Korean J Sports Med.
2022 Sep;40(3):204-208. 10.5763/kjsm.2022.40.3.204.
Adult Tillaux-Chaput Tubercle Fracture with Volkmann Fracture during Tennis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae Hospital, Gwangmyeong, Korea
- KMID: 2532898
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2022.40.3.204
Abstract
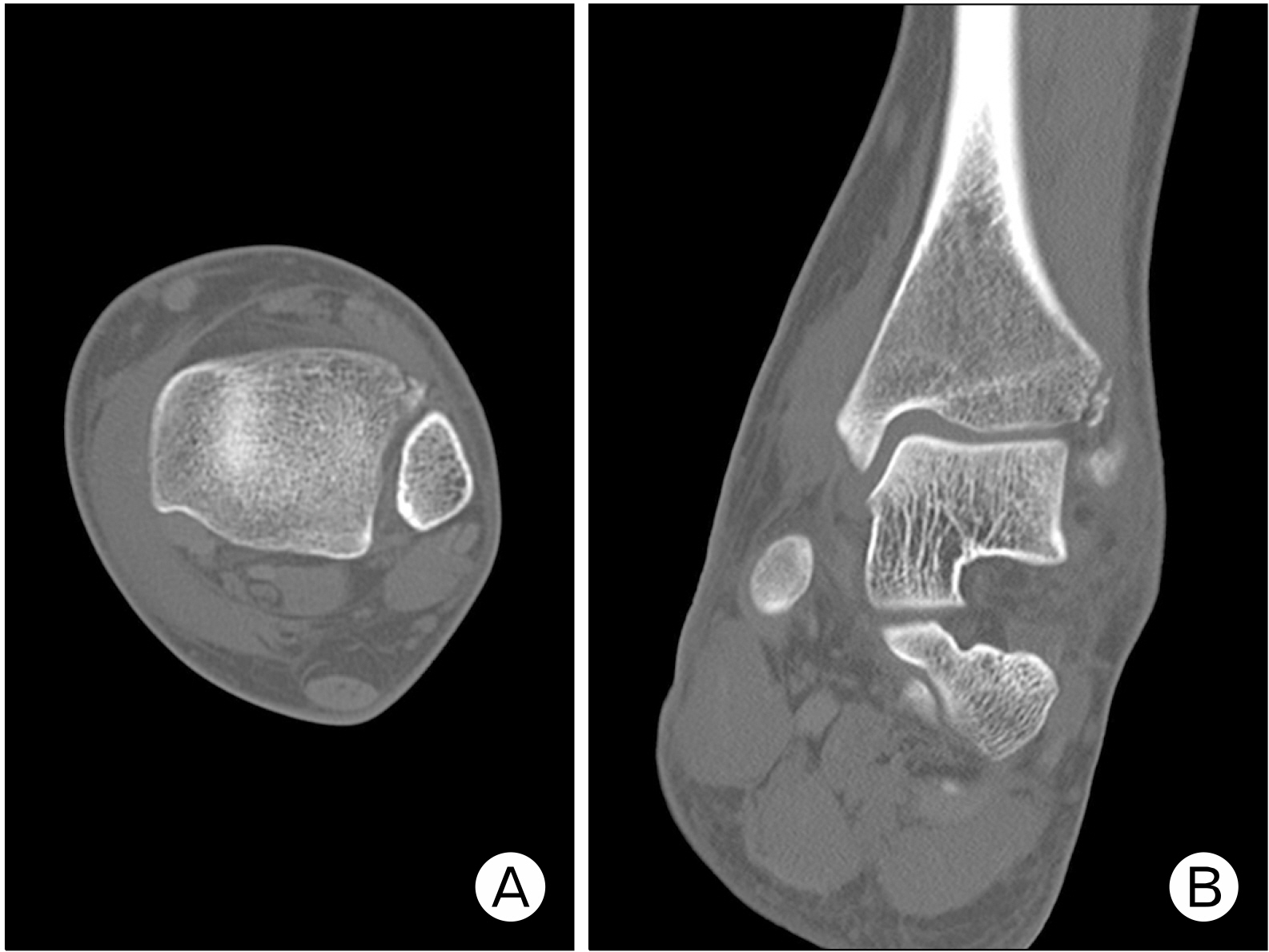
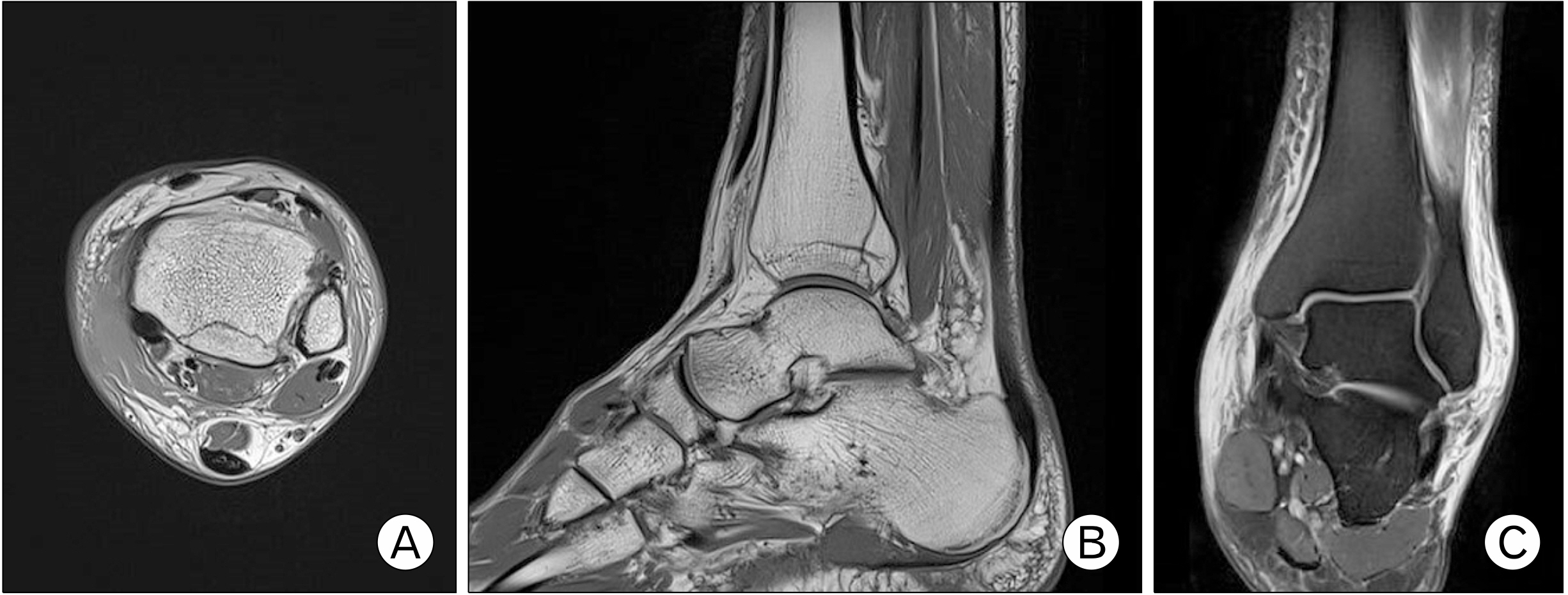
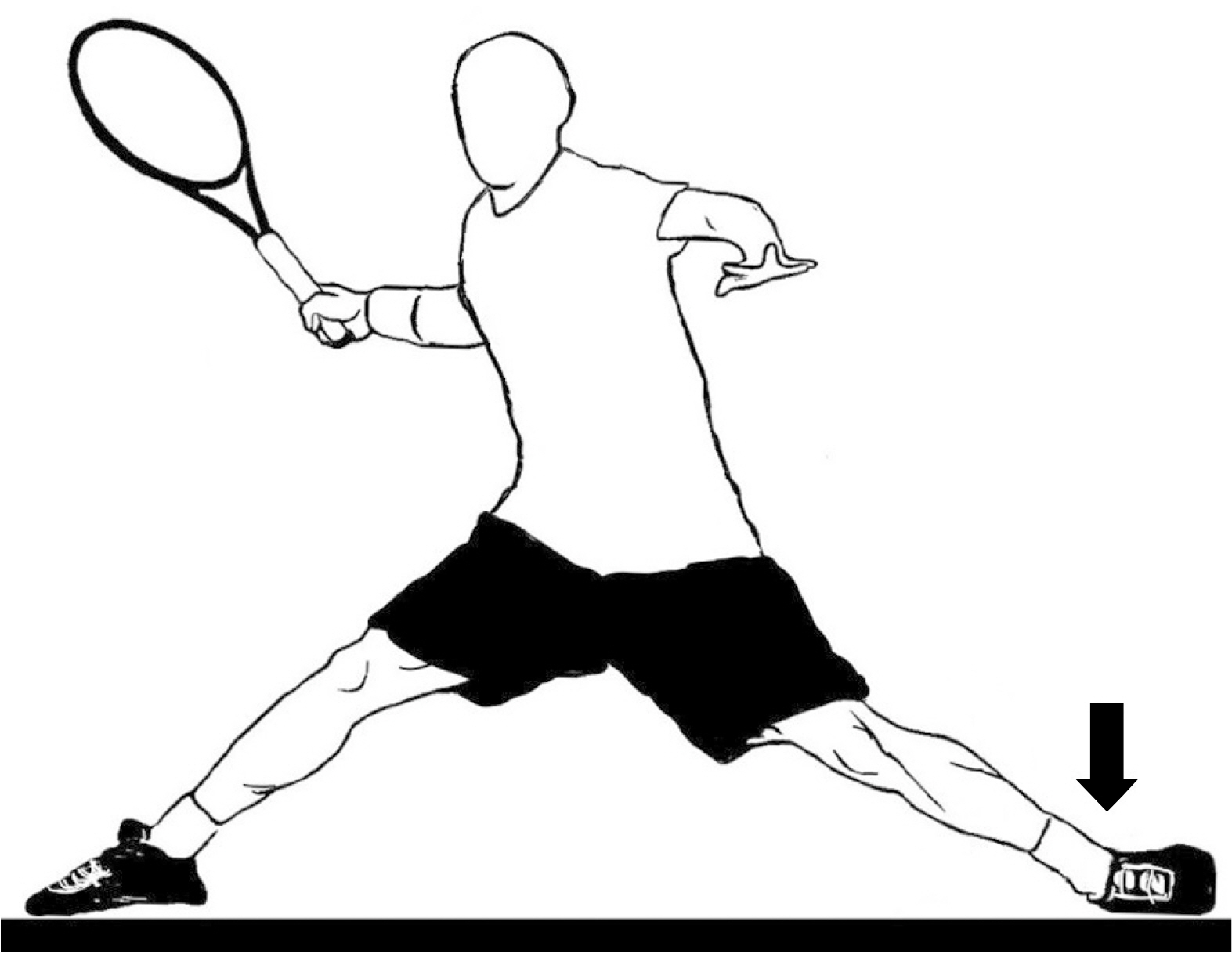
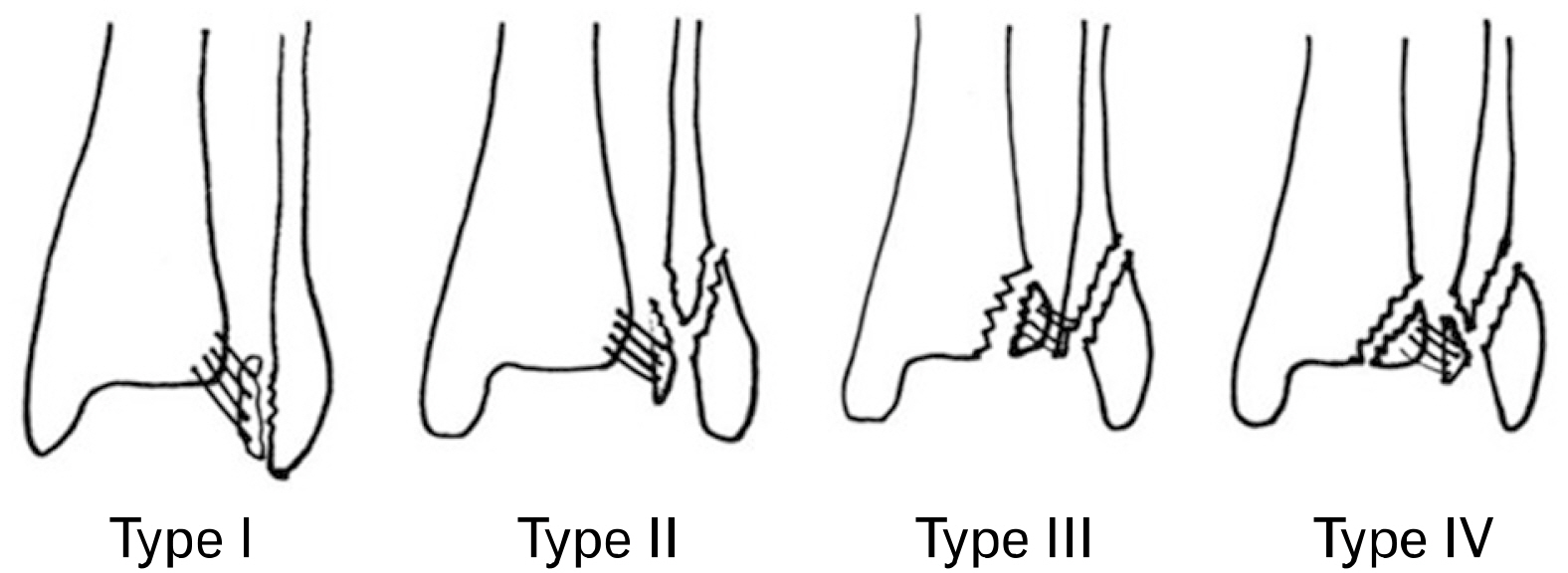
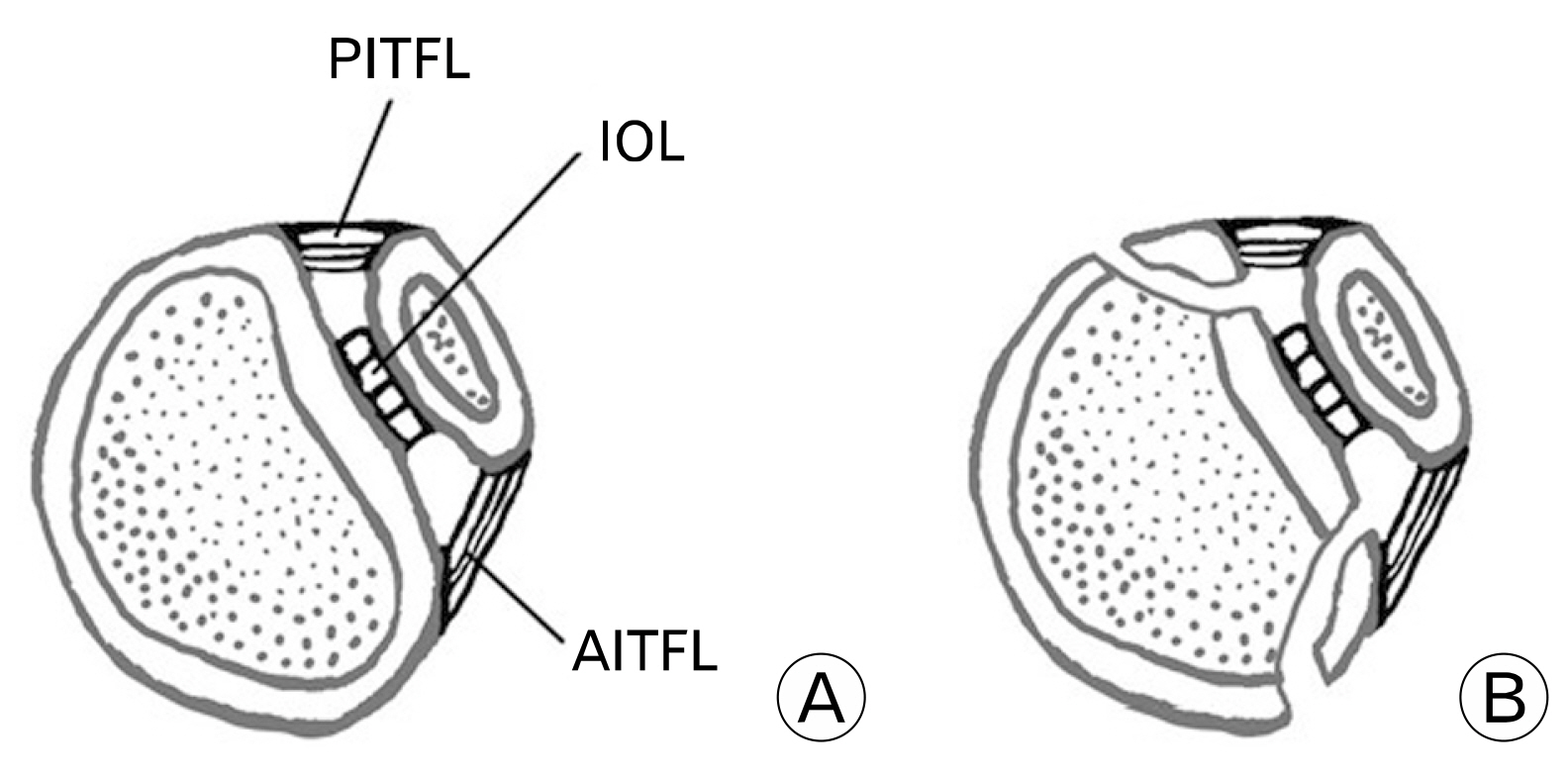
- An avulsion fracture of the anterolateral tibial epiphysis or Tillaux fracture is commonly seen in adolescents, reported first by Paul Jules Tillaux in 1892. Adolescent Tillaux fracture occurs during the period when the lateral physis is still open and the anterior-inferior tibiofibular