Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2021 Jul;38(3):231-234. 10.12701/yujm.2020.00675.
Metachronous extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma of nasal type and primary testicular lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2518665
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00675
Abstract
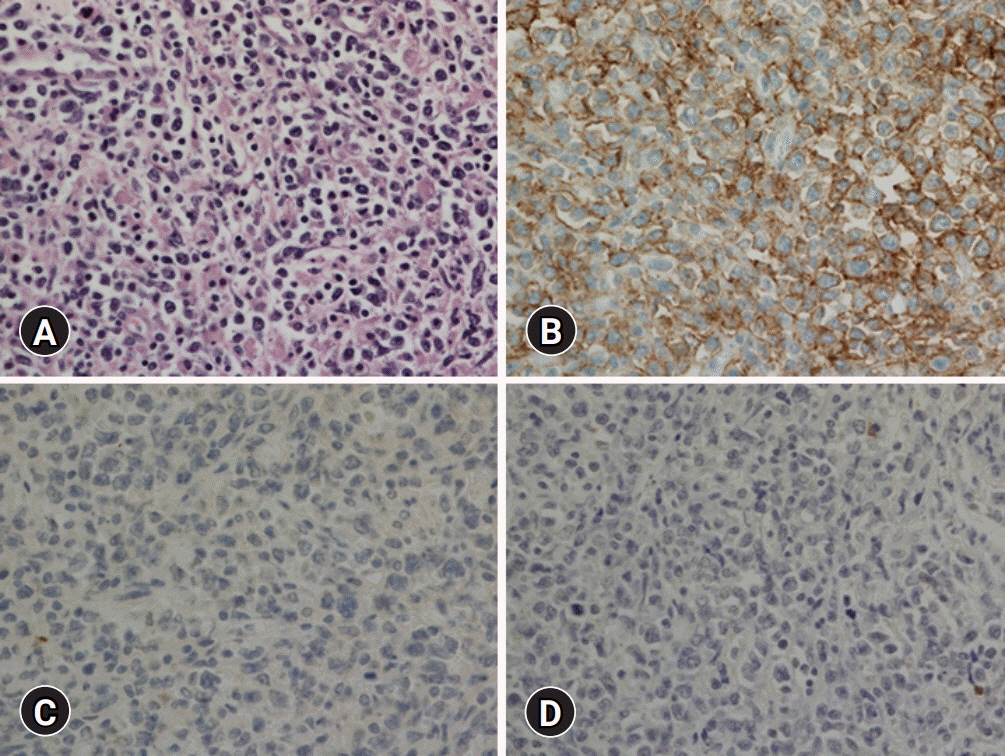
- We report a rare case of metachronous lymphoma with two distinct cell lineages in a 75-year-old man. The patient complained about having nasal obstruction for 2 years and extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma of the nasal type was diagnosed from a biopsy. The immunohistochemical staining for CD56 and in situ hybridization for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–encoded small RNA (EBER-ISH) were positive and the tumor cells were negative for CD20. After 13 months of concurrent chemoradiotherapy, the patient presented with swelling of the left testis. Positron emission tomography scan detected an abnormal uptake in the testis. A diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified, was diagnosed from subsequent radical orchiectomy. The immunohistochemical staining revealed to be positive for CD20, BCL2, BCL6, and MYC and negative for CD10 and EBER-ISH.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Møller MB, d'Amore F, Christensen BE; Danish Lymphoma Study Group. Testicular lymphoma: a population-based study of incidence, clinicopathological correlations and prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 1994; 30:1760–4.
Article2. Chan JK, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ferry JA. Extrannodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. In : Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2017. p. 368–71.3. Pileri SA, Weisenburger DD, Sng I, Nakamura S, Muller-Hermelink HK, Chan WC, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, NOS. In : Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2017. p. 403–6.4. King RL, Goodlad JR, Calaminici M, Dotlic S, Montes-Moreno S, Oschlies I, et al. Lymphomas arising in immune-privileged sites: insights into biology, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. Virchows Arch. 2020; 476:647–65.
Article5. Booman M, Douwes J, Glas AM, de Jong D, Schuuring E, Kluin PM. Primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphomas have activated B-cell-like subtype characteristics. J Pathol. 2006; 210:163–71.
Article6. Cheah CY, Wirth A, Seymour JF. Primary testicular lymphoma. Blood. 2014; 123:486–93.
Article7. Brunn A, Nagel I, Montesinos-Rongen M, Klapper W, Vater I, Paulus W, et al. Frequent triple-hit expression of MYC, BCL2, and BCL6 in primary lymphoma of the central nervous system and absence of a favorable MYC(low)BCL2 (low) subgroup may underlie the inferior prognosis as compared to systemic diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2013; 126:603–5.
Article8. Fonseca R, Habermann TM, Colgan JP, O'Neill BP, White WL, Witzig TE, et al. Testicular lymphoma is associated with a high incidence of extranodal recurrence. Cancer. 2000; 88:154–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type, Extranasal and Ulcerative Blister Variant, Case Report
- A Case of Extranodal Natural Killer/T Cell Lymphoma Combined With Actinomycosis
- A Case of Primary NK/T Cell Lymphoma of the Testis
- A Case of Nasal Type NK/T-cell Lymphoma
- Delayed Diagnosis Due to Septal Perforation in Patient with Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type