J Stroke.
2021 Sep;23(3):449-452. 10.5853/jos.2021.02068.
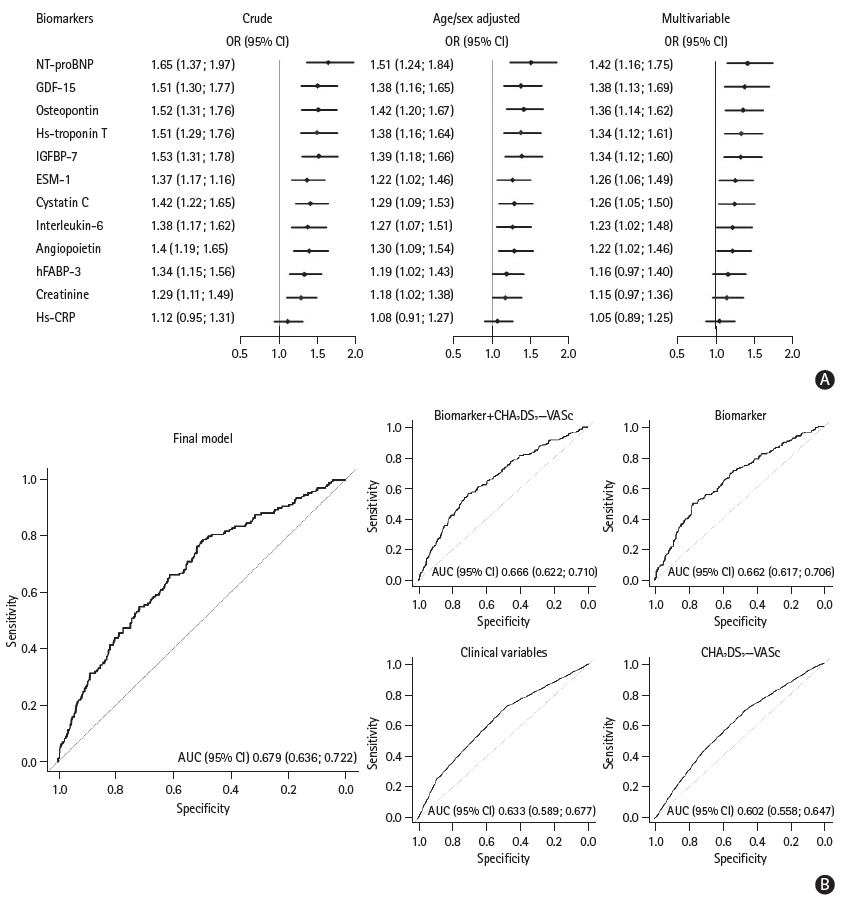
Biomarkers, Clinical Variables, and the CHA2DS2-VASc Score to Detect Silent Brain Infarcts in Atrial Fibrillation Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cardiovascular Research Institute Basel, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland
- 2Electrophysiology and Ablation Unit and L’Institut de Rythmologie et Modélisation Cardiaque (LIRYC), University Hospital Bordeaux, Bordeaux-Pessac, France
- 3Department of Cardiology, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland
- 4Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Penzberg, Germany
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Regional Hospital Lugano, Ticino, Switzerland
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Cantonal Hospital Baden, Baden, Switzerland
- 7Department of Cardiology, Inselspital, Bern University Hospital, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 8Department of General Internal Medicine, Inselspital, Bern University Hospital, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 9Institute of Primary Health Care (BIHAM), University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 10Department of Neurology, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland
- 11Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
- KMID: 2520923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2021.02068
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Conen D, Rodondi N, Müller A, Beer JH, Ammann P, Moschovitis G, et al. Relationships of overt and silent brain lesions with cognitive function in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 73:989–999.2. Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, et al. The montreal cognitive assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005; 53:695–699.
Article3. Conway DS, Buggins P, Hughes E, Lip GY. Relationship of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein to the prothrombotic state in chronic atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 43:2075–2082.
Article4. Lip GY, Patel JV, Hughes E, Hart RG. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and soluble CD40 ligand as indices of inflammation and platelet activation in 880 patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: relationship to stroke risk factors, stroke risk stratification schema, and prognosis. Stroke. 2007; 38:1229–1237.5. Sharma A, Hijazi Z, Andersson U, Al-Khatib SM, Lopes RD, Alexander JH, et al. Use of biomarkers to predict specific causes of death in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2018; 138:1666–1676.
Article6. Hijazi Z, Lindbäck J, Alexander JH, Hanna M, Held C, Hylek EM, et al. The ABC (age, biomarkers, clinical history) stroke risk score: a biomarker-based risk score for predicting stroke in atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:1582–1590.
Article7. Januzzi JL Jr, Packer M, Claggett B, Liu J, Shah AM, Zile MR, et al. IGFBP7 (insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7) and neprilysin inhibition in patients with heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2018; 11:e005133.
Article8. Wunderlich MT, Hanhoff T, Goertler M, Spener F, Glatz JF, Wallesch CW, et al. Release of brain-type and heart-type fatty acid-binding proteins in serum after acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol. 2005; 252:718–724.
Article9. Beck H, Acker T, Wiessner C, Allegrini PR, Plate KH. Expression of angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, and tie receptors after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Am J Pathol. 2000; 157:1473–1483.
Article10. Rocha SF, Schiller M, Jing D, Li H, Butz S, Vestweber D, et al. Esm1 modulates endothelial tip cell behavior and vascular permeability by enhancing VEGF bioavailability. Circ Res. 2014; 115:581–590.
Article11. Hohnloser SH, Hijazi Z, Thomas L, Alexander JH, Amerena J, Hanna M, et al. Efficacy of apixaban when compared with warfarin in relation to renal function in patients with atrial fibrillation: insights from the ARISTOTLE trial. Eur Heart J. 2012; 33:2821–2830.
Article12. Ellison JA, Velier JJ, Spera P, Jonak ZL, Wang X, Barone FC, et al. Osteopontin and its integrin receptor alpha(v)beta3 are upregulated during formation of the glial scar after focal stroke. Stroke. 1998; 29:1698–1706.13. Van Gelder IC, Healey JS, Crijns HJGM, Wang J, Hohnloser SH, Gold MR, et al. Duration of device-detected subclinical atrial fibrillation and occurrence of stroke in ASSERT. Eur Heart J. 2017; 38:1339–1344.
Article14. Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, Parmar P, Krishnamurthi R, Chugh S, et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016; 15:913–924.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antithrombotic Therapy for Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
- Left Ventricular Diastolic Function: The Link between CHA2DS2-VASc Score and Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- The usefulness of newly developed R2CHA2DS2-VASc score and comparison with CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores in atrial fibrillation patients
- Cardiac Structural or Functional Changes Associated with CHAâ‚‚DSâ‚‚-VASc Scores in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Echocardiography
- Incremental Value of Left Atrial Global Longitudinal Strain for Prediction of Post Stroke Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke