J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2021 Jun;23(2):99-107. 10.7461/jcen.2021.E2020.08.008.
Endovascular management of large and giant intracranial aneurysms: Experience from a tertiary care neurosurgery institute in India
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neuro-Surgery, Rajendra Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS), Jharkhand, India
- 2Department of Neuro-Surgery, Govind Ballabh Pant Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (GIPMER), New Delhi, India
- KMID: 2517022
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2021.E2020.08.008
Abstract
Objective
With the development of endovascular technique and devices, large and giant intracranial aneurysms are increasingly being managed by this less invasive method. Here we discuss our experience on managing such aneurysms via endovascular technique.
Methods
Retrospective data on 42 patients with large and giant intracranial aneurysms managed by endovascular techniques between September 2015 to December 2017 at our neurosurgery institute were included in this analysis.
Results
There were a total 42 patients with 9 giant and 33 large aneurysms in this study. Eight aneurysms were treated by parent vessel occlusion, 22 aneurysms with coils and rest 12 aneurysms were treated with stent assisted coiling. Following the procedure, Raymond class I occlusion was accomplished in 31 (73.8%) patients while class Ⅱ in 9 (21.4%) and class Ⅲ in 2 (4.8%) patients. Overall morbidity and mortality were 9.5% and 14.3% respectively and favorable outcome was seen in 80.9% patients. Significant correlation was observed with clinical outcome and initial neurological status.
Conclusions
The study indicates that endovascular intervention is a safe and effective method in managing large and giant intracranial aneurysms with lesser morbidity and mortality.
Keyword
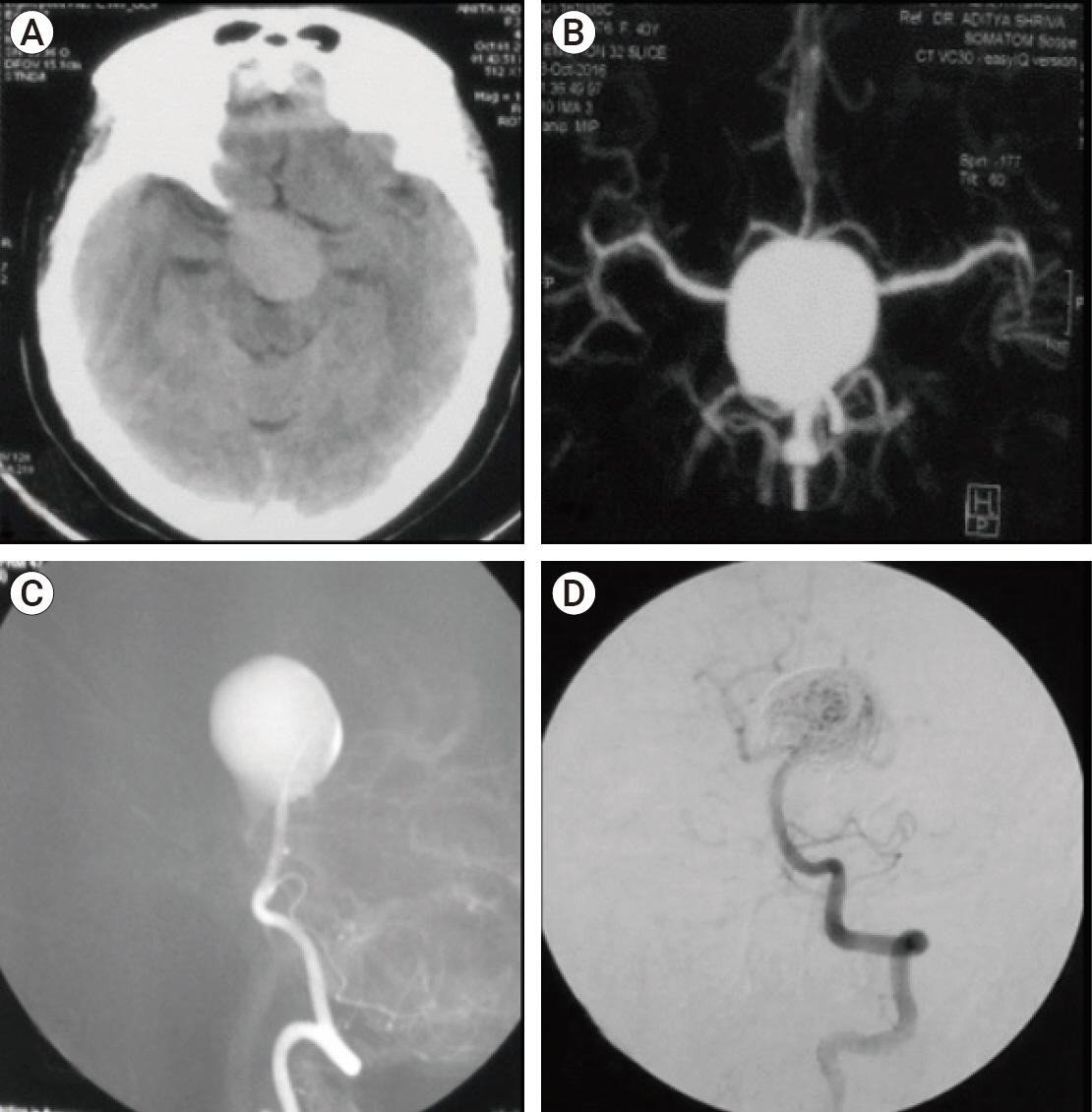
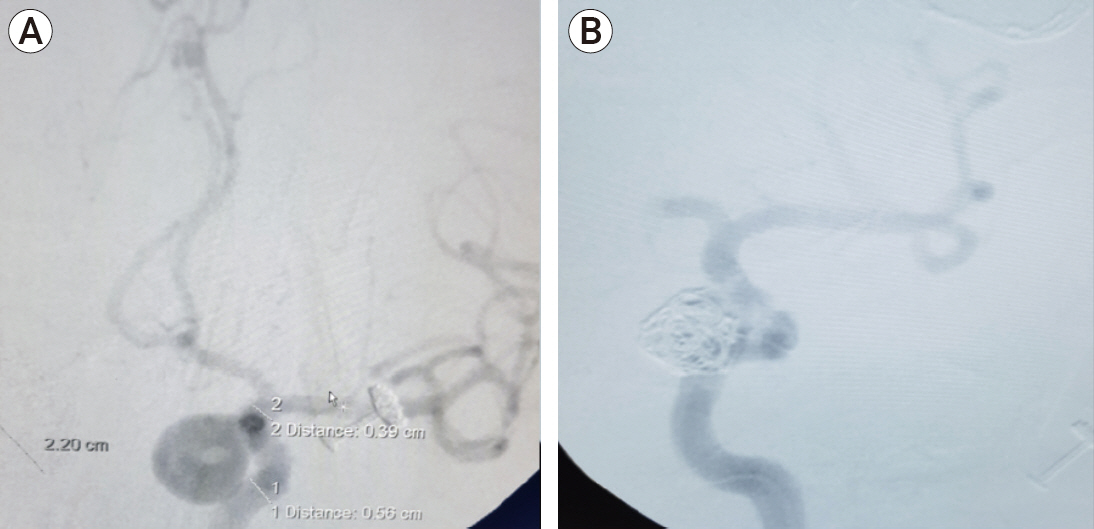
