Ewha Med J.
2022 Jan;45(1):17-19. 10.12771/emj.2022.45.1.17.
Pancreatic Panniculitis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2525287
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2022.45.1.17
Abstract
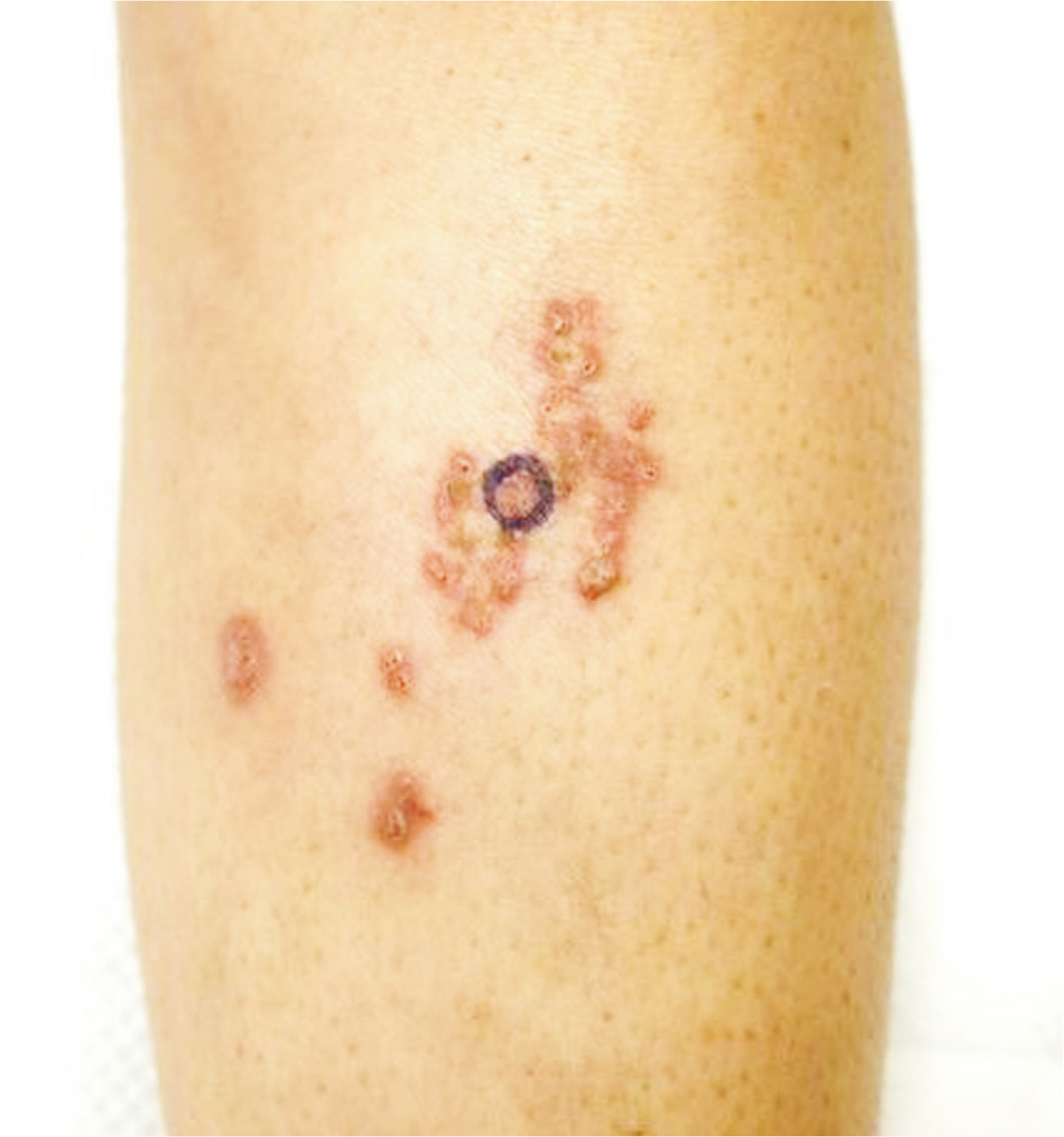
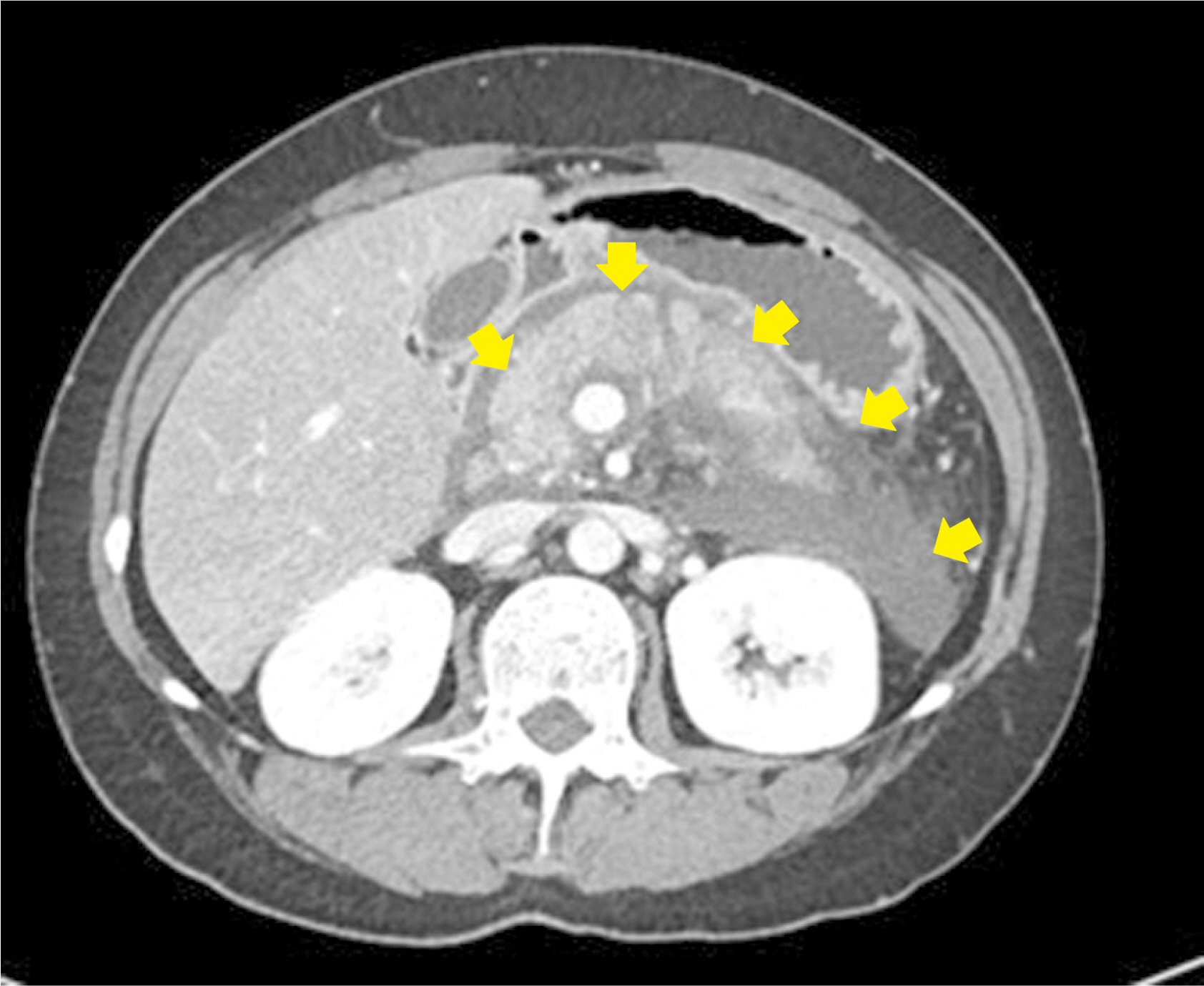
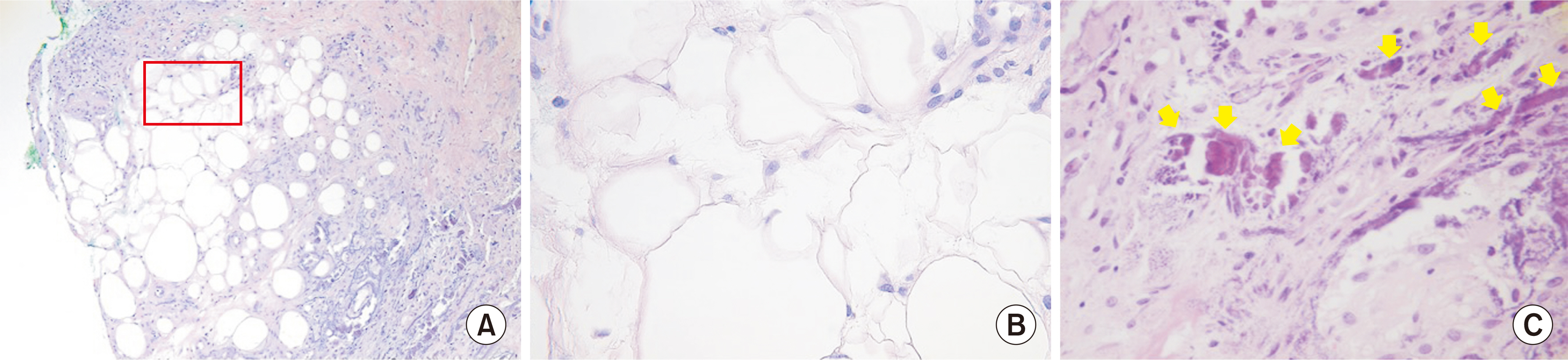
- Pancreatic panniculitis is a rare skin complication in which subcutaneous fat necrosis occurs in association with pancreatic disorders, most commonly acute or chronic pancreatitis. Erythematous subcutaneous nodules develop on the legs and spontaneously ulcerate or exude an oily substance. A 32-year-old Korean female patient presented with a 2-week-history of tender nodules with erythematous crusts on her left shin. She had a history of alcoholic liver cirrhosis and, 5 weeks earlier, had been diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. The histopathologic findings from a skin biopsy were consistent with lobular panniculitis, without signs of vasculitis, and diffuse fat necrosis. Basophilic calcium deposits were present in the dermis and subcutaneous fat. These findings were suggestive of pancreatic panniculitis. The skin lesion had a chronic course corresponding to