J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2021 Feb;47(1):25-33. 10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.1.25.
Length of hospital stay among oral and maxillofacial patients: a retrospective study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hospital Sultanah Nora Ismail, Batu Pahat, Malaysia
- 2Sector for Biostatistics & Data Repository, National Institutes of Health, Shah Alam, Malaysia
- KMID: 2513426
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.1.25
Abstract
Objectives
Many conditions of the oral and maxillofacial region require hospitalization and in-patient care. The average length of stay (LOS) of these patients varies and is usually affected by multiple confounding variables. However, even with an increasing number of hospital admissions, published evidence on the factors that affect the LOS of oral and maxillofacial patients is lacking. Therefore, this study assessed the LOS of in-patients at the oral and maxillofacial surgery department of a government-funded, multi-specialty hospital in Malaysia, based on their reasons for admission and other factors.
Materials and Methods
Our samples were collected retrospectively over a 5-year period and included patients with maxillofacial infections, posttrauma stabilization, facial bone fracture surgery, benign and malignant lesion surgery, dentoalveolar surgery, and other maxillofacial surgeries as reasons for admission. Factors potentially affecting LOS were also recorded, and their significance was determined using multiple logistic regression analyses. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
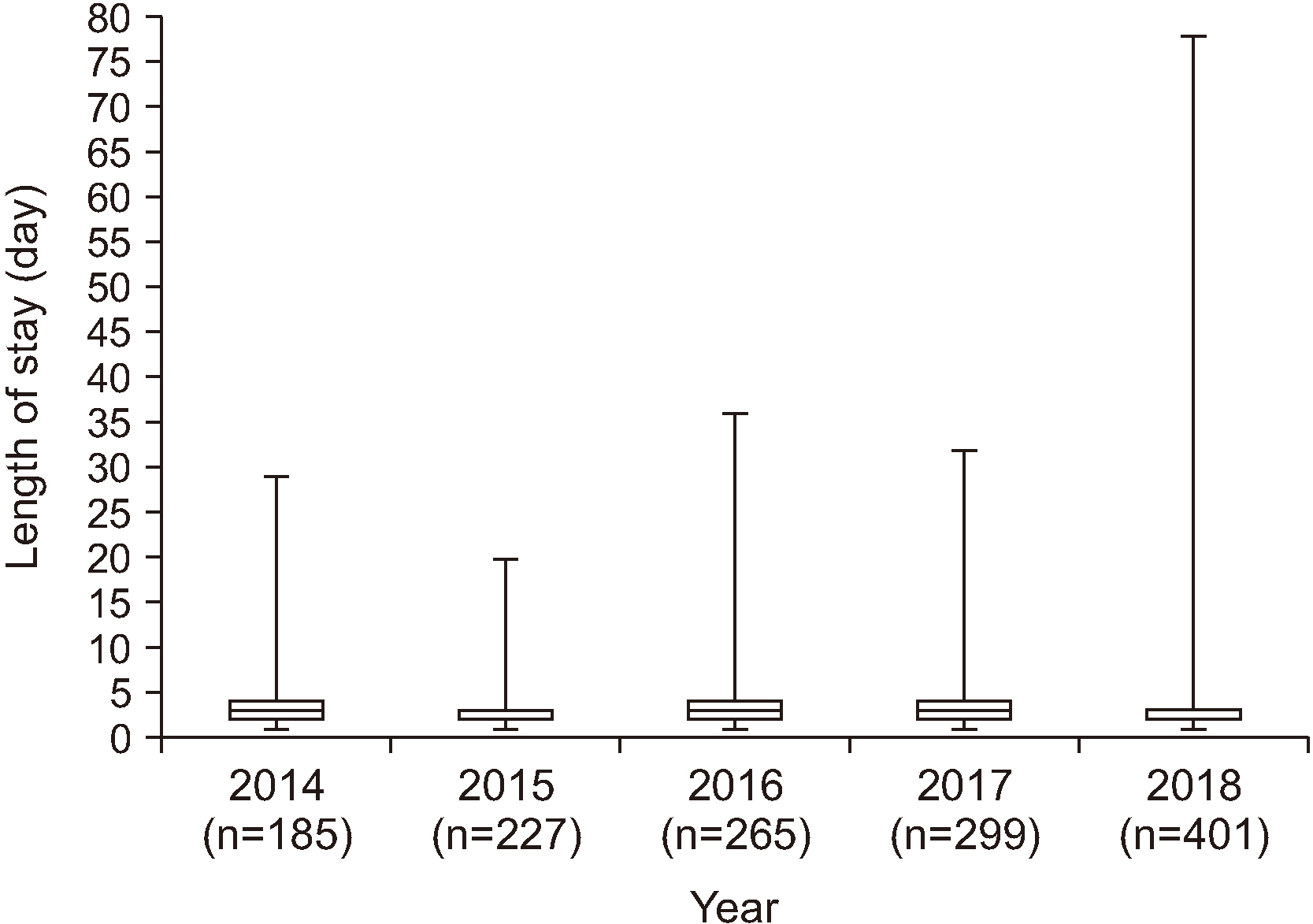
A total of 1,380 patients were included in this study. Most (84.5%) of our in-patients were of Malay ethnicity, and males outnumbered females in our sample by 502 subjects. The median LOS of our in-patients was 3 days. Sex, ethnicity, age, reason for admission, and American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) classification were factors that significantly affected LOS.
Conclusion
The median LOS reported in this study was 3 days. LOS was significantly affected by sex, ethnicity, age, reason of admission and ASA classification.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Islam MA, Haider IA, Uzzaman MH, Tymur FR, Ali MS. 2016; One year audit of in patient Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Dhaka Dental College Hospital. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 15:229–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-015-0822-1 . DOI: 10.1007/s12663-015-0822-1. PMID: 27298547. PMCID: PMC4871829.