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahmed SI, Javed G, Bareeqa SB, Samar SS, Shah A, Giani A, et al. Endovascular coiling versus neurosurgical clipping for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus. 2019; Mar. 11(3):e4320.
Article2. Bae HJ, Yoo DS, Huh PW, Lee TG, Cho KS, Lee SB. Endovascular treatment of the distal internal carotid artery large aneurysm. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2014; Sep. 16(3):200–8.
Article3. Bender MT, Colby GP, Lin LM, Jiang B, Westbroek EM, Xu R, et al. Predictors of cerebral aneurysm persistence and occlusion after flow diversion: a single-institution series of 445 cases with angiographic follow-up. J Neurosurg. 2018; Mar. 130(1):259–67.
Article4. Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with flow diverters: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013; Feb. 44(2):442–7.
Article5. Colby GP, Lin LM, Gomez JF, Paul AR, Huang J, Tamargo RJ, et al. Immediate procedural outcomes in 35 consecutive pipeline embolization cases: a single-center, single-user experience. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013; May. 5(3):237–46.
Article6. Dengler J, Maldaner N, Gläsker S, Endres M, Wagner M, Malzahn U, Giant Intracranial Aneurysm Study Group, et al. Outcome of surgical or endovascular treatment of giant intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on age, aneurysm location, and unruptured aneuryms--A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016; 41(3-4):187–98.7. Fiorella D, Albuquerque F, Gonzalez F, McDougall CG, Nelson PK. Reconstruction of the right anterior circulation with the Pipeline embolization device to achieve treatment of a progressively symptomatic, large carotid aneurysm. J Neurointerv Surg. 2010; Mar. 2(1):31–7.
Article8. Gruber A, Killer M, Bavinzski G, Richling B. Clinical and angiographic results of endosaccular coiling treatment of giant and very large intracranial aneurysms: a 7-year, single-center experience. Neurosurgery. 1999; Oct. 45(4):793–803. discussion 803-4.
Article9. Hanel RA, Spetzler RF. Surgical treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2008; Jun. (6 Suppl 3):1289–97. discussion 1297-9.
