J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2022 Nov;65(6):846-852. 10.3340/jkns.2021.0248.
Supraorbital Endoscopic Evacuation for Traumatic Intracerebral Hematomas in the Frontal Lobe
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departement of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea
- KMID: 2535845
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0248
Abstract
Objective
: Traumatic intracranial hematomas have been rarely evacuated by endoscopic surgery. The frontal lobe is the usual location for the traumatic intracerebral hematoma (TICH). Endoscopic evacuation for the frontal TICHs via an eyebrow incision is to be presented as minimally invasive surgery.
Methods
: Thirteen patients with frontal TICHs were managed with endoscopic hematoma evacuation via eyebrow incision. After making the incision in the lateral eyebrow, a small frontal craniotomy was made, and the hematoma was evacuated under direct visualization of a rigid endoscope. No catheter was placed. Orbital rim resection, hematoma evacuation rate, surgical complications, and outcome at discharge were analyzed.
Results
: Men were 11 and the mean age was 54 years old (range, 27–86). Orbitotomy was performed in four patients, and no effect on the hematoma evacuation rate was observed. More than 80% of the hematoma volume was successfully removed in 10 cases. Hematoma configuration was not related to the hematoma evacuation rate. None of the patients underwent revision operation or decompressive craniectomy.
Conclusion
: Endoscopic evacuation of the TICHs with the supraorbital approach may be a good method to evacuate the hematoma located in the frontal base.
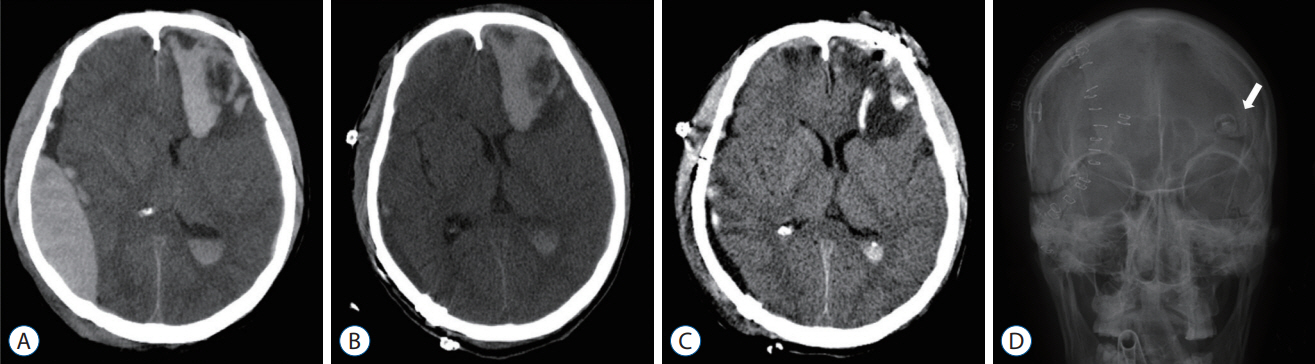
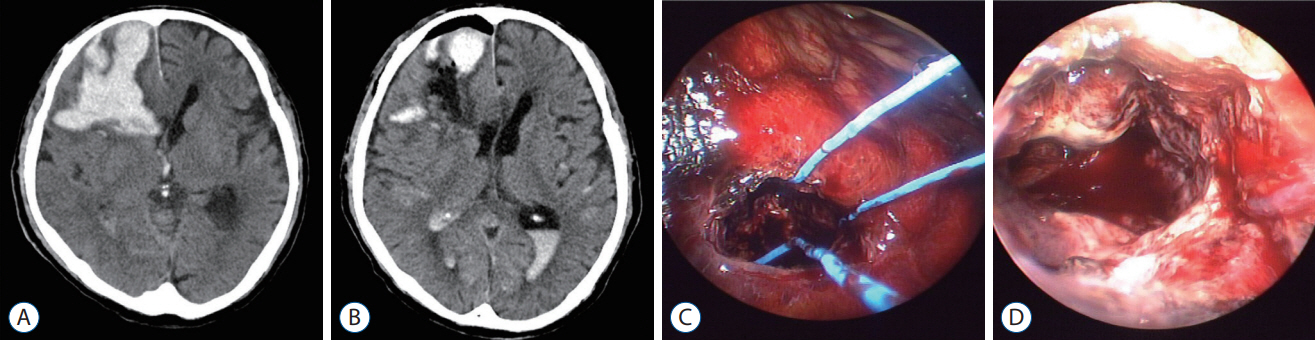
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Abdu E, Hanley DF, Newell DW. Minimally invasive treatment for intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurg Focus. 32:E3. 2012.2. Adams H, Kolias AG, Hutchinson PJ. The role of surgical intervention in traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 27:519–528. 2016.3. Al-Sarraj S. The pathology of traumatic brain injury (TBI): a practical approach. Diagn Histopathol. 22:318–326. 2016.4. Bullock MR, Chesnut R, Ghajar J, Gordon D, Hartl R, Newell DW, et al. Surgical management of traumatic parenchymal lesions. Neurosurgery. 58:S25–S46. 2006.5. Chalouhi N, Jabbour P, Ibrahim I, Starke RM, Younes P, El Hage G, et al. Surgical treatment of ruptured anterior circulation aneurysms: comparison of pterional and supraorbital keyhole approaches. Neurosurgery. 72:437–441. 2013.6. Chou A, Morganti JM, Rosi S. Frontal lobe contusion in mice chronically impairs prefrontal-dependent behavior. PLoS One. 11:e0151418. 2016.7. Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, Arabi YM, Davies AR, Ponsford J, et al. Patient outcomes at twelve months after early decompressive craniectomy for diffuse traumatic brain injury in the randomized DECRA clinical trial. J Neurotrauma. 37:810–816. 