J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2022 Sep;65(5):615-621. 10.3340/jkns.2021.0265.
Surgical Treatment for Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2533024
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0265
Abstract
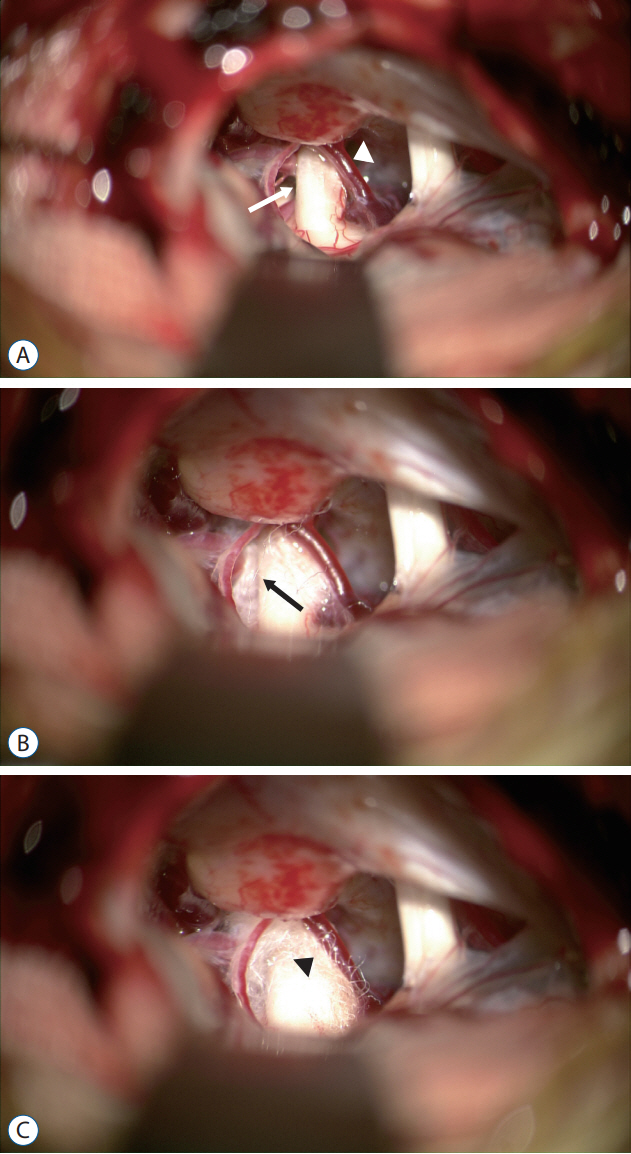
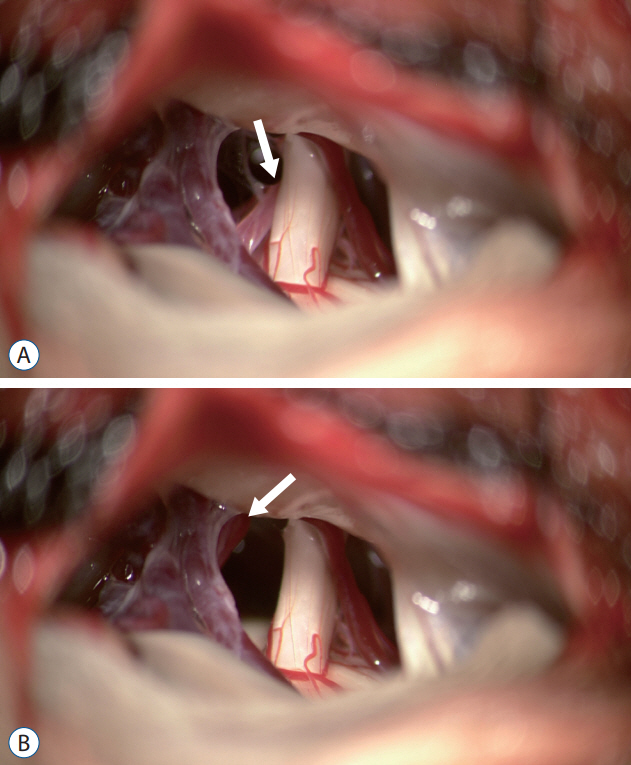
- Various treatments for trigeminal neuralgia (TN) are known to yield initial satisfactory results; however, the surgical treatment has excellent long-term outcomes and a low recurrence rate. Surgical treatment addresses the challenge of vascular compression, which accounts for 85% of the causes of TN. As for surgical treatment for TN, microvascular decompression (MVD) has become the surgical treatment of choice after Peter J. Jannetta reported the results of MVD surgery in 1996. Since then, many studies have reported a success rate of over 90% for the initial surgical treatment. Most MVDs aim to separate (decompress) the culprit vessel from the trigeminal nerve. To increase the success rate of surgery, accurate indications for MVD and management of the offender vessels without complications are critical. In addition, if there is no vascular compression, partial sensory rhizotomy or internal neurolysis can be performed to improve surgical outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Abi-Aad KR, Turcotte E, Patra DP, Welz ME, Maiti T, Hess R, et al. Vascular transposition of the superior cerebellar artery using a fenestrated clip and fibrin glue in trigeminal neuralgia: 2-dimensional operative video. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 19:E50–E51. 2020.2. Alford EN, Chagoya G, Elsayed GA, Bernstock JD, Bentley JN, Romeo A, et al. Risk factors for wound-related complications after microvascular decompression. Neurosurg Rev. 44:1093–1101. 2021.3. Amador N, Pollock BE. Repeat posterior fossa exploration for patients with persistent or recurrent idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 108:916–920. 2008.4. Ashkan K, Marsh H. Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia in the elderly: a review of the safety and efficacy. Neurosurgery. 55:840–848. 2004.5. Bakker NA, Van Dijk JM, Immenga S, Wagemakers M, Metzemaekers JD. Repeat microvascular decompression for recurrent idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 121:936–939. 2014.6. Barker FG 2nd, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD. The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med. 334:1077–1083. 1996.7. Bartindale M, Mohamed A, Bell J, Kircher M, Hill J, Anderson D, et al. Neurotologic complications following microvascular decompression: a retrospective study. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 81:37–42. 2020.8. Bayer DB, Stenger TG. Trigeminal neuralgia: an overview. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 48:393–399. 1979.9. Bendtsen L, Zakrzewska JM, Abbott J, Braschinsky M, Di Stefano G, Donnet A, et al. European academy of neurology guideline on trigeminal neuralgia. Eur J Neurol. 26:831–849. 2019.10. Broggi G, Ferroli P, Franzini A, Servello D, Dones I. Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: comments on a series of 250 cases, including 10 patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 68:59–64. 2000.11. Burchiel KJ. Trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 112:756–757. 2010.12. Chai S, Xu H, Wang Q, Li J, Wang J, Wang Y, et al. Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia caused by vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia: interposition technique versus transposition technique. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 162:2811–2821. 2020.13. Chakravarthi PS, Ghanta R, Kattimani V. Microvascular decompression treatment for trigeminal neuralgia. J Craniofac Surg. 22:894–898. 