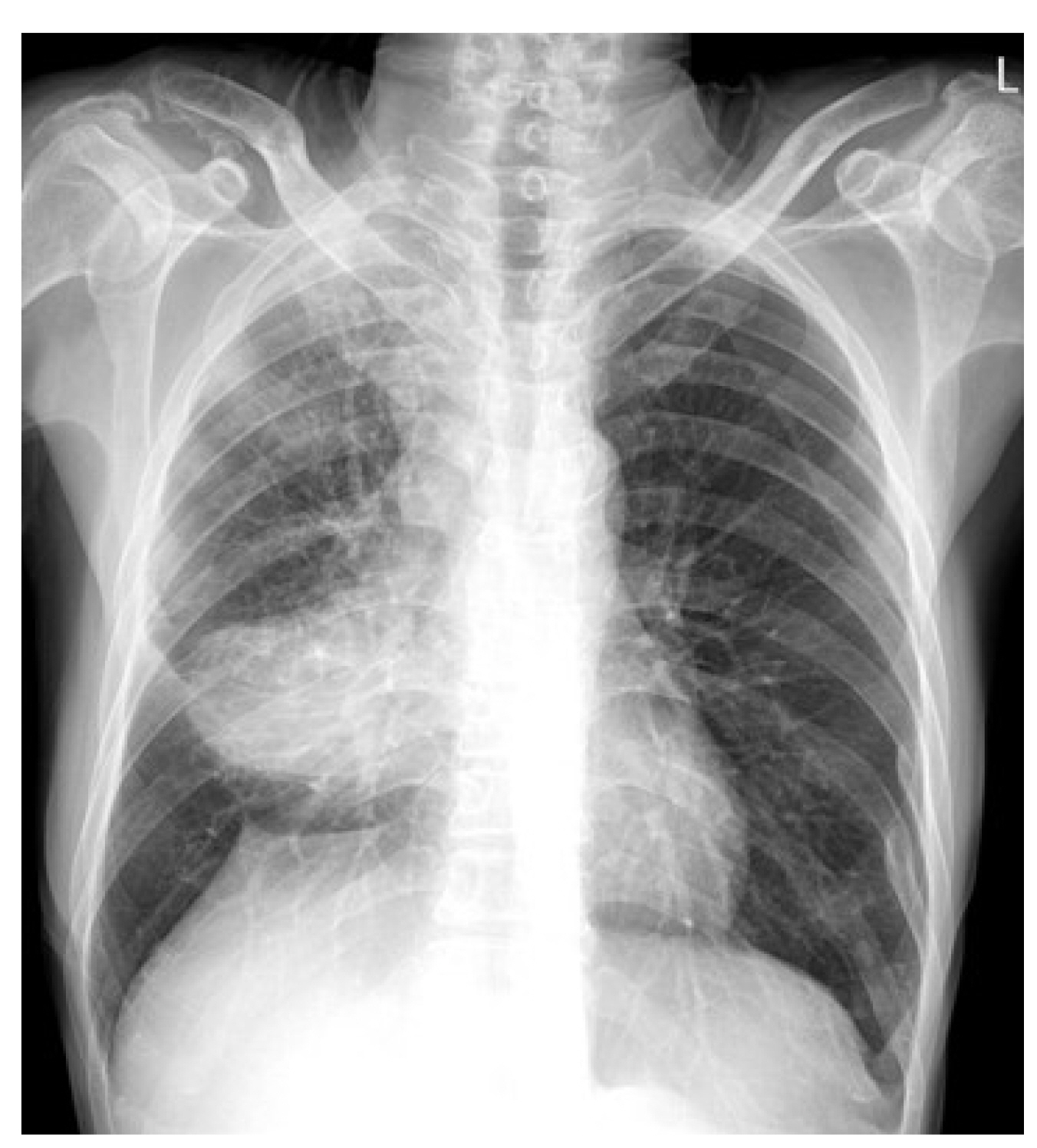
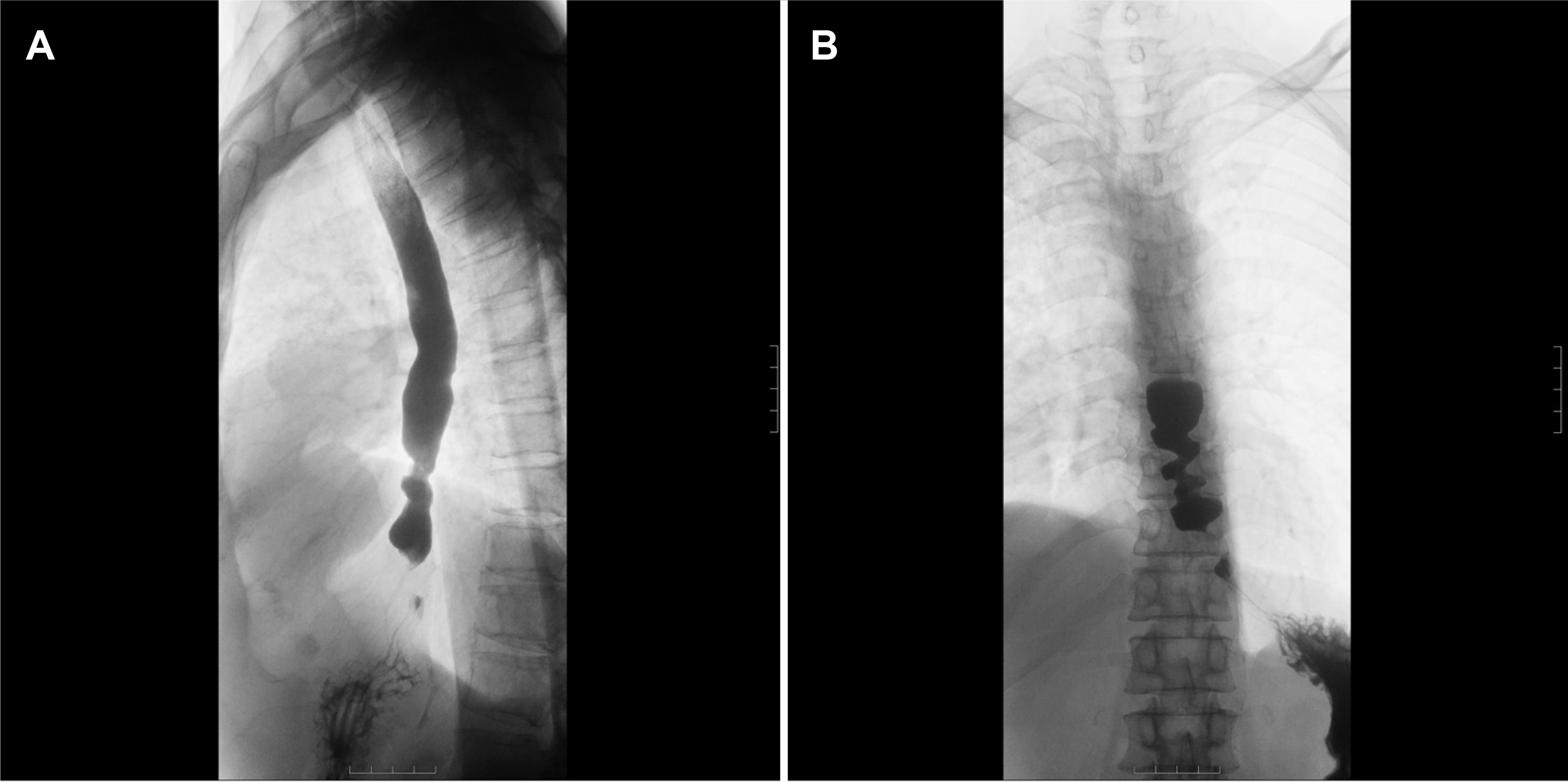
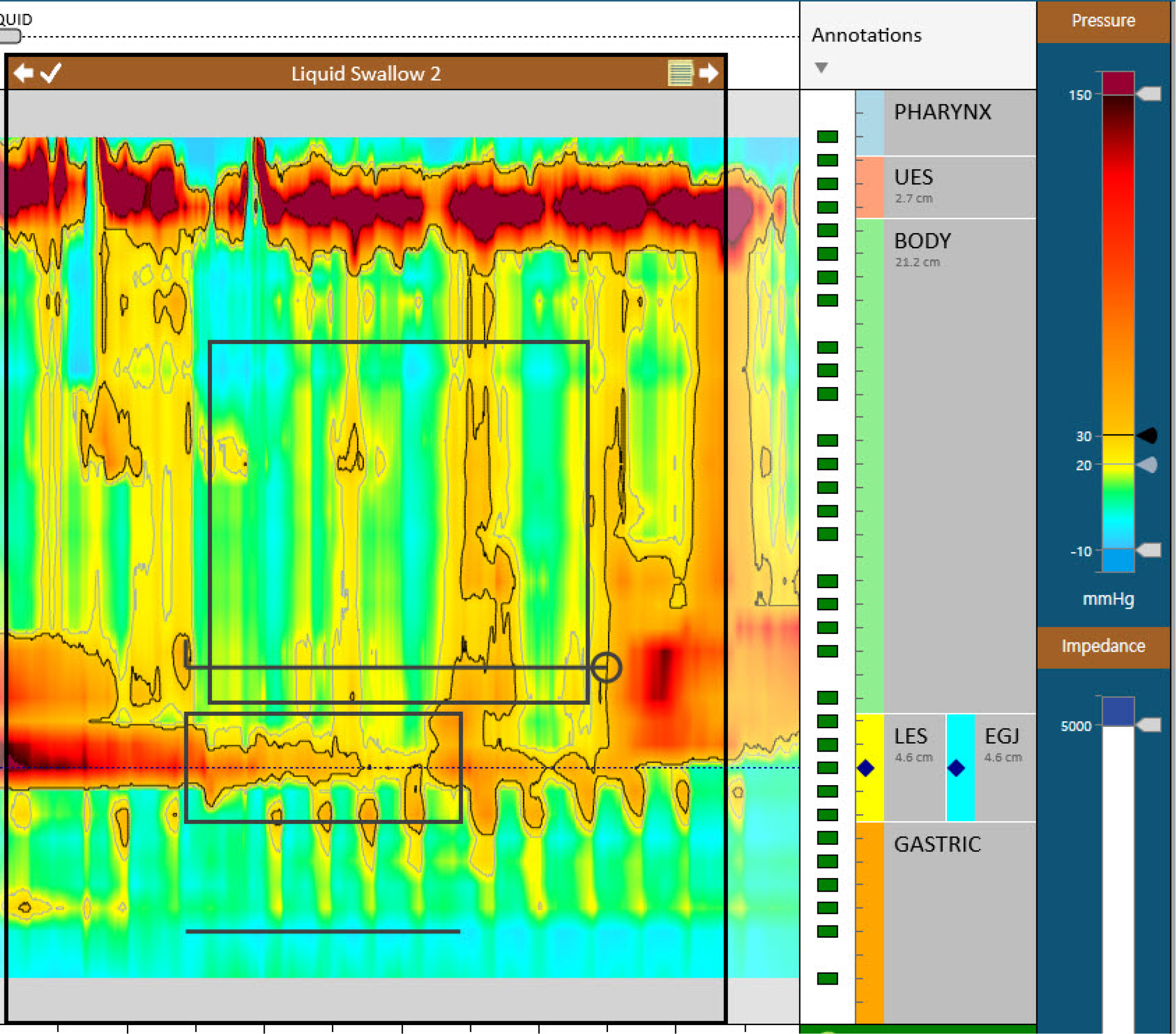
Korean J Gastroenterol.
2023 May;81(5):226-229. 10.4166/kjg.2023.034.
Paraneoplastic Pseudoachalasia Complicated with Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2542790
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.034
Figure
Reference
-
1. Savarino E, Bhatia S, Roman S, et al. 2022; Achalasia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 8:28. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-022-00356-8. PMID: 35513420.
Article2. Campo SM, Zullo A, Scandavini CM, Frezza B, Cerro P, Balducci G. 2013; Pseudoachalasia: A peculiar case report and review of the literature. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 5:450–454. DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i9.450. PMID: 24044045. PMCID: PMC3773858.
Article3. Tucker HJ, Snape WJ Jr, Cohen S. 1978; Achalasia secondary to carcinoma: manometric and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 89:315–318. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-315. PMID: 686541.
