Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2022 Apr;10(2):113-116. 10.14791/btrt.2022.0004.
Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Presenting as a Scalp Mass
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Anatomic Pathology, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 4Department of Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- KMID: 2529443
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2022.0004
Abstract
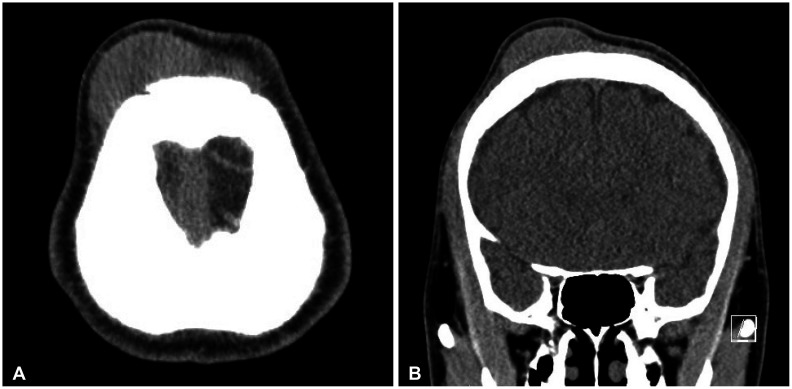
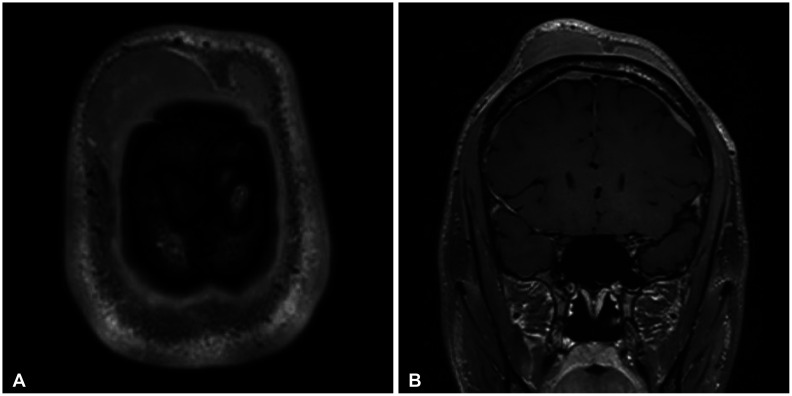
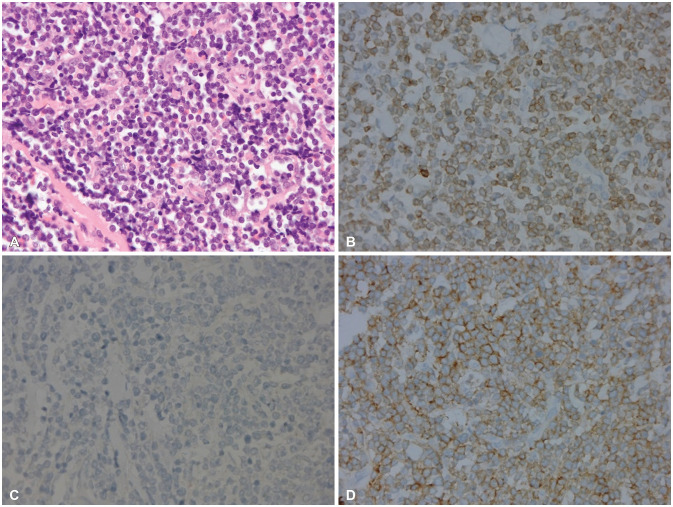
- Peripheral scalp T-cell lymphoma is a very rare disease. We report a case of a 22-year-old man who presented an indolent large scalp mass in the right frontal scalp region. The patient’s physical examination demonstrated no palpable mass in the chest, abdomen, and extremities. The brain CT revealed a high-density large scalp mass of the subgaleal layer in the right frontal and a small scalp mass of the subgaleal layer in the left frontal. The brain MRI showed multifocal enhancing masses in the bilateral dura, the subgaleal layer of the scalp, and the skull. The patient underwent removal of the tumor found in the right frontal scalp. The histologic diagnosis was peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Bone marrow aspiration showed the involvement of T-cell lymphoma. The patient received chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and prednisolone (CHOP protocol) for 3 cycles. The patient was discharged without neurological deficit. The patient showed no evidence of recurrence 15 months after surgery. We report a rare case of peripheral T-cell lymphoma mimicking benign scalp tumors.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berti E, Tomasini D, Vermeer MH, Meijer CJ, Alessi E, Willemze R. Primary cutaneous CD8-positive epidermotropic cytotoxic T cell lymphomas. A distinct clinicopathological entity with an aggressive clinical behavior. Am J Pathol. 1999; 155:483–492. PMID: 10433941.
Article2. Duyndam DA, Biesma DH, van Heesewijk JP. Primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the cranial vault; MRI features before and after treatment. Clin Radiol. 2002; 57:948–950. PMID: 12413922.
Article3. Batchelor TT. Primary central nervous sysytem lymphomas. Richard Winn H, editor. Youmans and Winn neurological surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2017. p. 1085–1090.4. Ikumi N, Fujita H, Terui T, Takahashi H, Miura K, Hatta Y, et al. Aggressive CD4–CD8–CD45RA+CCR10– primary cutaneous peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: a case report. Acta Derm Venereol. 2019; 99:1176–1177. PMID: 31502655.5. Lim T, Kim SJ, Kim K, Lee JI, Lim DH, Lee DJ, et al. Primary CNS lymphoma other than DLBCL: a descriptive analysis of clinical features and treatment outcomes. Ann Hematol. 2011; 90:1391–1398. PMID: 21479535.
Article6. Mongia S, Shukla D, Devi BI, Reddy TV. Primary cranial vault non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Neurol India. 2003; 51:293–294.7. El Asri AC, Akhaddar A, Baallal H, Boulahroud O, Mandour C, Chahdi H, et al. Primary lymphoma of the cranial vault: case report and a systematic review of the literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 154:257–265. PMID: 21842209.
Article8. Kantarci M, Erdem T, Alper F, Gundogdu C, Okur A, Aktas A. Imaging characteristics of diffuse primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma of the cranial vault with orbital and brain invasion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1324–1326. PMID: 12917120.9. Burg G, Dummer R, Kerl H. Classification of cutaneous lymphomas. Dermatol Clin. 1994; 12:213–217. PMID: 8045033.
Article10. da Rocha AJ, da Rocha TM, da Silva CJ, Paes RP, Bruniera P, Chiattone CS. Cranial vault lymphoma: a systematic review of five patients. J Neurooncol. 2010; 100:9–15. PMID: 20146083.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Peripheral T - cell Lymphoma
- Malignant Histiocytic Lymphoma of Scalp
- Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma of Urinary Bladder Presenting With Just Irritative Voiding Symptoms
- A Case of Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma Presenting as Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji
- Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma of the Spinal Epidural Spaces: Case Report