Anat Cell Biol.
2022 Jun;55(2):148-154. 10.5115/acb.21.217.
Patterns of superficial veins in the cubital fossa and its clinical implications among southern Ethiopian population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Human Anatomy, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dilla University, Dilla, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Human Anatomy, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Arba Minch University, Arba Minch, Ethiopia
- KMID: 2531201
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.21.217
Abstract
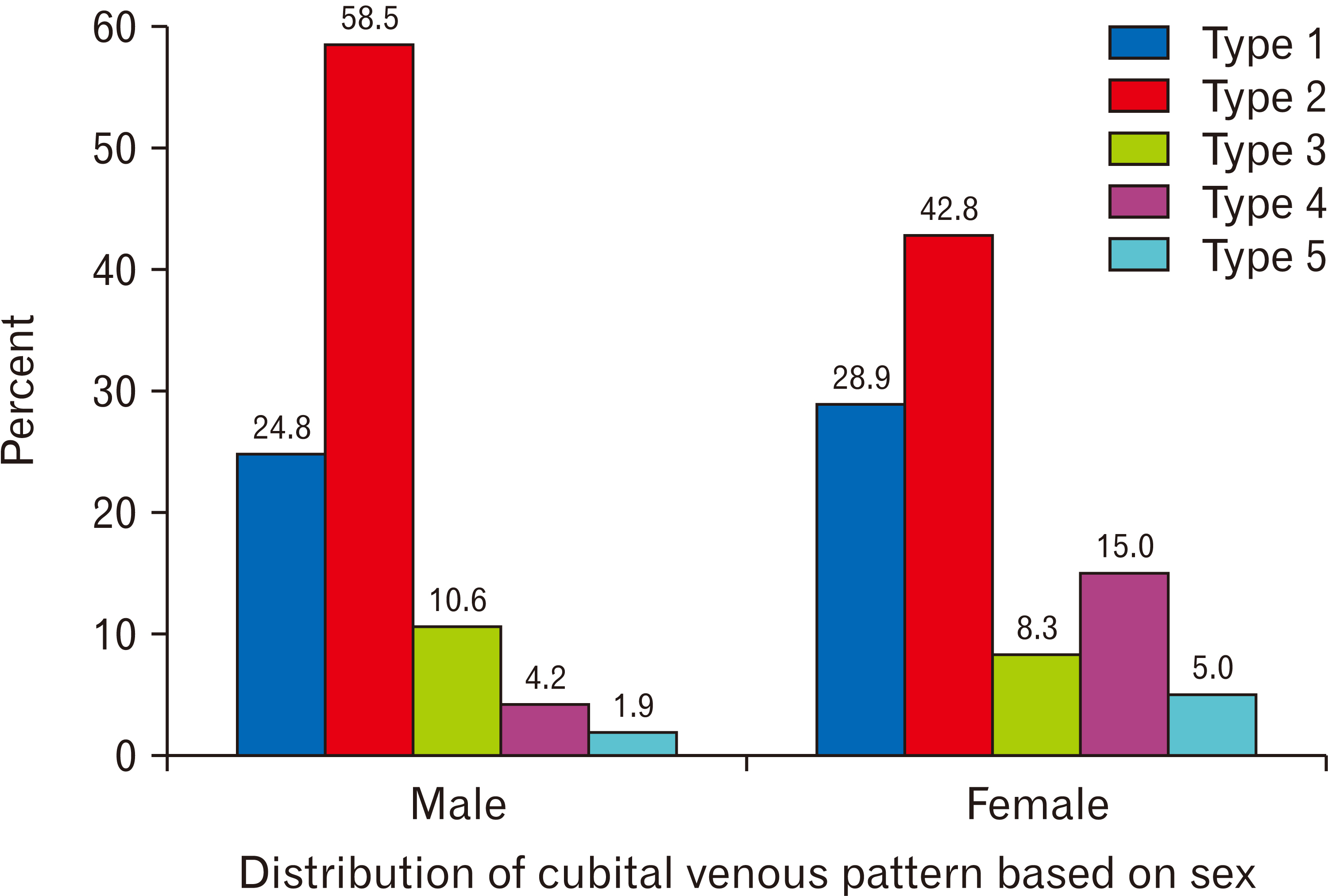
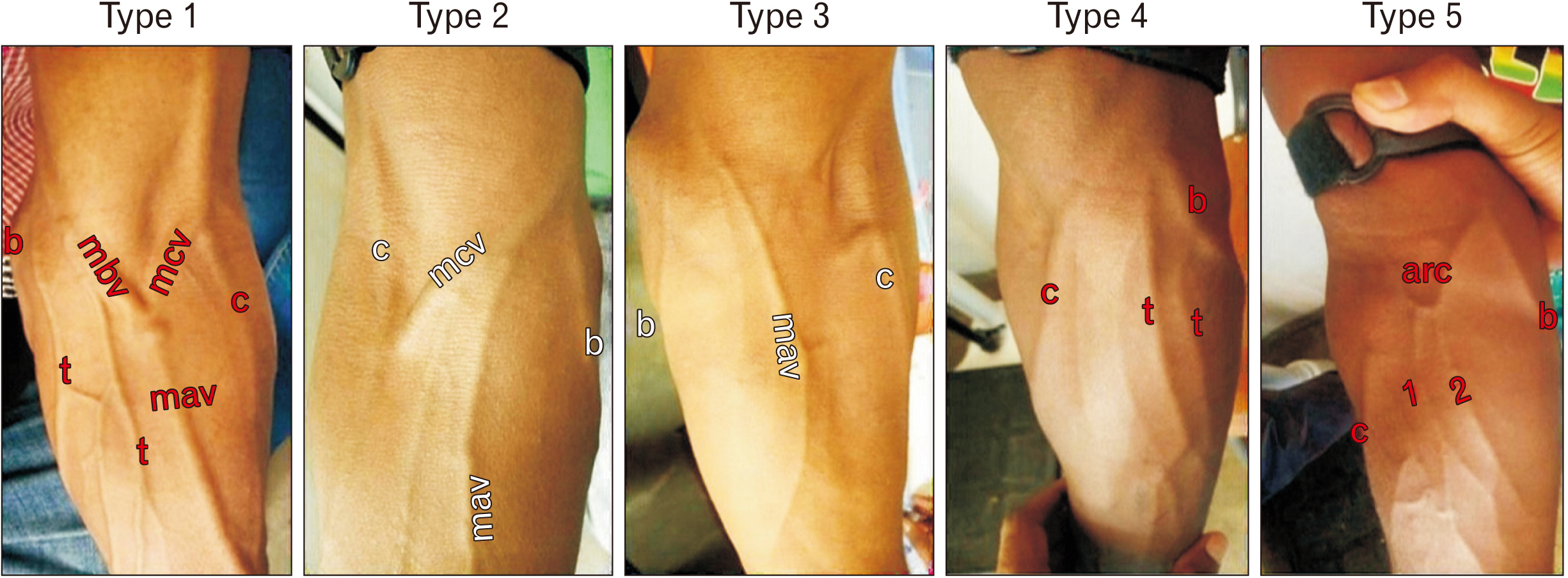
- Cubital fossa is the site where the venous accesses are frequently made. Superficial veins at this site display variations in their pattern among different populations. Knowledge of different venous pattern in the cubital fossa is important for diagnostic, surgical and therapeutic procedures. The purpose of this study was to report variations of the cubital superficial vein patterns in the southern Ethiopian subjects. An institution based cross-sectional study design was employed among 401 randomly selected patients presented at the triage room of Arba Minch General Hospital from January 15 to February 15, 2021. A questionnaire was used to collect socio-demographic data and images of the common and variant superficial venous patterns were recorded. Descriptive statistical analysis was performed. P<0.05 was considered as statistical significance. In the present study, a total of 802 cubital fossae from 401 study participants were examined. Five patterns of superficial veins were identified. Type 2 was the most common pattern and observed in 55.0% of cubital fossae (42.1% right and 67.8% left cubital fossae). The least common, type 5 variant was detected in 