Clin Endosc.
2021 Mar;54(2):256-260. 10.5946/ce.2020.081.
Utility of the Gel Immersion Method for Treating Massive Colonic Diverticular Bleeding
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, St. Luke’s International Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
- KMID: 2514181
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.081
Abstract
- Background/Aims
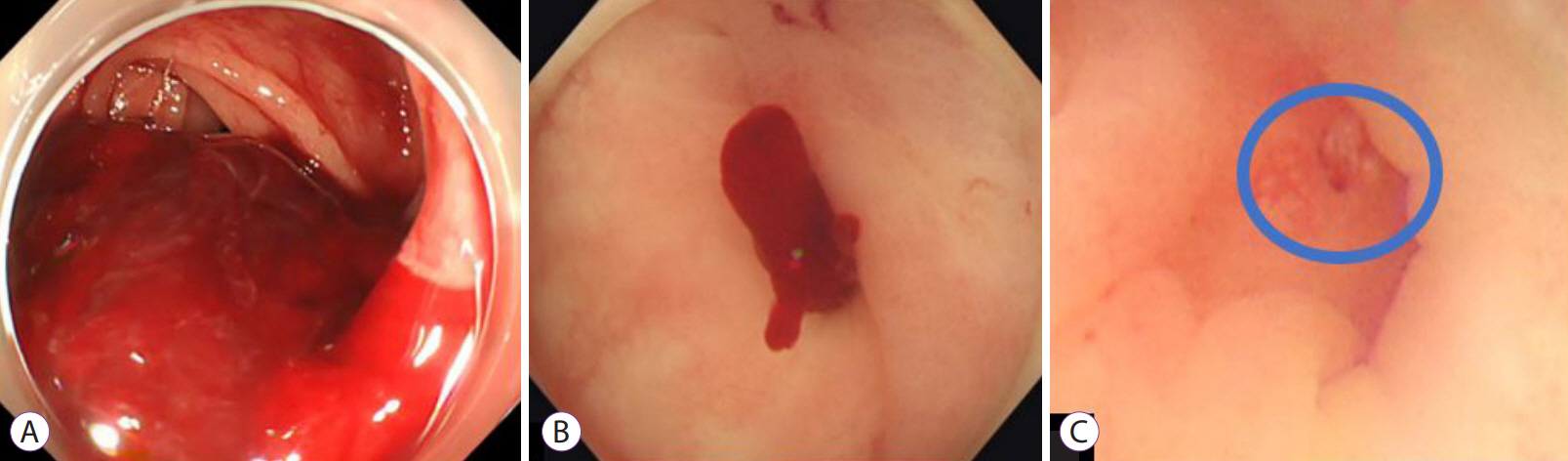
In Asia, right-sided diverticular bleeding is more common than that of the left side. It often causes massive bleeding and difficulties in identifying the stigmata of recent hemorrhage (SRH) of colonic diverticular bleeding (CDB). This case series demonstrates the efficacy of the gel immersion method using OS-1 Jelly (Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Factory, Tokushima, Japan) in patients with CDB.
Methods
This retrospective case series analyzed data of patients with CDB who underwent the gel immersion method from April 2016 to February 2020 at St. Luke’s International Hospital, Japan. All patients diagnosed with CDB who underwent the gel immersion method were included. We collected data on the site of bleeding, identification of SRH, and efficacy of the method from the electronic medical records.
Results
A total of 9 patients (including 7 with right-sided CDB) underwent gel immersion method and were included in this study. SRH were successfully found in 66.7% (6/9) of patients. Moreover, effective hemostasis was achieved in 85.7% (6/7) of patients with right-sided CDB. There were no adverse events.
Conclusions
The gel immersion method was found to be effective, especially for massive right-sided CDB.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Strate LL, Gralnek IM. ACG clinical guideline: management of patients with acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016; 111:459–474.
Article2. Ghassemi KA, Jensen DM. Lower GI bleeding: epidemiology and management. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2013; 15:333.
Article3. Gralnek IM, Neeman Z, Strate LL. Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:1054–1063.
Article4. Painter NS, Burkitt DP. Diverticular disease of the colon, a 20th century problem. Clin Gastroenterol. 1975; 4:3–21.
