Lab Med Online.
2022 Jan;12(1):46-52. 10.47429/lmo.2022.12.1.46.
Age-Specific Reference Values of Anti-Müllerian Hormone in Korean Women with Normal Menstruation: Time Trend and Clinical Suitability (2015–2021)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul Clinical Laboratories, Yongin, Korea
- KMID: 2538583
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2022.12.1.46
Abstract
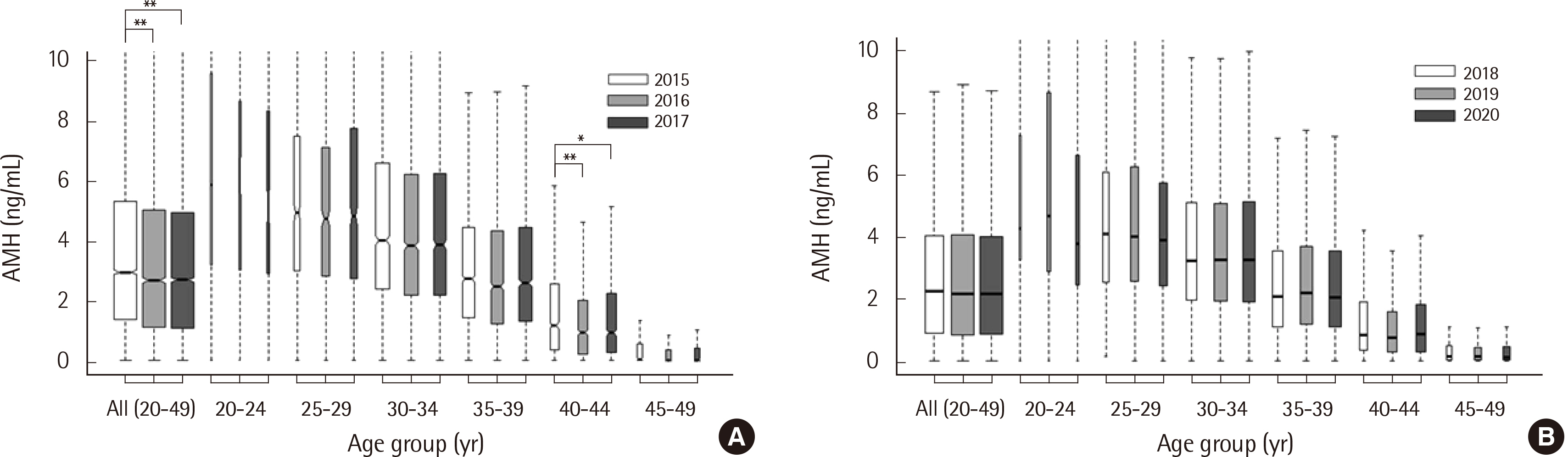
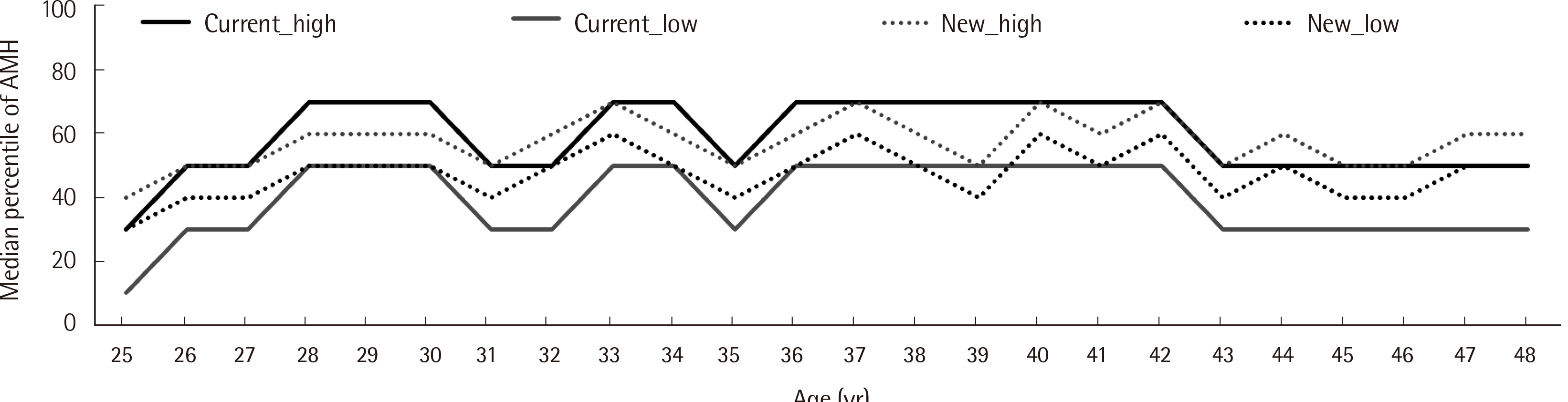
- Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels can be affected by various factors, including age, lifestyle, and test method. This study aimed to review the time trend of AMH levels and the clinical suitability of current age-specific AMH reference values in Korean women. Population-based data of AMH levels, collected from 2015 to 2021 at a clinical laboratory, in Korean women aged 20–49 year with normal menstruation were evaluated (N=19,032 for Gen II assay [Beckman Coulter, USA]; N=14,497 for Access assay [Beckman Coulter, USA]). We found significant differences of AMH levels over time measured using the Gen II assay, but not those assessed by the Access assay. Based on current age-specific reference values, the AMH levels in Korean women with normal menstruation were considered relatively low in the groups at both age extremes (late 20s and late 40s). The AMH levels of Korean women did not show any time trends, except for the influence of the test method. We found that in the case of the Gen II assay, current age-specific AMH reference values, based on an AMH-age regression model, may not be clinically suitable for age groups at both extremes. Therefore, we established new age-specific AMH reference values measured using the Access assay for the general population.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Keane K, Cruzat VF, Wagle S, Chaudhary N, Newsholme P, Yovich J. 2017; Specific ranges of anti-Mullerian hormone and antral follicle count correlate to provide a prognostic indicator for IVF outcome. Reprod Biol. 17:51–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.repbio.2016.12.002. PMID: 28132758.
Article2. National Institute for Health, Care Excellence. Fertility problems: assessment and treatment. Clinical guideline [CG156]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg156. Updated on Sep 2017.3. Clinical, Laboratory Standards Institute. 2010. Defining, establishing, and verifying reference values in the clinical laboratory, Approved guideline-Third edition. CLSI document EP28-A3c. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.4. Asada Y, Tsuiki M, Sonohara M, Fukunaga N, Hattori Y, Inoue D, et al. 2019; Performance of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels measured by Beckman Coulter Access AMH assay to predict oocyte yield following controlled ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization. Reprod Med Biol. 18:273–7. DOI: 10.1002/rmb2.12271. PMID: 31312106. PMCID: PMC6613014.
