Endocrinol Metab.
2021 Apr;36(2):256-269. 10.3803/EnM.2021.987.
Cardiorenal Protection in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Toronto General Hospital Research Institute, University Health Network, ON, Canada
- 2Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, ON, Canada
- 3Banting and Best Diabetes Centre, University of Toronto, ON, Canada
- 4Applied Health Research Centre, Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St Michael’s Hospital, ON, Canada
- 5Department of Physiology, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- 6Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- KMID: 2515453
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.987
Abstract
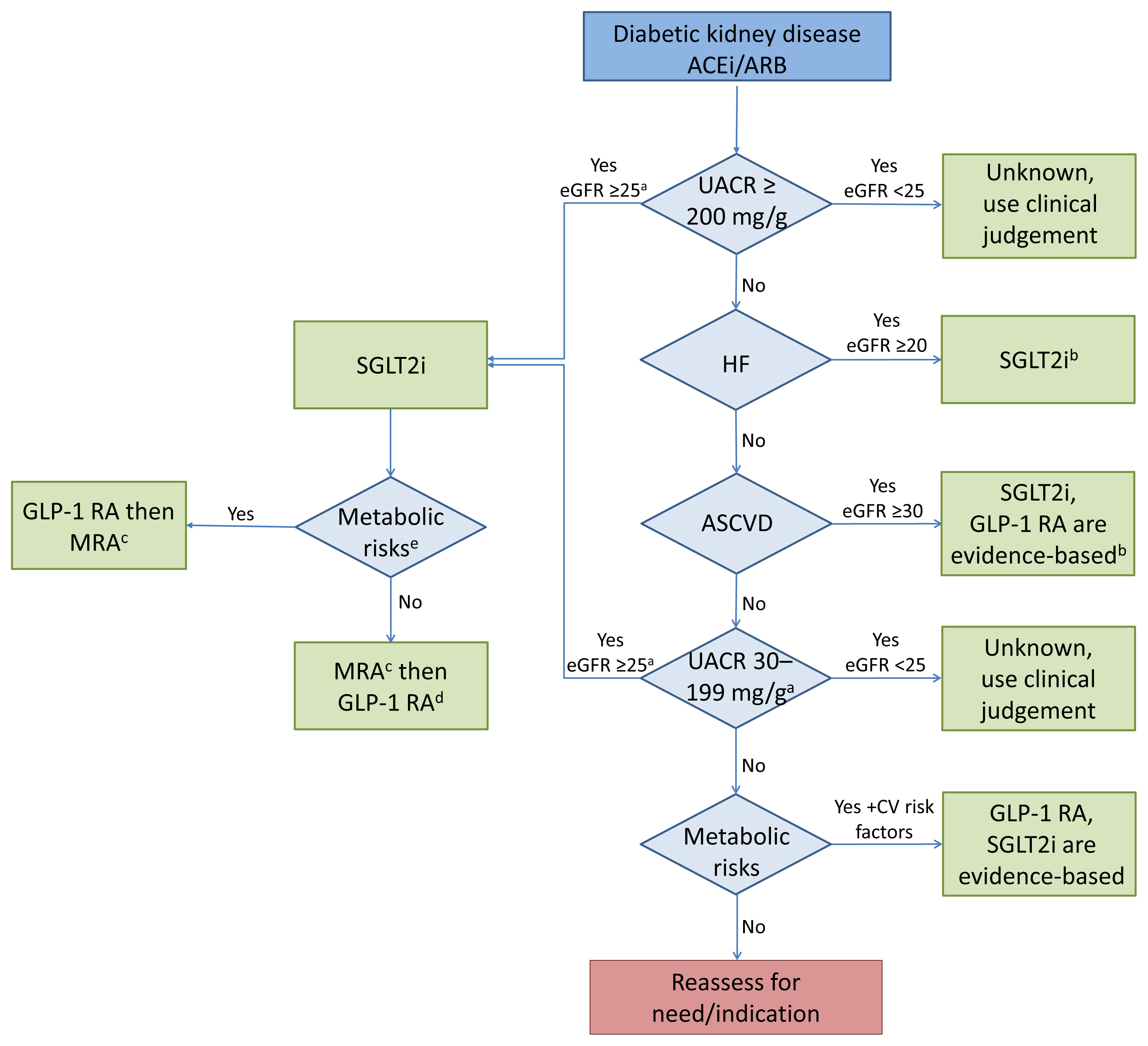
- Over the last 5 years there have been many new developments in the management of diabetic kidney disease. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors were initially used for glycemic control, but more recent studies have now shown that their benefits extend to cardiovascular and kidney outcomes. The recent addition of data on the novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) gives us another approach to further decrease the residual risk of diabetic kidney disease progression. In this review we describe the mechanism of action, key studies, and possible adverse effects related to these three classes of medications. The management of type 2 diabetes now includes an increasing number of medications for the management of comorbidities in a patient population at significant risk of cardiovascular disease and progression of chronic kidney disease. It is from this perspective that we seek to outline the rationale for the sequential and/or combined use of SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 RA and MRAs in patients with type 2 diabetes for heart and kidney protection.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):43-55. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1629.