Article5. Warner E, Crighton EJ, Moineddin R, Mamdani M, Upshur R. Fourteen-year study of hospital admissions for diverticular disease in Ontario. Can J Gastroenterol. 2007; 21:97–99.
Article6. Nagata N, Niikura R, Aoki T, et al. Increase in colonic diverticulosis and diverticular hemorrhage in an aging society: lessons from a 9-year colonoscopic study of 28,192 patients in Japan. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2014; 29:379–385.
Article7. Imaeda H, Hibi T. The burden of diverticular disease and its complications: West versus East. Inflamm Intest Dis. 2018; 3:61–68.
Article8. Sugihara K, Muto T, Morioka Y, Asano A, Yamamoto T. Diverticular disease of the colon in Japan. A review of 615 cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984; 27:531–537.
Article9. Markham NI, Li AK. Diverticulitis of the right colon--experience from Hong Kong. Gut. 1992; 33:547–549.
Article10. Ngoi SS, Chia J, Goh MY, Sim E, Rauff A. Surgical management of right colon diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992; 35:799–802.
Article11. Niikura R, Nagata N, Aoki T, et al. Predictors for identification of stigmata of recent hemorrhage on colonic diverticula in lower gastrointestinal bleeding. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015; 49:e24–e30.
Article12. Oguri N, Ikeya T, Kobayashi D, et al. Effectiveness of risk scoring systems in predicting endoscopic treatment in colonic diverticular bleeding. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 35:815–820.
Article13. McGuire HH Jr. Bleeding colonic diverticula. A reappraisal of natural history and management. Ann Surg. 1994; 220:653–656.
Article14. Longstreth GF. Epidemiology and outcome of patients hospitalized with acute lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92:419–424.15. Jensen DM, Ohning GV, Kovacs TO, et al. Natural history of definitive diverticular hemorrhage based on stigmata of recent hemorrhage and colonoscopic Doppler blood flow monitoring for risk stratification and definitive hemostasis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:416–423.
Article16. Nakatsu S, Yasuda H, Maehata T, et al. Urgent computed tomography for determining the optimal timing of colonoscopy in patients with acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Intern Med. 2015; 54:553–558.
Article17. Mohammed Ilyas MI, Szilagy EJ. Management of diverticular bleeding: evaluation, stabilization, intervention, and recurrence of bleeding and indications for resection after control of bleeding. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2018; 31:243–250.
Article18. Jensen DM, Machicado GA, Jutabha R, Kovacs TO. Urgent colonoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of severe diverticular hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:78–82.
Article19. Gilshtein H, Kluger Y, Khoury A, Issa N, Khoury W. Massive and recurrent diverticular hemorrhage, risk factors and treatment. Int J Surg. 2016; 33 Pt A:136–139.
Article20. Faucheron JL, Roblin X, Bichard P, Heluwaert F. The prevalence of right-sided colonic diverticulosis and diverticular haemorrhage. Colorectal Dis. 2013; 15:e266–e270.
Article21. Ishii N, Itoh T, Uemura M, et al. Endoscopic band ligation with a water-jet scope for the treatment of colonic diverticular hemorrhage. Dig Endosc. 2010; 22:232–235.
Article22. Yano T, Nemoto D, Ono K, et al. Gel immersion endoscopy: a novel method to secure the visual field during endoscopy in bleeding patients (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:809–811.
Article23. East JE, Suzuki N, Stavrinidis M, Guenther T, Thomas HJ, Saunders BP. Narrow band imaging for colonoscopic surveillance in hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer. Gut. 2008; 57:65–70.
Article24. Obana T, Fujita N, Sugita R, et al. Prospective evaluation of contrast-enhanced computed tomography for the detection of colonic diverticular bleeding. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:1985–1990.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The 3 cases of colonic diverticular bleeding treated by colonoscopic hemostatic procedures
- A Case of Colonic Diverticular Bleeding Treated with Endoscopic Hemoclip
- The usefulness of endoscopic hemostasis with hemoclipping in acute colonic diverticular bleeding
- Sigmoid Colon Diverticular Bleeding in a 75-year-old Woman
- Predictive Factors for Colonic Diverticular Rebleeding: A Retrospective Analysis of the Clinical and Colonoscopic Features of 111 Patients