J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2022 Sep;65(5):622-632. 10.3340/jkns.2022.0074.
Percutaneous Procedures for Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Brain Research Institute, Department of Neurosurgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2533025
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2022.0074
Abstract
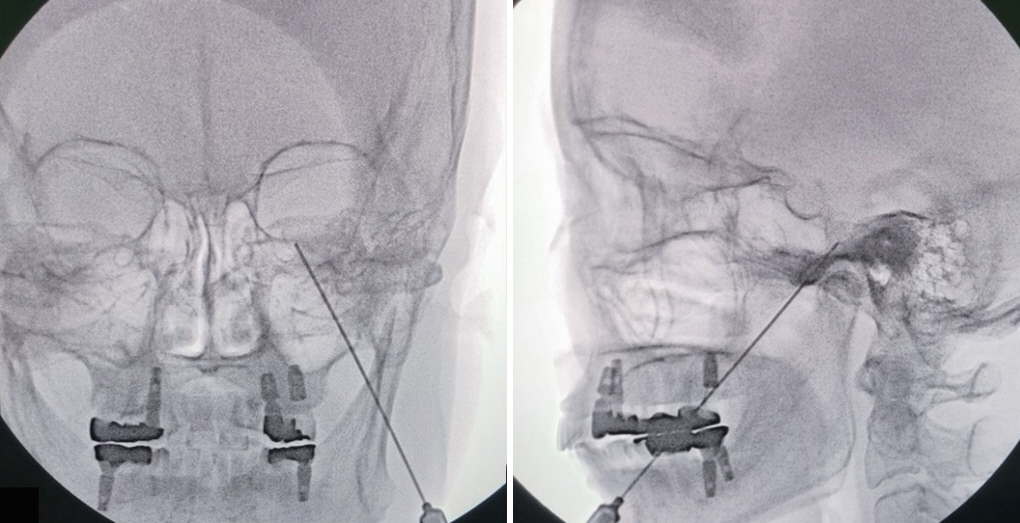
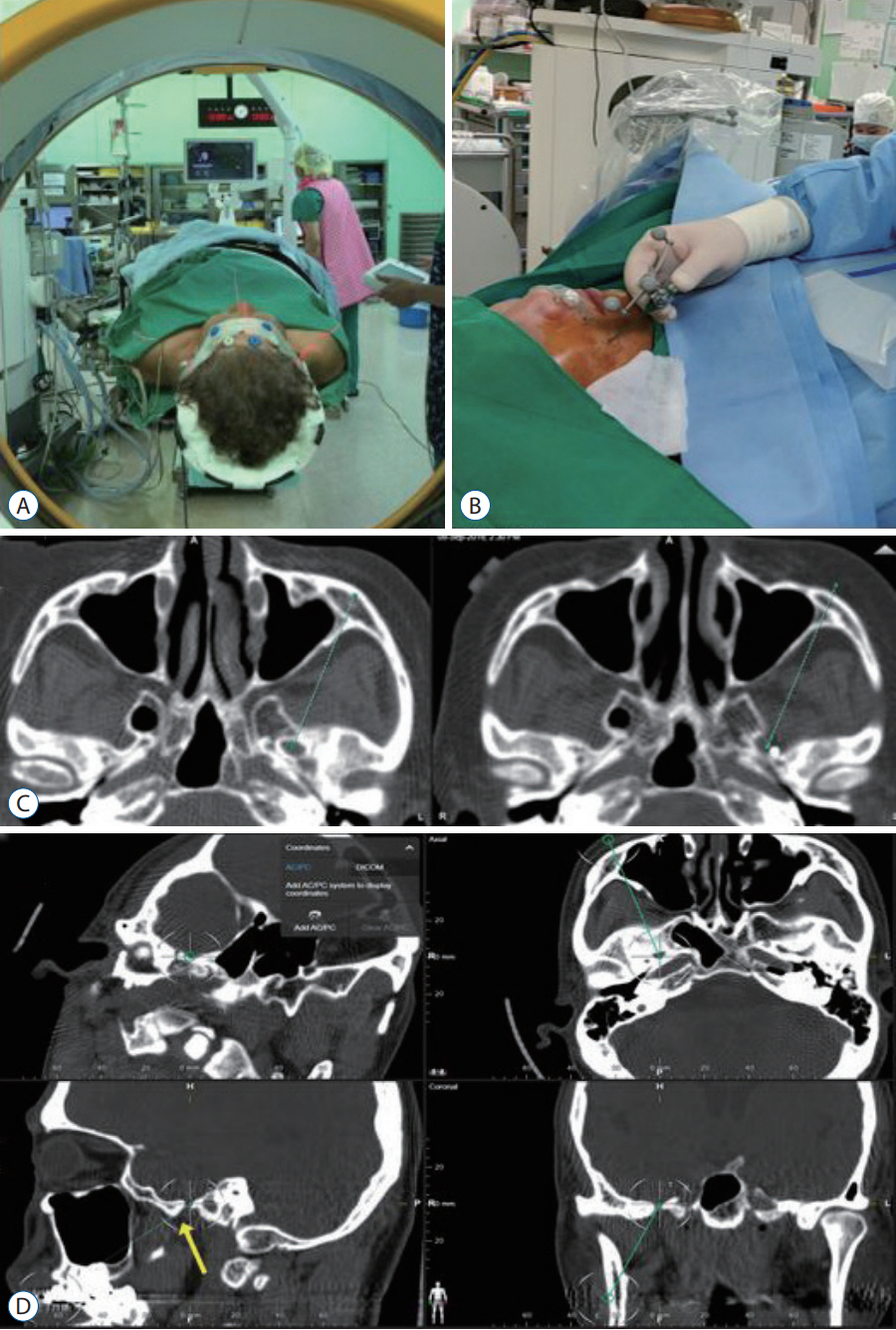
- Microvascular decompression is the gold standard for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia (TN). However, percutaneous techniques still play a role in treating patients with TN and offer several important advantages and efficiency in obtaining immediate pain relief, which is also durable in a less invasive and safe manner. Patients’ preference for a less invasive method can influence the procedure they will undergo. Neurovascular conflict is not always a prerequisite for patients with TN. In addition, recurrence and failure of the previous procedure can influence the decision to follow the treatment. Therefore, indications for percutaneous procedures for TN persist when patients experience idiopathic and episodic sharp shooting pain. In this review, we provide an overview of percutaneous procedures for TN and its outcome and complication.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Abdennebi B, Bouatta F, Chitti M, Bougatene B. Percutaneous balloon compression of the Gasserian ganglion in trigeminal neuralgia. Long-term results in 150 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 136:72–74. 1995.2. Agazzi S, Chang S, Drucker MD, Youssef AS, Van Loveren HR. Sudden blindness as a complication of percutaneous trigeminal procedures: mechanism analysis and prevention. J Neurosurg. 110:638–641. 2009.3. Asplund P, Blomstedt P, Bergenheim AT. Percutaneous balloon compression vs percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy for the primary treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 78:421–428. discussion 428. 2016.4. Barker FG 2nd, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD. The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med. 334:1077–1083. 1996.5. Bergenheim AT, Asplund P, Linderoth B. Percutaneous retrogasserian balloon compression for trigeminal neuralgia: review of critical technical details and outcomes. World Neurosurg. 79:359–368. 2013.6. Bergenheim AT, Hariz MI, Laitinen LV, Olivecrona M, Rabow L. Relation between sensory disturbance and outcome after retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 111:114–118. 1991.7. Bick SKB, Eskandar EN. Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 28:429–438. 2017.8. Blomstedt PC, Bergenheim AT. Technical difficulties and perioperative complications of retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 79:168–181. 2002.9. Brown JA, Hoeflinger B, Long PB, Gunning WT, Rhoades R, Bennett-Clarke CA, et al. Axon and ganglion cell injury in rabbits after percutaneous trigeminal balloon compression. Neurosurgery. 38:993–1003. discussion 1003-1004. 1996.10. Brown JA, McDaniel MD, Weaver MT. Percutaneous trigeminal nerve compression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: results in 50 patients. Neurosurgery. 32:570–573. 1993.11. Brown JA, Pilitsis JG. Percutaneous balloon compression for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: results in 56 patients based on balloon compression pressure monitoring. Neurosurg Focus. 