Article5. van Helden J, Weiskirchen R. 2015; Performance of the two new fully automated anti-Müllerian hormone immunoassays compared with the clinical standard assay. Hum Reprod. 30:1918–26. DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dev127. PMID: 26093541.
Article6. Beckman Coulter. Urgent field safety notice-FSN 20434-3 AMH Gen II ELISA (REF A79765). http://www.hpra.ie/img/uploaded/documents/fsn/FSNJun2013/V16335_FSN.pdf. Updated on Jun 2013.7. Lee JY, Jee BC, Lee JR, Kim CH, Park T, Yeon BR, et al. 2012; Age-related distributions of anti-Müllerian hormone level and anti-Müllerian hormone models. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 91:970–5. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0412.2012.01448.x. PMID: 22574827.
Article8. Lee JY, Ahn S, Lee JR, Jee BC, Kim CH, Seo S, et al. 2017; Reference values for the revised anti-Müllerian hormone generation II assay: Infertile population-based study. J Korean Med Sci. 32:825–9. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.5.825. PMID: 28378557. PMCID: PMC5383616.
Article9. Lee JE, Park DS, Kim ML, Yoon BS, Song T, Kim MK, et al. 2012; Age-related distribution of anti-Müllerian hormone levels in 2,879 Korean women with regular menstruation. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 55:920–8. DOI: 10.5468/KJOG.2012.55.12.920.
Article10. Yoo JH, Kim HO, Cha SW, Park CW, Yang KM, Song IO, et al. 2011; Age specific serum anti-Müllerian hormone levels in 1,298 Korean women with regular menstruation. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 38:93–7. DOI: 10.5653/cerm.2011.38.2.93. PMID: 22384425. PMCID: PMC3283054.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Age specific serum anti-Mullerian hormone levels in 1,298 Korean women with regular menstruation
- Age-related distribution of anti-Mullerian hormone levels in 2,879 Korean women with regular menstruation
- Correlation between the Serum Luteinizing Hormone to Folliclestimulating Hormone Ratio and the Anti-Mullerian Hormone Levels in Normo-ovulatory Women
- The likelihood of achieving pregnancy through timed coitus in young infertile women with decreased ovarian reserve
- The Author Response: Serum anti-Mullerian hormone levels and phenotypes of polycystic ovary syndrome