ligament is stronger than the physis, so rarely occurs in adults. An avulsion fracture of the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, Volkmann fracture, occurs counterpart of Tillaux fracture. In this study, a tennis player injured during sliding and diagnosed as the rare simultaneous Tillaux-Chaput fracture and Volkmann fracture, is reported with the mechanism of injury, clinical importance of syndesmosis, sprain, and fracture of the ankle joint.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Koury SI, Stone CK, Harrell G, La Charité DD. 1999; Recognition and management of Tillaux fractures in adolescents. Pediatr Emerg Care. 15:37–9. DOI: 10.1097/00006565-199902000-00011. PMID: 10069311.
Article2. Birnie MF, van Schilt KL, Sanders FR, Kloen P, Schepers T. 2019; Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament avulsion fractures in operatively treated ankle fractures: a retrospective analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 139:787–93. DOI: 10.1007/s00402-019-03138-2. PMID: 30770996. PMCID: PMC6514069.
Article3. Tak S, Qureshi MK, Ackland JA, Arshad R, Salim J. 2021; Adolescent Tillaux fractures: a systematic review of the literature. Cureus. 13:e12860. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12860.
Article4. Wagstaffe WW. An unusual form of fracture of the fibula. St thomas Hosp Rep. 1875; 6:43.5. Park JW, Kim SK, Hong JS, Park JH. 2002; Anterior tibiofibular ligament avulsion fracture in weber type B lateral malleolar fracture. J Trauma. 52:655–9. DOI: 10.1097/00005373-200204000-00007. PMID: 11956378.