Reference
-
1. Tuttle KR, Cherney DZ. Diabetic Kidney Disease Task Force of the American Society of Nephrology. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition heralds a call-to-action for diabetic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020; 15:285–8.
Article2. Tsapas A, Avgerinos I, Karagiannis T, Malandris K, Manolopoulos A, Andreadis P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of glucose-lowering drugs for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2020; 173:278–86.3. Sridhar VS, Rahman HU, Cherney DZI. What have we learned about renal protection from the cardiovascular outcome trials and observational analyses with SGLT2 inhibitors? Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020; 22(Suppl 1):55–68.
Article4. Lytvyn Y, Bjornstad P, van Raalte DH, Heerspink HL, Cherney DZI. The new biology of diabetic kidney disease-mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Endocr Rev. 2020; 41:202–31.
Article5. Dubrofsky L, Srivastava A, Cherney DZ. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in nephrology practice: a narrative review. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2020; 7:2054358120935701.
Article6. Sridhar VS, Dubrofsky L, Boulet J, Cherney DZ. Making a case for the combined use of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1 receptor agonists for cardiorenal protection. J Bras Nefrol. 2020; 42:467–77.
Article7. van Bommel EJM, Lytvyn Y, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, Fagan NM, Koitka-Weber A, et al. Renal hemodynamic effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in hyperfiltering people with type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes and normal kidney function. Kidney Int. 2020; 97:631–5.8. Cherney DZ, Kanbay M, Lovshin JA. Renal physiology of glucose handling and therapeutic implications. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020; 35(Suppl 1):i3–12.
Article9. Heerspink HJL, Kosiborod M, Inzucchi SE, Cherney DZI. Renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2018; 94:26–39.
Article10. Cherney DZI, Dekkers CCJ, Barbour SJ, Cattran D, Abdul Gafor AH, Greasley PJ, et al. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on proteinuria in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (DIAMOND): a randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020; 8:582–93.
Article11. Heerspink HJL, Karasik A, Thuresson M, Melzer-Cohen C, Chodick G, Khunti K, et al. Kidney outcomes associated with use of SGLT2 inhibitors in real-world clinical practice (CVD- REAL 3): a multinational observational cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020; 8:27–35.
Article12. Cherney DZI, Zinman B, Inzucchi SE, Koitka-Weber A, Mattheus M, von Eynatten M, et al. Effects of empagliflozin on the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease: an exploratory analysis from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 5:610–21.
Article13. Cherney DZ, Odutayo A, Aronson R, Ezekowitz J, Parker JD. Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition and cardiorenal protection: JACC review topic of the week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 74:2511–24.14. Lopaschuk GD, Verma S. Mechanisms of cardiovascular benefits of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: a state-of-the-art review. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020; 5:632–44.15. Neuen BL, Cherney DZ, Jardine MJ, Perkovic V. Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: thinking beyond glucose lowering. CMAJ. 2019; 191:E1128–35.