2011.14. Chen J, Lee S, Lui T, Yeh Y, Chen T, Tzaan W. Teflon granuloma after microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Surg Neurol. 53:281–287. 2000.15. Cheng J, Long J, Hui X, Lei D, Zhang H. Effects of microvascular decompression on depression and anxiety in trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective cohort study focused on risk factors and prognosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 161:59–64. 2017.16. Cheng J, Meng J, Lei D, Hui X. Repeat microvascular decompression for patients with persistent or recurrent trigeminal neuralgia: prognostic factors and long-term outcomes. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e15167. 2019.17. Cheshire WP Jr. Trigeminal neuralgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 11:69–74. 2007.18. Dandy WE. An operation for the cure of tic douloureux: partial section of the sensory root at the pons. Arch Surg. 18:687–734. 1929.19. Dandy WE. The treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by the cerebellar route. Ann Surg. 96:787–795. 1932.20. Degn J, Brennum J. Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. results from the use of glycerol injection, microvascular decompression, and rhizotomia. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 152:2125–2132. 2010.21. Eseonu CI, Goodwin CR, Zhou X, Theodros D, Bender MT, Mathios D, et al. Reduced CSF leak in complete calvarial reconstructions of microvascular decompression craniectomies using calcium phosphate cement. J Neurosurg. 123:1476–1479. 2015.22. Fukushima T. Posterior cranial fossa neurovascular decompression (Jannetta method) for trigeminal neuralgia and facial spasm. No Shinkei Geka. 10:1257–1261. 1982.23. Gardner WJ, Miklos MV. Response of trigeminal neuralgia to decompression of sensory root; discussion of cause of trigeminal neuralgia. J Am Med Assoc. 170:1773–1776. 1959.24. Gardner WJ, Pinto JP. The tarrnhoj operation; relief of trigeminal neuralgia without numbness. Cleve Clin Q. 20:364–367. 1953.25. Harris W. A history of the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Postgrad Med J. 27:18–21. 1951.26. Heinskou TB, Maarbjerg S, Wolfram F, Rochat P, Brennum J, Olesen J, et al. Favourable prognosis of trigeminal neuralgia when enrolled in a multidisciplinary management program - a two-year prospective real-life study. J Headache Pain. 20:23. 2019.27. Holste K, Chan AY, Rolston JD, Englot DJ. Pain outcomes following microvascular decompression for drug-resistant trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery. 86:182–190. 2020.28. Jannetta PJ. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by suboccipital and transtentorial cranial operations. Clin Neurosurg. 24:538–549. 1977.29. Kabatas S, Karasu A, Civelek E, Sabanci AP, Hepgul KT, Teng YD. Microvascular decompression as a surgical management for trigeminal neuralgia: long-term follow-up and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev. 32:87–93. 2009.30. Kang IH, Park BJ, Park CK, Malla HP, Lee SH, Rhee BA. A clinical analysis of secondary surgery in trigeminal neuralgia patients who failed prior treatment. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 59:637–642. 2016.31. Kasuya H, Tani S, Kubota Y, Yokosako S, Ohbuchi H, Arai N, et al. Characteristics and management of the offending veins in microvascular decompression surgery for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Rev. 44:2337–2347. 2021.32. Khan SA, Laulloo A, Vats A, Nath F. Microvascular decompression: incidence and prevention of postoperative CSF leakage in a consecutive series of 134 patients. Br J Neurosurg. 34:416–418. 2020.33. Ko AL, Ozpinar A, Lee A, Raslan AM, McCartney S, Burchiel KJ. Long-term efficacy and safety of internal neurolysis for trigeminal neuralgia without neurovascular compression. J Neurosurg. 122:1048–1057. 2015.34. Lee SH, Levy EI, Scarrow AM, Kassam A, Jannetta PJ. Recurrent trigeminal neuralgia attributable to veins after microvascular decompression. Neurosurgery. 