Article6. Kose O, Yuksel HY, Guler F, Ege T. 2016; Isolated adult Tillaux fracture associated with Volkmann fracture-a unique com-bination of injuries: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Foot Ankle Surg. 55:1057–62. DOI: 10.1053/j.jfas.2015.10.005. PMID: 26711834.
Article7. Lu J, Holledge MM. 2016; Tillaux and Volkmann fractures: a report on two cases, treatment determined by syndesmosis instability. Trauma Cases Rev. 2:042. DOI: 10.23937/2469-5777/1510042.
Article8. Abrams GD, Renstrom PA, Safran MR. 2012; Epidemiology of musculoskeletal injury in the tennis player. Br J Sports Med. 46:492–8. DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2012-091164. PMID: 22554841.
Article9. Miller TL, Skalak T. 2014; Evaluation and treatment recommen-dations for acute injuries to the ankle syndesmosis without associated fracture. Sports Med. 44:179–88. DOI: 10.1007/s40279-013-0106-1. PMID: 24127279.
Article10. Oliveira N, Pinho P, Baptista M, Freitas D, Varanda P, Pereira BS. 2021; Missed Tillaux fracture and syndesmosis injury in adult: arthroscopic assisted reduction and fixation. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 56:399–402.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tillaux Fracture in an Adolescent with a Trimalleolar Ankle Fracture
- A Clinical Study of the Mechanism of Injury of Juvenile Tillaux Fracture and Triplane Fracture
- Surgical Treatment of Maisonneuve Fracture Accompanied by Tillaux-Like Fracture: A Case Report
- A vertically split fracture of the marginal tubercle of the zygoma in a 3-year-old boy: a case report
- Concomitant Fracture of Lateral Process and Posteromedial Tubercle of Talus: A Case Report