Article4. Gockel I, Eckardt VF, Schmitt T, Junginger T. 2005; Pseudoachalasia: a case series and analysis of the literature. Scand J Gastroenterol. 40:378–385. DOI: 10.1080/00365520510012118. PMID: 16028431.
Article5. Kahrilas PJ, Kishk SM, Helm JF, Dodds WJ, Harig JM, Hogan WJ. 1987; Comparison of pseudoachalasia and achalasia. Am J Med. 82:439–446. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90443-8. PMID: 3548347.
Article6. Hejazi RA, Zhang D, McCallum RW. 2009; Gastroparesis, pseudoachalasia and impaired intestinal motility as paraneoplastic manifestations of small cell lung cancer. Am J Med Sci. 338:69–71. DOI: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31819b93e5. PMID: 19506460.
Article7. Brown WR, Dee E. 2013; Dysphagia in a patient with recurrent small-cell lung cancer. Gastroenterology. 144:34252–253. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.08.007. PMID: 23159301.
Article8. De Giorgio R, Bovara M, Barbara G, et al. 2003; Anti-HuD-induced neuronal apoptosis underlying paraneoplastic gut dysmotility. Gastroenterology. 125:70–79. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00664-4. PMID: 12851872.
Article9. Hirano T, Miyauchi E, Inoue A, et al. 2016; Two cases of pseudo-achalasia with lung cancer: Case report and short literature review. Respir Investig. 54:494–499. DOI: 10.1016/j.resinv.2016.04.006. PMID: 27886865.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of Wegener's granulomatosis complicated by non-small cell lung cancer
- A Case of Eosinophilia as a Manifestation of Paraneoplastic Syndrome in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- A Case of Cancer Associated Retinopathy with Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
- A Case of Intramedullary Myelopathy Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Paraneoplastic Chorea Associated with Anti-Hu Antibody and Small Cell Lung Carcinoma