2.6% cubital fossae (2.7% right and 2.5% left). Statistically significant association based on sex and laterality was noted. The current study concluded that type 2 and type 3 patterns were more frequent superficial venous patterns in the cubital fossa and more common in males than female. Awareness of these uncommon cubital venous patterns and their incidence is very useful for those performing venipuncture or venisection especially under emergency conditions.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Standring S. 2016. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 41st ed. Elsevier;Edinburg:2. Lee H, Lee SH, Kim SJ, Choi WI, Lee JH, Choi IJ. 2015; Variations of the cubital superficial vein investigated by using the intravenous illuminator. Anat Cell Biol. 48:62–5. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2015.48.1.62. PMID: 25806123. PMCID: PMC4371182.
Article3. Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. 2010. Gray's anatomy for students. 2nd ed. Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier;Philadelphia:4. Darabi MR, Shams A, Bayat P, Bayat M, Babaee S, Ghahremani B. 2015; A case report: variation of the cephalic and external jugular veins. Anat Sci J. 12:203–5. PMID: aa4a05e4ef64407ea2e18abbca0d4008.5. Jain T, Yadav SK. 2015; Case study: variation of superficial veins pattern of upper limb found in dissection. Int Ayurvedic Med J. 3:2223–5.6. Jasiński R, Poradnik E. 2003; Superficial venous anastomosis in the human upper extremity--a post-mortem study. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 62:191–9. PMID: 14507046.7. Mikuni Y, Chiba S, Tonosaki Y. 2013; Topographical anatomy of superficial veins, cutaneous nerves, and arteries at venipuncture sites in the cubital fossa. Anat Sci Int. 88:46–57. DOI: 10.1007/s12565-012-0160-z. PMID: 23131916.