46:356–361. 2000.35. Li GW, Zhang WC, Min Y, Ma QF, Zhong WX. Surgical skills of adhesions and transposition of trigeminal nerve for primary trigeminal neuralgia. J Craniofac Surg. 25:1296–1298. 2014.36. Li MW, Jiang XF, Niu C. Efficacy of internal neurolysis for trigeminal =neuralgia without vascular compression. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 82:364–368. 2021.37. Lin CF, Chen HH, Hernesniemi J, Lee CC, Liao CH, Chen SC, et al. An easy adjustable method of ectatic vertebrobasilar artery transposition for microvascular decompression. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 114:951–956. 2012.38. Masuoka J, Matsushima T, Kawashima M, Nakahara Y, Funaki T, Mineta T. Stitched sling retraction technique for microvascular decompression: procedures and techniques based on an anatomical viewpoint. Neurosurg Rev. 34:373–379. 2011.39. McLaughlin MR, Jannetta PJ, Clyde BL, Subach BR, Comey CH, Resnick DK. Microvascular decompression of cranial nerves: lessons learned after 4400 operations. J Neurosurg. 90:1–8. 1999.40. Melek LN, Devine M, Renton T. The psychosocial impact of orofacial pain in trigeminal neuralgia patients: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 47:869–878. 2018.41. Meybodi AT, Habibi Z, Miri M, Tabatabaie SA. Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia using the 'stitched sling retraction' technique in recurrent cases after previous microvascular decompression. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 156:1181–1187. 2014.42. Mitsos AP, Georgakoulias N, Lafazanos SA, Konstantinou EA. The "hanging technique" of vascular transposition in microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: technical report of four cases. Neurosurg Rev. 31:327–330. 2008.43. Nunta-Aree S, Patiwech K, Sitthinamsuwan B. Microvascular decompression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: factors that predict complete pain relief and study of efficacy and safety in older patients. World Neurosurg. 110:e979–e988. 2018.44. Oishi M, Fukuda M, Noto Y, Kawaguchi T, Hiraishi T, Fujii Y. Trigeminal neuralgia associated with the specific bridging pattern of transverse pontine vein: diagnostic value of three-dimensional multifusion volumetric imaging. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 89:226–233. 2011.45. Otani N, Toyooka T, Fujii K, Kumagai K, Takeuchi S, Tomiyama A, et al. "Birdlime" technique using tachosil tissue sealing sheet soaked with fibrin glue for sutureless vessel transposition in microvascular decompression: operative technique and nuances. J Neurosurg. 128:1522–1529. 2018.46. Otani N, Toyooka T, Takeuchi S, Tomiyama A, Wada K, Mori K. Novel technical variations and increased adhesive strength in the "Birdlime" transposition technique for microvascular decompression. World Neurosurg. 116:e460–e468. 2018.47. Phan K, Rao PJ, Dexter M. Microvascular decompression for elderly patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Clin Neurosci. 29:7–14. 2016.48. Pines AR, Butterfield RJ, Turcotte EL, Garcia JO, De Lucia N, Algier EJ, et al. Microvascular transposition without teflon: a single institution's 17-year experience treating trigeminal neuralgia. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 20:397–405. 2021.49. Rzaev DA, Kulikova EV, Moysak GI, Voronina EI, Ageeva TA. Teflon granuloma after microvascular decompression of the trigeminal nerve root in a patient with recurrent trigeminal neuralgia. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 80:78–83. 2016.50. Sato O, Kanazawa I, Kokunai T. Trigeminal neuralgia caused by compression of trigeminal nerve by pontine vein. Surg Neurol. 11:285–286. 1979.51. Seo HJ, Park CK, Choi MK, Ryu J, Park BJ. Clinical outcome of percutaneous trigeminal nerve block in elderly patients in outpatient clinics. