Kosin Med J.
2022 Jun;37(2):163-168. 10.7180/kmj.21.036.
Overcoming high pre-transplant isoagglutinin titers using high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin, salvage plasmapheresis, and booster rituximab without splenectomy in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2532047
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.21.036
Abstract
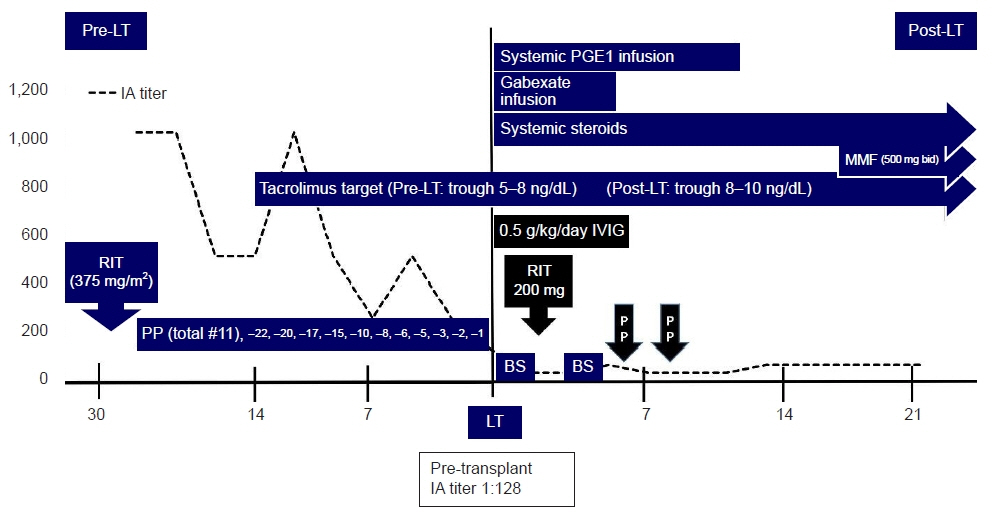
- High pre-transplant isoagglutinin is a risk factor for antibody-mediated rejection in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation. A 55-year-old man with alcoholic liver cirrhosis underwent ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation. The initial isoagglutinin immunoglobulin G titer was 1:1,024. Despite five sessions of plasmapheresis, the isoagglutinin titer was not significantly reduced (from 1:1,024 to 1:512). We decided to perform 11 plasmaphereses and proceed with liver transplantation regardless of the isoagglutinin titer (1:128 at transplantation day). Instead, we planned to administer 0.5 g/kg intravenous immunoglobulin and booster rituximab (200 mg) after transplant. On postoperative day 6, the isoagglutinin titer increased from 1:32 to 1:64, and the patient received plasmapheresis twice. The patient maintained stable liver function without evidence of further complications or rejection. The high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin, salvage plasmapheresis, and booster rituximab protocol might be able to overcome a pre-transplant high isoagglutinin titer in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation without splenectomy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim JM, Kwon CH, Joh JW, Kang ES, Park JB, Lee JH, et al. ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation is suitable in patients without ABO-matched donor. J Hepatol. 2013; 59:1215–22.
Article2. Oh J, Kim JM. Immunologic strategies and outcomes in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020; 26:1–6.
Article3. Tanabe M, Kawachi S, Obara H, Shinoda M, Hibi T, Kitagawa Y, et al. Current progress in ABO-incompatible liver transplantation. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010; 40:943–9.
Article4. Lee B, Cho JY, Lee HW, Choi Y, Yoon YS, Han HS. Successful ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation using splenectomy and intravenous immunoglobulin in high isoagglutinin titer patients. Korean J Transplant. 2020; 34:109–13.
Article5. Song GW. ABO incompatability in liver transplantation. Hanyang Med Rev. 2014; 34:202–10.
Article6. Kozaki K, Egawa H, Ueda M, Oike F, Yoshizawa A, Fukatsu A, et al. The role of apheresis therapy for ABO incompatible living donor liver transplantation: the Kyoto University experience. Ther Apher Dial. 2006; 10:441–8.
Article7. Saitoh Y, Fujio A, Miyagi S, Tokodai K, Unno M, Kamei T. ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation with high preoperative antibody titer: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021; 85:106260.
Article8. Ikegami T, Taketomi A, Soejima Y, Iguchi T, Sanefuji K, Kayashima H, et al. Successful ABO incompatible living donor liver transplantation in a patient with high isoagglutinin titer using high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Transplant Proc. 2007; 39:3491–4.
Article9. Lee SD, Kim SH, Kong SY, Kim YK, Lee SA, Park SJ. ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation without graft local infusion and splenectomy. HPB (Oxford). 2014; 16:807–13.
Article10. Song GW, Lee SG, Hwang S, Kim KH, Ahn CS, Moon DB, et al. ABO-incompatible adult living donor liver transplantation under the desensitization protocol with rituximab. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16:157–70.
Article11. Raut V, Uemoto S. Management of ABO-incompatible living-donor liver transplantation: past and present trends. Surg Today. 2011; 41:317–22.
Article12. Lee CF, Cheng CH, Wang YC, Soong RS, Wu TH, Chou HS, et al. Adult living donor liver transplantation across ABO-incompatibility. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e1796.
Article13. Goss MB, Rana A. ABO-incompatible liver transplantation: is it a viable option with modern innovation? Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2017; 10:124–9.
Article14. Egawa H, Umeshita K, Uemoto S. Optimal dosage regimen for rituximab in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2017; 24:89–94.
Article15. Egawa H, Teramukai S, Haga H, Tanabe M, Mori A, Ikegami T, et al. Impact of rituximab desensitization on blood-type-incompatible adult living donor liver transplantation: a Japanese multicenter study. Am J Transplant. 2014; 14:102–14.
Article16. Ikegami T, Taketomi A, Soejima Y, Yoshizumi T, Uchiyama H, Harada N, et al. Rituximab, IVIG, and plasma exchange without graft local infusion treatment: a new protocol in ABO incompatible living donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2009; 88:303–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The overcoming high pre-transplant isoagglutinin titers using intravenous immunoglobulin, booster rituximab, salvage plasmapheresis in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation: a case report
- Successful ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation using splenectomy and intravenous immunoglobulin in high isoagglutinin titer patients
- ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation with a simplified desensitization and immunosuppression protocol: a single center retrospective study
- Case of ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Kidney Transplantation without Blood Products in a Jehovah's Witness