18:E10. 2005.12. Burchiel KJ. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizolysis in the management of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 69:361–366. 1988.13. Chen JF, Tu PH, Lee ST. Repeated percutaneous balloon compression for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia: a long-term study. World Neurosurg. 77:352–356. 2012.14. Chen L, Xu M, Zou Y. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with percutaneous glycerol injection into Meckel's cavity: experience in 4012 patients. Cell Biochem Biophys. 58:85–89. 2010.15. Cheng JS, Lim DA, Chang EF, Barbaro NM. A review of percutaneous treatments for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 10 Suppl. 1:25–33. discussion 33. 2014.16. Cole CD, Liu JK, Apfelbaum RI. Historical perspectives on the diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Focus. 18:E4. 2005.17. Cruccu G, Gronseth G, Alksne J, Argoff C, Brainin M, Burchiel K, et al. AAN-EFNS guidelines on trigeminal neuralgia management. Eur J Neurol. 15:1013–1028. 2008.18. Cruccu G, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS, Scholz J, Sindou M, Svensson P, et al. Trigeminal neuralgia: new classification and diagnostic grading for practice and research. Neurology. 87:220–228. 2016.19. de Siqueira SR, da Nóbrega JC, de Siqueira JT, Teixeira MJ. Frequency of postoperative complications after balloon compression for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: prospective study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 102:e39–e45. 2006.20. Degn J, Brennum J. Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Results from the use of glycerol injection, microvascular decompression, and rhizotomia. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 152:2125–2132. 2010.21. Dieckmann G, Bockermann V, Heyer C, Henning J, Roesen M. Five-and-a-half years' experience with percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Appl Neurophysiol. 50:401–413. 1987.22. Eller JL, Raslan AM, Burchiel KJ. Trigeminal neuralgia: definition and classification. Neurosurg Focus. 18:E3. 2005.23. Fraioli B, Esposito V, Guidetti B, Cruccu G, Manfredi M. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by thermocoagulation, glycerolization, and percutaneous compression of the gasserian ganglion and/or retrogasserian rootlets: long-term results and therapeutic protocol. Neurosurgery. 24:239–245. 1989.24. Fujimaki T, Fukushima T, Miyazaki S. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol injection in the management of trigeminal neuralgia: long-term follow-up results. J Neurosurg. 73:212–216. 1990.25. Håkanson S. Trigeminal neuralgia treated by the injection of glycerol into the trigeminal cistern. Neurosurgery. 9:638–646. 1981.26. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia. 33:629–808. 2013.27. Jin HS, Shin JY, Kim YC, Lee SC, Choi EJ, Lee PB, et al. Predictive factors associated with success and failure for radiofrequency thermocoagulation in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Pain Physician. 18:537–545. 2015.28. Jones MR, Urits I, Ehrhardt KP, Cefalu JN, Kendrick JB, Park DJ, et al. A comprehensive review of trigeminal neuralgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 23:74. 2019.29. Kanpolat Y, Savas A, Bekar A, Berk C. Percutaneous controlled radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy for the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: 25-year experience with 1,600 patients. Neurosurgery. 