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 63:814–820. 2020.52. Shibahashi K, Morita A, Kimura T. Surgical results of microvascular decompression procedures and patient's postoperative quality of life: review of 139 cases. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 53:360–364. 2013.53. Sindou M, Leston J, Decullier E, Chapuis F. Microvascular decompression for primary trigeminal neuralgia: long-term effectiveness and prognostic factors in a series of 362 consecutive patients with clear-cut neurovascular conflicts who underwent pure decompression. J Neurosurg. 107:1144–1153. 2007.54. Sindou M, Leston JM, Decullier E, Chapuis F. Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: the importance of a noncompressive technique--kaplan-meier analysis in a consecutive series of 330 patients. Neurosurgery. 63:341–350. 2008.55. Soni P, Potter T, Soni PP, Estemalik E, Recinos PF, Kshettry VR. Outcomes of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia with purely venous compression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 198:106230. 2020.56. Stoker MA, Forbes JA, Hanif R, Cooper C, Nian H, Konrad PE, et al. Decreased rate of CSF leakage associated with complete reconstruction of suboccipital cranial defects. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 73:281–286. 2012.57. Sweet WH. The history of the development of treatment for trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Neurosurg. 32:294–318. 1985.58. Taarnhoj P. Trigeminal neuralgia and decompression of the trigeminal root. Surg Clin North Am. 1145–1157. 1956.59. Taarnhøj P. Decompression of the trigeminal root. J Neurosurg. 11:299–305. 1954.60. Tang X, Wang Y, Shu Z, Hou Y. Efficacy and prognosis of trigeminal neuralgia treated with surgical excision or gamma knife surgery. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 37:616–620. 2012.61. Terrier LM, Amelot A, François P, Destrieux C, Zemmoura I, Velut S. Therapeutic failure in trigeminal neuralgia: from a clarification of trigeminal nerve somatotopy to a targeted partial sensory rhizotomy. World Neurosurg. 117:e138–e145. 2018.62. Theodros D, Rory Goodwin C, Bender MT, Zhou X, Garzon-Muvdi T, De la Garza-Ramos R, et al. Efficacy of primary microvascular decompression versus subsequent microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 126:1691–1697. 2017.63. Tomasello F, Esposito F, Abbritti RV, Angileri FF, Conti A, Cardali SM, et al. Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: technical refinement for complication avoidance. World Neurosurg. 94:26–31. 2016.64. Xia L, Zhong J, Zhu J, Wang YN, Dou NN, Liu MX, et al. Effectiveness and safety of microvascular decompression surgery for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review. J Craniofac Surg. 25:1413–1417. 2014.65. Young JN, Wilkins RH. Partial sensory trigeminal rhizotomy at the pons for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 79:680–687. 1993.66. Yue Y, Zhao ZR, Liu DC, Liu HJ, Lu DL, Zhang H, et al. Life-threatening complications after microvascular decompression procedure: lessons from a consecutive series of 596 patients. J Clin Neurosci. 86:64–70. 2021.67. Zhang D, Barata A, Pires P, Soares P, Marques L. Transposition of superior cerebellar artery for microvascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia using an in situ superior petrosal vein sling technique. World Neurosurg. 134:402–407. 2020.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia with Low-frequency Electrical Acupuncture
- Bilateral Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Anesthetic management of percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal ganglion for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: Two cases report
- Alcohol Neurolyisis for the Treatment of Tregeminal Neuralgia
- Trigeminal Neuralgia and Neural Blockade