Article10. International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms--risk of rupture and risks of surgical intervention. N Engl J Med. 1998; Dec. 339(24):1725–33.11. Ishikawa T, Kamiyama H, Kobayashi N, Tanikawa R, Takizawa K, Kazumata K. Experience from “double-insurance bypass.” Surgical results and additional techniques to achieve complex aneurysm surgery in a safer manner. Surg Neurol. 2005; May. 63(5):485–90. discussion 490.12. Kallmes DF, Hanel R, Lopes D, Boccardi E, Bonafé A, Cekirge S, et al. International retrospective study of the pipeline embolization device: a multicenter aneurysm treatment study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015; Jan. 36(1):108–15.
Article13. Kerezoudis P, McCutcheon BA, Murphy M, Rayan T, Gilder H, Rinaldo L, et al. Predictors of 30-day perioperative morbidity and mortality of unruptured intracranial aneurysm surgery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016; Oct. 149:75–80.
Article14. Lempert TE, Malek AM, Halbach VV, Phatouros CC, Meyers PM, Dowd CF, et al. Endovascular treatment of ruptured posterior circulation cerebral aneurysms. Clinical and angiographic outcomes. Stroke. 2000; Jan. 31(1):100–10.15. Lozier AP, Connolly ES Jr, Lavine SD, Solomon RA. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of posterior circulation aneurysms: a systematic review of the literature. Stroke. 2002; Oct. 33(10):2509–18.16. Lozier AP, Kim GH, Sciacca RR, Connolly ES Jr, Solomon RA. Microsurgical treatment of basilar apex aneurysms: perioperative and long-term clinical outcome. Neurosurgery. 2004; Feb. 54(2):286–96. discussion 296-9.
Article17. Lylyk P, Miranda C, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Scrivano E, Luna HR, et al. Curative endovascular reconstruction of cerebral aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device: the Buenos Aires experience. Neurosurgery. 2009; Apr. 64(4):632–42. quiz N6.18. Mack WJ, Ducruet AF, Angevine PD, Komotar RJ, Shrebnick DB, Edwards NM, et al. Deep hypothermic circulatory arrest for complex cerebral aneurysms: lessons learned. Neurosurgery. 2007; May. 60(5):815–27. discussion 815-27.
Article19. Nelson PK, Lylyk P, Szikora I, Wetzel SG, Wanke I, Fiorella D. The pipeline embolization device for the intracranial treatment of aneurysms trial. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; Jan. 32(1):34–40.
Article20. Ogilvy CS, Carter BS. Stratification of outcome for surgically treated unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2003; Jan. 52(1):82–7. discussion 87-8.
Article21. Peschillo S, Caporlingua A, Resta MC, Peluso JPP, Burdi N, Sourour N, et al. Endovascular treatment of large and giant carotid aneurysms with flow-diverter stents alone or in combination with coils: A multicenter experience and long-term follow-up. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2017; Aug. 13(4):492–502.
Article22. Schaller B. Extracranial-intracranial bypass to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke in intracranial aneurysms of the anterior cerebral circulation: a systematic review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008; 17(5):287–98.
Article23. Sharma DP, Singh D, Jagetia A, Singh H, Tandon M, Ganjoo P. Intra procedure rupture of intracranial aneurysm during endovascular coiling: neurosurgeons’ experience and review of the literature. Neurol India. 2011; Sep-Oct. 59(5):690–5.
Article24. Sluzewski M, Menovsky T, van Rooij WJ, Wijnalda D. Coiling of very large or giant cerebral aneurysms: long-term clinical and serial angiographic results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; Feb. 24(2):257–62.25. Spetzler RF, Carter LP. Revascularization and aneurysm surgery: current status. Neurosurgery. 1985; Jan. 16(1):111–6.
Article26. Sullivan BJ, Sekhar LN, Duong DH, Mergner G, Alyano D. Profound hypothermia and circulatory arrest with skull base approaches for treatment of complex posterior circulation aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1999; 141(1):1–11. discussion 11-2.
Article27. Wang B, Gao BL, Xu GP, Xiang C, Liu XS. Endovascular embolization is applicable for large and giant intracranial aneurysms: experience in one center with long-term angiographic follow-up. Acta Radiol. 2015; Jan. 56(1):105–13.
Article28. Wang JB, Li MH, Fang C, Wang W, Cheng YS, Zhang PL, et al. Endovascular treatment of giant intracranial aneurysms with willis covered stents: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2008; May. 62(5):E1176–7. discussion E1177.29. Yu SC, Kwok CK, Cheng PW, Chan KY, Lau SS, Lui WM, et al. Intracranial aneurysms: midterm outcome of pipeline embolization device--a prospective study in 143 patients with 178 aneurysms. Radiology. 2012; Dec. 265(3):893–901.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Analysis of Giant Intracranial Aneurysms with Endovascular Embolization
- Endovascular Management of Intracranial Aneurysms: Advances in Stenting Techniques and Technology
- Surgical Management of Intracranial Aneurysms in the Endovascular Era : Review Article
- Guideline for Management of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: Preliminary Report
- Current Update on the Randomized Controlled Trials of Intracranial Aneurysms