48:524–532. discussion 532-534. 2001.30. Kosugi S, Shiotani M, Otsuka Y, Suzuki T, Katori N, Hashiguchi S, et al. Long-term outcomes of percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation of gasserian ganglion for 2nd- and multiple-division trigeminal neuralgia. Pain Pract. 15:223–228. 2015.31. Kouzounias K, Lind G, Schechtmann G, Winter J, Linderoth B. Comparison of percutaneous balloon compression and glycerol rhizotomy for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 113:486–492. 2010.32. Kouzounias K, Schechtmann G, Lind G, Winter J, Linderoth B. Factors that influence outcome of percutaneous balloon compression in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 67:925–934. discussion 934. 2010.33. Lichtor T, Mullan JF. A 10-year follow-up review of percutaneous microcompression of the trigeminal ganglion. J Neurosurg. 72:49–54. 1990.34. Lobato RD, Rivas JJ, Sarabia R, Lamas E. Percutaneous microcompression of the gasserian ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 72:546–553. 1990.35. Maarbjerg S, Di Stefano G, Bendtsen L, Cruccu G. Trigeminal neuralgia - diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia. 37:648–657. 2017.36. Maarbjerg S, Wolfram F, Gozalov A, Olesen J, Bendtsen L. Significance of neurovascular contact in classical trigeminal neuralgia. Brain. 138(Pt 2):311–319. 2015.37. McQuay H, Carroll D, Jadad AR, Wiffen P, Moore A. Anticonvulsant drugs for management of pain: a systematic review. BMJ. 311:1047–1052. 1995.38. Montano N, Conforti G, Di Bonaventura R, Meglio M, Fernandez E, Papacci F. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 11:289–299. 2015.39. Mullan S, Lichtor T. Percutaneous microcompression of the trigeminal ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 59:1007–1012. 1983.40. Nomura T, Ikezaki K, Matsushima T, Fukui M. Trigeminal neuralgia: differentiation between intracranial mass lesions and ordinary vascular compression as causative lesions. Neurosurg Rev. 17:51–57. 1994.41. Noorani I, Lodge A, Vajramani G, Sparrow O. Comparing percutaneous treatments of trigeminal neuralgia: 19 years of experience in a single centre. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 94:75–85. 2016.42. North RB, Kidd DH, Piantadosi S, Carson BS. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy. Predictors of success and failure in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 72:851–856. 1990.43. Omeis I, Smith D, Kim S, Murali R. Percutaneous balloon compression for the treatment of recurrent trigeminal neuralgia: long-term outcome in 29 patients. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 86:259–265. 2008.44. Pal HK, Dinda AK, Roy S, Banerji AK. Acute effect of anhydrous glycerol on peripheral nerve: an experimental study. Br J Neurosurg. 3:463–469. 1989.45. Pandia MP, Dash HH, Bithal PK, Chouhan RS, Jain V. Does egress of cerebrospinal fluid during percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy influence long term pain relief? Reg Anesth Pain Med. 33:222–226. 2008.46. Patel SK, Liu JK. Overview and history of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 27:265–276. 2016.47. Peker S, Kurtkaya O, Uzün I, Pamir MN. Microanatomy of the central myelin-peripheral myelin transition zone of the trigeminal nerve. Neurosurgery. 59:354–359. discussion 354-359. 