Article8. Vučinić N, Erić M, Macanović M. 2016; Patterns of superficial veins of the middle upper extremity in Caucasian population. J Vasc Access. 17:87–92. DOI: 10.5301/jva.5000429. PMID: 26109546.
Article9. Horowitz SH. 1994; Peripheral nerve injury and causalgia secondary to routine venipuncture. Neurology. 44:962–4. DOI: 10.1212/WNL.44.5.962. PMID: 8190306.
Article10. Newman B. 2001; Venipuncture nerve injuries after whole-blood donation. Transfusion. 41:571–2. DOI: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.2001.41040571.x. PMID: 11316914.
Article11. Stevens RJ, Mahadevan V, Moss AL. 2012; Injury to the lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm after venous cannulation: a case report and literature review. Clin Anat. 25:659–62. DOI: 10.1002/ca.21285. PMID: 22025401.
Article12. Bekel AA, Bekalu AB, Moges AM, Gebretsadik MA. 2018; Anatomical variations of superficial veins pattern in Cubital fossa among North West Ethiopians. Anat J Afr. 7:1238–43. DOI: 10.4314/aja.v7i2.174144.
Article13. Ukoha UU, Oranusi CK, Okafor JI, Ogugua PC, Obiaduo AO. 2013; Patterns of superficial venous arrangement in the cubital fossa of adult Nigerians. Niger J Clin Pract. 16:104–9. DOI: 10.4103/1119-3077.106777. PMID: 23377482.
Article14. Newman BH, Waxman DA. 1996; Blood donation-related neurologic needle injury: evaluation of 2 years' worth of data from a large blood center. Transfusion. 36:213–5. DOI: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1996.36396182137.x. PMID: 8604504.
Article15. Yammine K, Erić M. 2017; Patterns of the superficial veins of the cubital fossa: a meta-analysis. Phlebology. 32:403–14. DOI: 10.1177/0268355516655670. PMID: 27343223.
Article16. Vasudha TK. 2013; A study on superficial veins of upper limb. Nat J Clin Anat. 2:204–8. DOI: 10.4103/2277-4025.297895. PMID: b47b9fe6acfb46138e543bc1b9fe2b6a.
Article17. Elamurugan E, Hemachandar R. 2017; Brachiocephalic arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis through the median antecubital vein. Indian J Nephrol. 27:177–80. DOI: 10.4103/0971-4065.179333. PMID: 28553035. PMCID: PMC5434681.
Article18. Yamada K, Yamada K, Katsuda I, Hida T. 2008; Cubital fossa venipuncture sites based on anatomical variations and relationships of cutaneous veins and nerves. Clin Anat. 21:307–13. DOI: 10.1002/ca.20622. PMID: 18428997.
Article19. Dharap AS, Shaharuddin MY. 1994; Patterns of superficial veins of the cubital fossa in Malays. Med J Malaysia. 49:239–41. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-199808000-00075. PMID: 7845272.20. Wasfi FA, Dabbagh AW, AlAthari FM, Salman SS. 1986; Biostatistical study on the arrangement of the superficial veins of the cubital fossa in Iraqis. Acta Anat (Basel). 126:183–6. DOI: 10.1159/000146212. PMID: 3751488.
Article21. Hamzah AA, Ramasamy S, Adnan AS, Khan AH. 2014; Pattern of superficial venous of the cubital fossa among volunteers in a tertiary hospital. Trop Med Surg. 2:1000164. DOI: 10.4172/2329-9088.1000164.
Article22. AlBustami F, Altarawneh I, Rababah E. 2014; Patterns of superficial venous arrangement in the cubital fossa of adult Jordanians. Jordan Med J. 48:269–74. DOI: 10.12816/0025077.23. Żytkowski A, Tubbs RS, Iwanaga J, Olszewska A, Kunikowska B, Wysiadecki G. 2021; Duplication of the median cubital vein- case report with commentaries on clinical significance. Transl Res Anat. 24:100114. DOI: 10.1016/j.tria.2021.100114.24. Del Sol M, De Angelis MA, Bolini PAD. 1988; Formacoes venosas de fossa cubital crianca. Pediatria Mod. 23:225–31. Portuguese.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Variations of the cubital superficial vein investigated by using the intravenous illuminator
- A Case of Superficial Brachial Artery
- Nodular Fasciitis of the Cubital Fossa in a Young Female Mimicking a Neurogenic Tumor
- Regional and Sexual Differences in Corneocytes among Young Korean Adults
- Bicipitoradial Bursitis: A Case Report