Article2. OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development). 2017. Health care activities. Health at a glance 2017: OECD indicators. OECD Publishing;Paris: p. 167–83.3. Kamat RD, Dhupar V, Akkara F, Shetye O. 2015; A comparative analysis of odontogenic maxillofacial infections in diabetic and nondiabetic patients: an institutional study. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 41:176–80. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.4.176 . DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.4.176. PMID: 26339575. PMCID: PMC4558185.
Article4. Al-Hassani A, Ahmad K, El-Menyar A, Abutaka A, Mekkodathil A, Peralta R, et al. 2019; Prevalence and patterns of maxillofacial trauma: a retrospective descriptive study. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-019-01174-6 [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1007/s00068-019-01174-6. PMID: 31227848.
Article5. Ferraro Bezerra M, Avelar RL, de Oliveira RB, Studart-Soares EC, Pretto MS. 2011; Assessment of the oral and maxillofacial surgery service in a teaching hospital in Brazil. J Craniofac Surg. 22:50–3. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181f6c436 . DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181f6c436. PMID: 21187779.
Article6. Seppänen L, Lauhio A, Lindqvist C, Suuronen R, Rautemaa R. 2008; Analysis of systemic and local odontogenic infection complications requiring hospital care. J Infect. 57:116–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2008.06.002 . DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2008.06.002. PMID: 18649947.
Article7. Appelblatt R, Krutoy J, Karlis V. 2014; Associated factors involved in presentation and care of severe odontogenic infections. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 72(9 Suppl):E37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2014.06.064 .
Article8. Yuvaraj V. 2016; Maxillofacial infections of odontogenic origin: epidemiological, microbiological and therapeutic factors in an Indian population. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 68:396–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0823-x . DOI: 10.1007/s12070-015-0823-x. PMID: 27833861. PMCID: PMC5083637.
Article9. Zheng L, Yang C, Zhang W, Cai X, Kim E, Jiang B, et al. 2012; Is there association between severe multispace infections of the oral maxillofacial region and diabetes mellitus? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 70:1565–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2011.07.010 . DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.07.010. PMID: 22014938.
Article10. Jundt JS, Gutta R. 2012; Characteristics and cost impact of severe odontogenic infections. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 114:558–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2011.10.044 . DOI: 10.1016/j.oooo.2011.10.044. PMID: 22819453.
Article11. Wang J, Ahani A, Pogrel MA. 2005; A five-year retrospective study of odontogenic maxillofacial infections in a large urban public hospital. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 34:646–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2005.03.001 . DOI: 10.1016/j.ijom.2005.03.001. PMID: 15955663.
Article12. Low LF, Audimulam H, Lim HW, Selvaraju K, Balasundram S. 2017; Steroids in maxillofacial space infection: a retrospective cohort study. Open J Stomatol. 7:397–407. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2017.79034 .
Article13. Kent S, Hennedige A, McDonald C, Henry A, Dawoud B, Kulkarni R, et al. 2019; Systematic review of the role of corticosteroids in cervicofacial infections. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 57:196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2019.01.010 . DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2019.01.010. PMID: 30770139.
Article14. Klein NC, Go CH, Cunha BA. 2001; Infections associated with steroid use. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 15:423–32. viii. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5520(05)70154-9 . DOI: 10.1016/s0891-5520(05)70154-9. PMID: 11447704.
Article15. Aberdein J, Singer M. 2006; Clinical review: a systematic review of corticosteroid use in infections. Crit Care. 10:203. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc3904 . DOI: 10.1186/cc3904. PMID: 16356204. PMCID: PMC1550829.
Article16. Saperi BS, Ramli R, Ahmed Z, Muhd Nur A, Ibrahim MI, Rashdi MF, et al. 2017; Cost analysis of facial injury treatment in two university hospitals in Malaysia: a prospective study. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 9:107–13. https://doi.org/10.2147/CEOR.S119910 . DOI: 10.2147/CEOR.S119910. PMID: 28223831. PMCID: PMC5304986.
Article17. Khalkhali HR, Samarei R, Alilu SK, Habibzadeh H, Rezaei S. 2018; Modeling factors influence stay duration in unit due to maxillofacial fracture. J Adv Pharm Educ Res. 8:36–40.18. Farias IPSE, Bernardino ÍM, Nóbrega LMD, Grempel RG. D’Avila S. 2017; Maxillofacial trauma, etiology and profile of patients: an exploratory study. Acta Ortop Bras. 25:258–61. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-785220172506152670 . DOI: 10.1590/1413-785220172506152670. PMID: 29375255. PMCID: PMC5782859.
Article19. Boffano P, Roccia F, Zavattero E, Dediol E, Uglešić V, Kovačič Ž, et al. 2015; European Maxillofacial Trauma (EURMAT) project: a multicentre and prospective study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 43:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2014.10.011 . DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms.2014.10.011. PMID: 25457465.
Article20. Martins JC Jr, Keim FS, de Santa Helena ET. 2010; Epidemiological characteristics of trauma patients maxillofacial surgery at the Hospital Geral de Blumenau SC from 2004 to 2009. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 14:192–8. https://doi.org/10.7162/S1809-48722010000200008 .
Article21. Berge TI. 1996; Incidence of large third-molar-associated cystic lesions requiring hospitalization. Acta Odontol Scand. 54:327–31. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016359609003546 . DOI: 10.3109/00016359609003546. PMID: 8923928.
Article22. Schwam ZG, Sosa JA, Roman S, Judson BL. 2015; Complications and mortality following surgery for oral cavity cancer: analysis of 408 cases. Laryngoscope. 125:1869–73. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25328 . DOI: 10.1002/lary.25328. PMID: 26063059.
Article23. Black D, