DH, Kang HS, Cho WS, Kim JE, et al. Endovascular treatment of bilateral cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: therapeutic strategy and follow-up outcomes. Korean J Radiol. 2018; Mar-Apr. 19(2):334–41.
Article69. Roy D, Raymond J. The role of transvenous embolization in the treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurgery. 1997; Jun. 40(6):1133–44.
Article70. Saito A, Takahashi N, Furuno Y, Kamiyama H, Nishimura S, Midorikawa H, et al. Multiple isolated sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas associated with antithrombin III deficiency--case report--. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2008; Oct. 48(10):455–9.71. Sarma D, ter Brugge K. Management of intracranial dural arteriovenous shunts in adults. Eur J Radiol. 2003; Jun. 46(3):206–20.
Article72. Seo Y, Kim DG, Dho YS, Kim JW, Kim YH, Park CK, et al. A retrospective analysis of the outcomes of dural arteriovenous fistulas treated with gamma knife radiosurgery: a single-institution experience. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2018; 96(1):46–53.
Article73. Shin Y, Nakase H, Nakamura M, Shimada K, Konishi N, Sakaki T. Expression of angiogenic growth factor in the rat DAVF model. Neurol Res. 2007; Oct. 29(7):727–33.
Article74. Singh R, Chen CJ, Didwania P, Kotecha R, Fariselli L, Pollock BE, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for dural arteriovenous fistulas: a systematic review and meta-analysis and international stereotactic radiosurgery society practice guidelines. Neurosurgery. 2022; Jul. 91(1):43–58.
Article75. Spetzler RF, Moon K, Almefty RO. Arteriovenous and cavernous malformations. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Volume 143. 3rd series. Amsterdam: Elsevier;2017. p. 2–324.76. Strom RG, Botros JA, Refai D, Moran CJ, Cross DT, Chicoine MR, et al. Cranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: asymptomatic cortical venous drainage portends less aggressive clinical course. Neurosurgery. 2009; Feb. 64(2):241–7. discussion 247-8.77. Terada T, Higashida RT, Halbach VV, Dowd CF, Tsuura M, Komai N, et al. Development of acquired arteriovenous fistulas in rats due to venous hypertension. J Neurosurg. 1994; May. 80(5):884–9.
Article78. Tsai LK, Jeng JS, Yip PK. Ultrasonography in intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula. J Med Ultrasound. 2008; Nov. 16(1):57–64.
Article79. Wicks RT, Zhao X, Hardesty DA, Liebelt BD, Nakaji P. Mini-pterional approach for clip ligation of ethmoidal dural arteriovenous fistula. Neurosurg Focus. 2019; Apr. 46(Suppl_2):V9.
Article80. Yang H, Kano H, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Horowitz MB, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery with or without embolization for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurgery. 2010; Nov. 67(5):1276–83.
Article81. Yoshida K, Melake M, Oishi H, Yamamoto M, Arai H. Transvenous embolization of dural carotid cavernous fistulas: a series of 44 consecutive patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; Apr. 31(4):651–5.
Article82. Zipfel GJ, Shah MN, Refai D, Dacey RG, Derdeyn CP. Cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: modification of angiographic classification scales based on new natural history data. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; May. 26(5):e14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Occurrence of Metachronous Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula after Embolization of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
- Endovascular management of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas: Overall review and considerations
- Pathophysiology and classification of intracranial and spinal dural AVF
- Surgical Treatment of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula and Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
- Borden Type I Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting as Subarachnoid Hemorrhage from a Feeding Artery Aneurysm of the Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery: A Case Report