2020.8. Gao L, Wu X, Hu J, Jin Y, Han X, Wu X, et al. Intensive management and prognosis of 127 cases with traumatic bilateral frontal contusions. World Neurosurg. 80:879–888. 2013.9. Gregson BA, Rowan EN, Francis R, McNamee P, Boyers D, Mitchell P, et al. Surgical trial in traumatic intracerebral haemorrhage (STITCH): a randomised controlled trial of early surgery compared with initial conservative treatment. Health Technol Assess. 19:1–138. 2015.10. Hernesniemi J, Ishii K, Niemelä M, Smrcka M, Kivipelto L, Fujiki M, et al. Lateral supraorbital approach as an alternative to the classical pterional approach. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 94:17–21. 2005.11. Hung KS, Liang CL, Wang CH, Chang HW, Park N, Juo SH. Outcome after traumatic frontal intracerebral haemorrhage: a comparison of unilateral and bilateral haematomas. J Clin Neurosci. 11:849–853. 2004.12. Hwang SC, Yeo DG, Shin DS, Kim BT. Soft membrane sheath for endoscopic surgery of intracerebral hematomas. World Neurosurg. 90:268–272. 2016.13. Jane JA, Park TS, Pobereskin LH, Winn HR, Butler AB. The supraorbital approach: technical note. Neurosurgery. 11:537–542. 1982.14. Kwon YS, Yang KH, Lee YH. Craniotomy or decompressive craniectomy for acute subdural hematomas: surgical selection and clinical outcome. Korean J Neurotrauma. 12:22–27. 2016.15. Mino M, Fujimura M, Yoshida M, Sonobe S, Tominaga T. Application of neuro-endoscopic target aspiration of the necrotic core for cerebral contusion with delayed progression: technical note. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 161:225–230. 2019.16. Monk TG, Saini V, Weldon BC, Sigl JC. Anesthetic management and one-year mortality after noncardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 100:4–10. 2005.17. Nagasaka T, Tsugeno M, Ikeda H, Okamoto T, Inao S, Wakabayashi T. A novel monoshaft bipolar cautery for use in endoscopic intracranial surgery. A short technical note. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 113:607–611. 2011.18. Reisch R, Perneczky A. Ten-year experience with the supraorbital subfrontal approach through an eyebrow skin incision. Neurosurgery. 57:242–255. 2005.19. Stuss DT. Traumatic brain injury: relation to executive dysfunction and the frontal lobes. Curr Opin Neurol. 24:584–589. 2011.20. Turrentine FE, Wang H, Simpson VB, Jones RS. Surgical risk factors, morbidity, and mortality in elderly patients. J Am Coll Surg. 203:865–877. 2006.21. Wilson DA, Duong H, Teo C, Kelly DF. The supraorbital endoscopic approach for tumors. World Neurosurg. 82:e243–e256. 2014.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Analysis on 96 Cases of Traumatic Intracerebral Hematoma Treated with Operation
- The Use of Urokinase in Traumatic Intracerebral Hematoma Treatment
- Clinical Analysis of Traumatic Intracerebral Hematoma
- Comparison of the Surgical Approaches for Frontal Traumatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- Supraorbital Approach to Anterior Skull Base and Intraorbital Lesions