2006.48. Pickett GE, Bisnaire D, Ferguson GG. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy in the treatment of tic douloureux associated with multiple sclerosis. Neurosurgery. 56:537–545. discussion 537-545. 2005.49. Pollock BE. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy for patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective analysis of factors related to pain relief. J Neurosurg. 102:223–228. 2005.50. Rappaport ZH, Gomori JM. Recurrent trigeminal cistern glycerol injections for tic douloureux. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 90:31–34. 1988.51. Rath GP, Dash HH, Bithal PK, Goyal V. Intracranial hemorrhage after percutaneous radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy. Pain Pract. 9:82–84. 2009.52. Skirving DJ, Dan NG. A 20-year review of percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal ganglion. J Neurosurg. 94:913–917. 2001.53. Slettebø H, Hirschberg H, Lindegaard KF. Long-term results after percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 122:231–235. 1993.54. Smith HP, McWhorter JM, Challa VR. Radiofrequency neurolysis in a clinical model. Neuropathological correlation. J Neurosurg. 55:246–253. 1981.55. Sweet WH, Wepsic JG. Controlled thermocoagulation of trigeminal ganglion and rootlets for differential destruction of pain fibers. 1. Trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 40:143–156. 1974.56. Taha JM, Tew JM Jr. Comparison of surgical treatments for trigeminal neuralgia: reevaluation of radiofrequency rhizotomy. Neurosurgery. 38:865–871. 1996.57. Taha JM, Tew JM Jr. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by percutaneous radiofrequency rhizotomy. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 8:31–39. 1997.58. Tatli M, Satici O, Kanpolat Y, Sindou M. Various surgical modalities for trigeminal neuralgia: literature study of respective long-term outcomes. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 150:243–255. 2008.59. Tronnier VM, Rasche D, Hamer J, Kienle AL, Kunze S. Treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: comparison of long-term outcome after radiofrequency rhizotomy and microvascular decompression. Neurosurgery. 48:1261–1267. discussion 1267-1268. 2001.60. Wang JY, Bender MT, Bettegowda C. Percutaneous procedures for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 27:277–295. 2016.61. Weßling H, Duda S. ioCT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for trigeminal neuralgia: how I do it. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 161:935–938. 2019.62. Zanusso M, Curri D, Landi A, Colombo F, Volpin L, Cervellini P. Pressure monitoring inside Meckel's cave during percutaneous microcompression of gasserian ganglion. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 56:37–43. 1991.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anesthetic management of percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal ganglion for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: Two cases report
- A Case of Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated with Percutaneous Radiofrequency Lesions
- Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia by Percutaneous Retrogasserian Glycerol Injection
- Percutaneous radiofrequency Thermal Rhizotomy for Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Percutaneous Streotaxic Gasserian Ganglionotomy with Radiofrequency Current in Trigeminal Neuralgia