Article16. Heerspink HJ, Perkins BA, Fitchett DH, Husain M, Cherney DZ. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: cardiovascular and kidney effects, potential mechanisms, and clinical applications. Circulation. 2016; 134:752–72.
Article17. Cherney DZI, Cooper ME, Tikkanen I, Pfarr E, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, et al. Pooled analysis of Phase III trials indicate contrasting influences of renal function on blood pressure, body weight, and HbA1c reductions with empagliflozin. Kidney Int. 2018; 93:231–44.18. Ferrannini E, Mark M, Mayoux E. CV protection in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial: a “thrifty substrate” hypothesis. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:1108–14.
Article19. Rojas-Morales P, Tapia E, Pedraza-Chaverri J. β-Hydroxyb-utyrate: a signaling metabolite in starvation response? Cell Signal. 2016; 28:917–23.
Article20. Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, Goldberg EL, Bodogai M, Kim D, et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015; 21:263–9.
Article21. Osataphan S, Macchi C, Singhal G, Chimene-Weiss J, Sales V, Kozuka C, et al. SGLT2 inhibition reprograms systemic metabolism via FGF21-dependent and -independent mechanisms. JCI Insight. 2019; 4:e123130.
Article22. Umino H, Hasegawa K, Minakuchi H, Muraoka H, Kawaguchi T, Kanda T, et al. High basolateral glucose increases sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and reduces sirtuin-1 in renal tubules through glucose transporter-2 detection. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:6791.
Article23. Packer M. Cardioprotective effects of sirtuin-1 and its downstream effectors: potential role in mediating the heart failure benefits of sglt2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) inhibitors. Circ Heart Fail. 2020; 13:e007197.24. Hesp AC, Schaub JA, Prasad PV, Vallon V, Laverman GD, Bjornstad P, et al. The role of renal hypoxia in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease: a promising target for newer renoprotective agents including SGLT2 inhibitors? Kidney Int. 2020; 98:579–89.25. Burns KD, Cherney D. Renal angiotensinogen and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition: insights from experimental diabetic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2019; 49:328–30.
Article26. Cherney D, Perkins BA, Lytvyn Y, Heerspink H, Rodriguez-Ortiz ME, Mischak H. The effect of sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibition on the urinary proteome. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0186910.
Article27. Cherney DZ, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, Xiao F, Zimpelmann J, Woerle HJ, et al. Sodium glucose cotransport-2 inhibition and intrarenal RAS activity in people with type 1 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2014; 86:1057–8.
Article28. Dekkers CCJ, Petrykiv S, Laverman GD, Cherney DZ, Gansevoort RT, Heerspink HJL. Effects of the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on glomerular and tubular injury markers. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:1988–93.
Article29. Kopecky C, Lytvyn Y, Domenig O, Antlanger M, Kovarik JJ, Kaltenecker CC, et al. Molecular regulation of the renin-angiotensin system by sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2019; 62:1090–3.
Article30. Clementi A, Virzi GM, Brocca A, de Cal M, Vescovo G, Granata A, et al. Cardiorenal syndrome type 4: management. Blood Purif. 2013; 36:200–9.
Article31. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2117–28.
Article32. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:347–57.
Article33. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:644–57.
Article34. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:323–34.
Article35. Neuen BL, Young T, Heerspink HJL, Neal B, Perkovic V, Billot L, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:845–54.
Article36. Zelniker TA, Raz I, Mosenzon O, Dwyer JP, Heerspink HJL, Cahn A, et al. 192 Effect of dapagliflozin on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes according to baseline renal function and albuminuria status: insights from DECLARE-TIMI 58. Eur Heart J. 2019; 40(Suppl 1):ehz747.0052.37. Cooper ME, Inzucchi SE, Zinman B, Hantel S, von Eynatten M, Wanner C, et al. Glucose control and the effect of empagliflozin on kidney outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019; 74:713–5.
Article38. Inzucchi SE, Zinman B, Fitchett D, Wanner C, Ferrannini E, Schumacher M, et al. How does empagliflozin reduce cardiovascular mortality? Insights from a mediation analysis of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:356–63.