repeated exacerbations of the patient’s pancreatitis. Thus, in the differential diagnosis of subcutaneous nodules, clinicians should consider pancreatic panniculitis as a cutaneous manifestation of pancreatic disease.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rongioletti F, Caputo V. 2013; Pancreatic panniculitis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 148:419–425. PMID: 23900163.2. Guanziroli E, Colombo A, Coggi A, Gianotti R, Marzano AV. 2018; Pancreatic panniculitis: the "bright" side of the moon in solid cancer patients. BMC Gastroenterol. 18:1. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-017-0727-1. PMID: 29301491. PMCID: PMC5755411.
Article3. Lee WS, Kim MY, Kim SW, Paik CN, Kim HO, Park YM. 2007; Fatal pancreatic panniculitis associated with acute pancreatitis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 22:914–917. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.914. PMID: 17982246. PMCID: PMC2693864.
Article4. Patel R, Khan A, Naveed S, Brazleton J, Wilcox M. 2015; Pancreatic panniculitis: a rare manifestation of acute pancreatitis. J Pancreas. 16:303–306.5. Laureano A, Mestre T, Ricardo L, Rodrigues AM, Cardoso J. 2014; Pancreatic panniculitis: a cutaneous manifestation of acute pancreatitis. J Dermatol Case Rep. 8:35–37. DOI: 10.3315/jdcr.2014.1167. PMID: 24748910. PMCID: PMC3989096.6. Lyon MJ. 2010; Metabolic panniculitis: alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency panniculitis and pancreatic panniculitis. Dermatol Ther. 23:368–374. DOI: 10.1111/j.1529-8019.2010.01337.x. PMID: 20666824.
Article7. Heykarts B, Anseeuw M, Degreef H. 1999; Panniculitis caused by acinous pancreatic carcinoma. Dermatology. 198:182–183. DOI: 10.1159/000018107. PMID: 10325476.
Article8. Kim EJ, Chu MS, Sohn KC, Cho DH, Na GH, Kim HC, et al. 2017; Pancreatic panniculitis in patients with chronic pancreatitis: case report and review of literature. Korean J Gastroenterol. 69:83–86. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2017.69.1.83. PMID: 28135797.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pancreatic Panniculitis Associated with Acute Pancreatitis and Hemorrhagic Pseudocysts: A Case Report
- Two Cases of Pancreatic Panniculitis
- A Case of Pancreatitis Presenting with Pancreatic Panniculitis: A Case Report
- Polyarthritis and Pancreatic Panniculitis in a Patient with Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma
- A Case of Pancreatic Panniculitis