Korean Circ J.
2021 Sep;51(9):792-796. 10.4070/kcj.2021.0202.
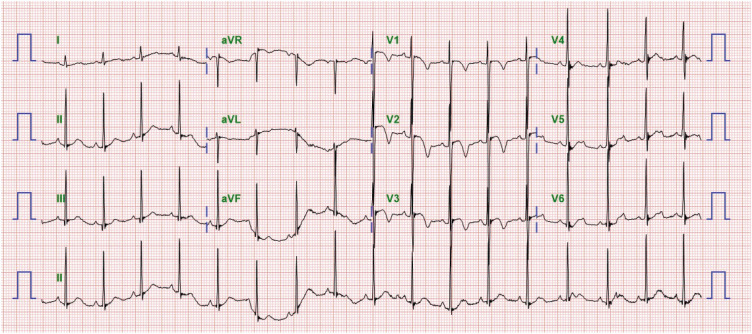
Congenital Long QT Syndrome Type 2 with Symptomatic 2:1 Atrioventricular Block and Ventricular Arrhythmia in a Preterm Baby Who Presented with Fetal Ventricular Tachycardia and Hydrops
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2519842
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2021.0202
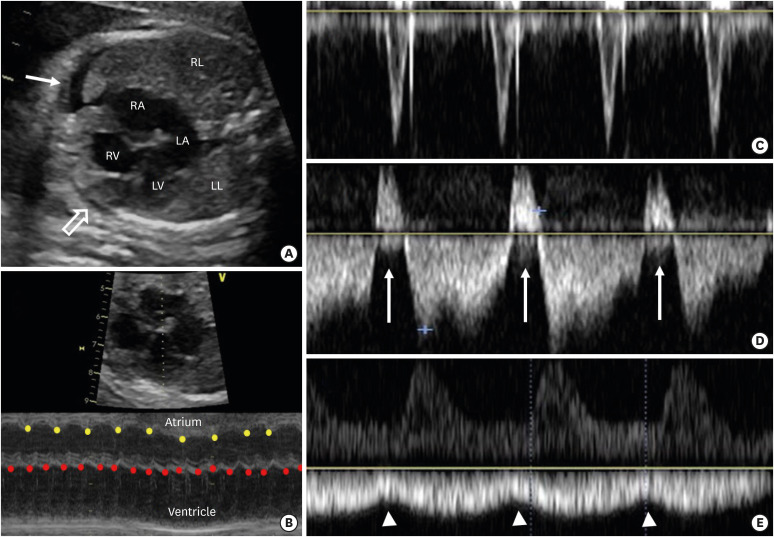
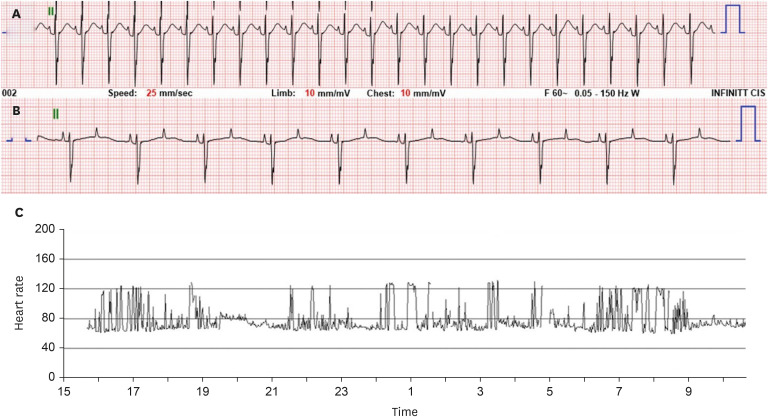
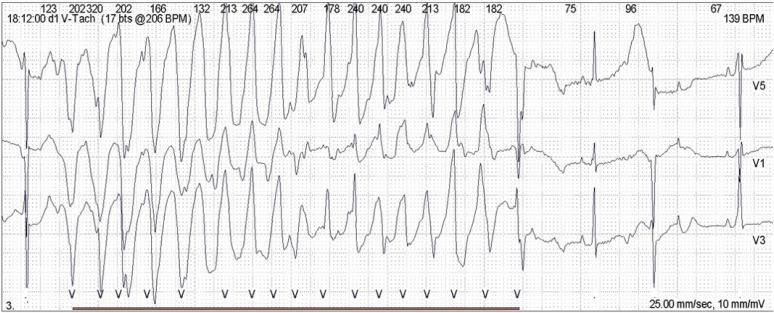
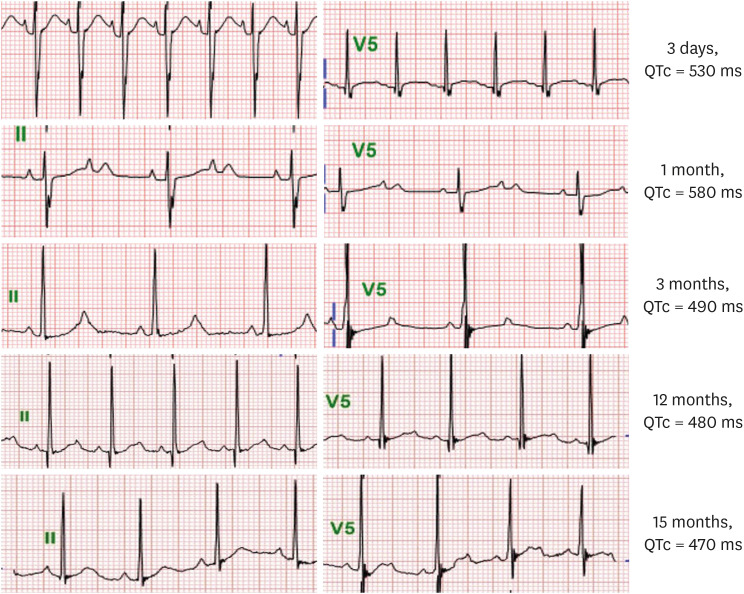
Figure
Reference
-
1. Li Y, Fang J, Zhou K, et al. Prediction of fetal outcome without intrauterine intervention using a cardiovascular profile score: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015; 28:1965–1972. PMID: 25308207.
Article2. Miyake A, Sakaguchi H, Miyazaki A, Miyoshi T, Aiba T, Shiraishi I. Successful prenatal management of ventricular tachycardia and second-degree atrioventricular block in fetal long QT syndrome. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2016; 3:53–57. PMID: 28491768.
Article3. Aziz PF, Tanel RE, Zelster IJ, et al. Congenital long QT syndrome and 2:1 atrioventricular block: an optimistic outcome in the current era. Heart Rhythm. 2010; 7:781–785. PMID: 20197117.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Congenital Long OT Syndrome with Pseudo - Atrioventricular Block
- Two Cases of 2:1 Atrioventricular Block in Infants with Idiopathic Long QT Syndrome
- A Case of Congenital Long QT Syndrome Associated with Deafness and Syncope
- Left Stellate Ganglion Block Prior to Induction of Anesthesia for Surgical Sympathectomy in a Patient with Long QT Syndrome
- Congenital Long QT Syndrome Type 8 Characterized by Fetal Onset of Bradycardia and 2:1 Atrioventricular Block