Article39. Li J, Neal B, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw D, Neuen BL, Arnott C, et al. Mediators of the effects of canagliflozin on kidney protection in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2020; 98:769–77.
Article40. Li J, Woodward M, Perkovic V, Figtree GA, Heerspink HJL, Mahaffey KW, et al. Mediators of the effects of canagliflozin on heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes. JACC Heart Fail. 2020; 8:57–66.
Article41. Cannon CP, Pratley R, Dagogo-Jack S, Mancuso J, Huyck S, Masiukiewicz U, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1425–35.
Article42. Cherney DZI, Charbonnel B, Cosentino F, Dagogo-Jack S, McGuire DK, Pratley R, et al. Effects of ertugliflozin on kidney composite outcomes, renal function and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analysis from the randomised VERTIS CV trial. Diabetologia. 2021. Mar. 4. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-021-05407-5.
Article43. Cherney DZI, McGuire DK, Charbonnel B, Cosentino F, Pratley R, Dagogo-Jack S, et al. Gradient of risk and associations with cardiovascular efficacy of ertugliflozin by measures of kidney function: observations from VERTIS CV. Circulation. 2021; 143:602–5.
Article44. Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Pitt B, Cannon CP, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:129–39.
Article45. Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Steg PG, Cannon CP, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:117–28.
Article46. Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2295–306.
Article47. Heerspink HJL, Stefansson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1436–46.
Article48. McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Kober L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381:1995–2008.49. Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Khan MS, Marx N, Lam CSP, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with heart failure by baseline diabetes status: results from the EMPEROR-reduced trial. Circulation. 2021; 143:337–49.
Article50. Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1413–24.51. Jhund PS, Solomon SD, Docherty KF, Heerspink HJL, Anand IS, Bohm M, et al. Efficacy of dapagliflozin on renal function and outcomes in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: results of DAPA-HF. Circulation. 2021; 143:298–309.
Article52. Jardine MJ, Zhou Z, Mahaffey KW, Oshima M, Agarwal R, Bakris G, et al. Renal, cardiovascular, and safety outcomes of canagliflozin by baseline kidney function: a secondary analysis of the CREDENCE randomized trial. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020; 31:1128–39.
Article53. Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, Im K, Goodrich EL, Bonaca MP, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. 2019; 393:31–9.
Article54. Huang CY, Lee JK. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and major adverse limb events: a trial-level meta-analysis including 51 713 individuals. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020; 22:2348–55.
Article55. Sridhar VS, Tuttle KR, Cherney DZI. We can finally stop worrying about SGLT2 inhibitors and acute kidney injury. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020; 76:454–6.
Article56. van Raalte DH, Cherney DZI. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition and renal ischemia: implications for future clinical trials. Kidney Int. 2018; 94:459–62.57. Maiorino MI, Chiodini P, Bellastella G, Capuano A, Esposito K, Giugliano D. Insulin and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist combination therapy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40:614–24.
Article58. van Can J, Sloth B, Jensen CB, Flint A, Blaak EE, Saris WH. Effects of the once-daily GLP-1 analog liraglutide on gastric emptying, glycemic parameters, appetite and energy metabolism in obese, non-diabetic adults. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014; 38:784–93.
Article59. Astrup A, Carraro R, Finer N, Harper A, Kunesova M, Lean ME, et al. Safety, tolerability and sustained weight loss over 2 years with the once-daily human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012; 36:843–54.
Article60. van Baar MJB, van Ruiten CC, Muskiet MHA, van Bloemendaal L, IJzerman RG, van Raalte DH. SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy: from mechanisms to clinical considerations in type 2 diabetes management. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:1543–56.
Article61. Richards P, Parker HE, Adriaenssens AE, Hodgson JM, Cork SC, Trapp S, et al. Identification and characterization of GLP-1 receptor-expressing cells using a new transgenic mouse model. Diabetes. 2014; 63:1224–33.
Article62. Sun F, Wu S, Guo S, Yu K, Yang Z, Li L, et al. Impact of GLP-1 receptor agonists on blood pressure, heart rate and hypertension among patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015; 110:26–37.
Article63. Pyke C, Heller RS, Kirk RK, Orskov C, Reedtz-Runge S, Kaastrup P, et al. GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology. 2014; 155:1280–90.
Article64. Schlatter P, Beglinger C, Drewe J, Gutmann H. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor expression in primary porcine proximal tubular cells. Regul Pept. 2007; 141:120–8.
Article65. Muskiet MH, Tonneijck L, Smits MM, Kramer MH, Diamant M, Joles JA, et al. Acute renal haemodynamic effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist exenatide in healthy overweight men. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016; 18:178–85.
Article66. Thomson SC, Kashkouli A, Liu ZZ, Singh P. Renal hemodynamic effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist are mediated by nitric oxide but not prostaglandin. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017; 313:F854–8.
Article67. Skov J, Dejgaard A, Frokiaer J, Holst JJ, Jonassen T, Rittig S, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1): effect on kidney hemodynamics and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:E664–71.
Article68. Gutzwiller JP, Tschopp S, Bock A, Zehnder CE, Huber AR, Kreyenbuehl M, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 induces natriuresis in healthy subjects and in insulin-resistant obese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:3055–61.
Article69. Skov J, Pedersen M, Holst JJ, Madsen B, Goetze JP, Rittig S, et al. Short-term effects of liraglutide on kidney function and vasoactive hormones in type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016; 18:581–9.
Article70. Tonneijck L, Smits MM, Muskiet MH, Hoekstra T, Kramer MH, Danser AH, et al. Renal effects of DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin or GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes: a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:2042–50.
Article71. Pessoa TD, Campos LC, Carraro-Lacroix L, Girardi AC, Malnic G. Functional role of glucose metabolism, osmotic stress, and sodium-glucose cotransporter isoform-mediated transport on Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 activity in the renal proximal tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014; 25:2028–39.72. Crajoinas RO, Oricchio FT, Pessoa TD, Pacheco BP, Lessa LM, Malnic G, et al. Mechanisms mediating the diuretic and natriuretic actions of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011; 301:F355–63.
Article73. Farah LX, Valentini V, Pessoa TD, Malnic G, McDonough AA, Girardi AC. The physiological role of glucagon-like peptide-1 in the regulation of renal function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016; 310:F123–7.
Article74. Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an exploratory analysis of the REWIND randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2019; 394:131–8.75. Mann JFE, Orsted DD, Brown-Frandsen K, Marso SP, Poulter NR, Rasmussen S, et al. Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:839–48.
Article76. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jodar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1834–44.
Article77. Kodera R, Shikata K, Kataoka HU, Takatsuka T, Miyamoto S, Sasaki M, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist ameliorates renal injury through its anti-inflammatory action without lowering blood glucose level in a rat model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2011; 54:965–78.
Article78. Kristensen SL, Rorth R, Jhund PS, Docherty KF, Sattar N, Preiss D, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:776–85.
Article79. Aroor AR, Mandavia CH, Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and heart failure: molecular mechanisms. Heart Fail Clin. 2012; 8:609–17.80. Nikolaidis LA, Sturzu A, Stolarski C, Elahi D, Shen YT, Shannon RP. The development of myocardial insulin resistance in conscious dogs with advanced dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res. 2004; 61:297–306.
Article81. Margulies KB, Anstrom KJ, Hernandez AF, Redfield MM, Shah MR, Braunwald E, et al. GLP-1 agonist therapy for advanced heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: design and rationale for the functional impact of GLP-1 for heart failure treatment study. Circ Heart Fail. 2014; 7:673–9.82. Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. McFarlane P, Cherney D, Gilbert RE, Senior P. Chronic kidney disease in diabetes. Can J Diabetes. 2018; 42(Suppl 1):S201–9.
Article83. Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Ganeva M, Ene-Iordache B, Remuzzi G. BENEDICT Study Group. Impact of blood pressure control and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy on new-onset microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes: a post hoc analysis of the BENEDICT trial. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17:3472–81.84. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Woodward M, et al. Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007; 370:829–40.
Article85. Parving HH, Lehnert H, Brochner-Mortensen J, Gomis R, Andersen S, Arner P, et al. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:870–8.
Article86. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:851–60.
Article87. Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, Dyal L, Schumacher H, Pogue J, et al. Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet. 2008; 372:547–53.
Article88. Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M, Conner TA, Duckworth W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:1892–903.
Article89. Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JJ, de Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon SD, et al. Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:2204–13.
Article90. Viengchareun S, Le Menuet D, Martinerie L, Munier M, Pascual-Le Tallec L, Lombes M. The mineralocorticoid receptor: insights into its molecular and (patho)physiological biology. Nucl Recept Signal. 2007; 5:e012.
Article91. Belden Z, Deiuliis JA, Dobre M, Rajagopalan S. The role of the mineralocorticoid receptor in inflammation: focus on kidney and vasculature. Am J Nephrol. 2017; 46:298–314.
Article92. Jaisser F, Farman N. Emerging roles of the mineralocorticoid receptor in pathology: toward new paradigms in clinical pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 2016; 68:49–75.
Article93. Nagase M, Fujita T. Role of Rac1-mineralocorticoid-receptor signalling in renal and cardiac disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013; 9:86–98.
Article94. Hollenberg NK. Aldosterone in the development and progression of renal injury. Kidney Int. 2004; 66:1–9.
Article95. Fullerton MJ, Funder JW. Aldosterone and cardiac fibrosis: in vitro studies. Cardiovasc Res. 1994; 28:1863–7.
Article96. Kawarazaki W, Fujita T. The role of aldosterone in obesity-related hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2016; 29:415–23.
Article97. Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013; 496:445–55.
Article98. Chung EY, Ruospo M, Natale P, Bolignano D, Navaneethan SD, Palmer SC, et al. Aldosterone antagonists in addition to renin angiotensin system antagonists for preventing the progression of chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020; 10:CD007004.
Article99. Cherney DZI, Bakris GL. Novel therapies for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2018; 8:18–25.
Article100. Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Pitt B, Ruilope LM, Rossing P, et al. Effect of finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:2219–29.
Article101. Pitt B, Kober L, Ponikowski P, Gheorghiade M, Filippatos G, Krum H, et al. Safety and tolerability of the novel non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist BAY 94-8862 in patients with chronic heart failure and mild or moderate chronic kidney disease: a randomized, double-blind trial. Eur Heart J. 2013; 34:2453–63.
Article102. Frias JP, Guja C, Hardy E, Ahmed A, Dong F, Ohman P, et al. Exenatide once weekly plus dapagliflozin once daily versus exenatide or dapagliflozin alone in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy (DURATION-8): a 28 week, multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016; 4:1004–16.
Article103. Ludvik B, Frias JP, Tinahones FJ, Wainstein J, Jiang H, Robertson KE, et al. Dulaglutide as add-on therapy to SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes (AWARD-10): a 24-week, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018; 6:370–81.
Article104. Zinman B, Bhosekar V, Busch R, Holst I, Ludvik B, Thielke D, et al. Semaglutide once weekly as add-on to SGLT-2 inhibitor therapy in type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 9): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:356–67.
Article105. Clegg LE, Penland RC, Bachina S, Boulton DW, Thuresson M, Heerspink HJL, et al. Effects of exenatide and open-label SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, given in parallel or sequentially, on mortality and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: insights from the EXSCEL trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019; 18:138.
Article106. Kristensen SL, Docherty KF, Jhund PS, Bengtsson O, Demets DL, Inzucchi SE, et al. Dapagliflozin reduces the risk of hyperkalaemia in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: a secondary analysis DAPA-HF. Eur Heart J. 2020; 41(Suppl 2):ehaa946.093.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- SGLT2 Inhibition for Diabetic and Non-diabetic Kidney Disease
- Cardiorenal Syndrome
- Diagnosis and test for diabetic kidney disease
- 2021 Korean Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Characteristics and Survival of Dialysis Patients due to Type 2 Cardiorenal Syndrome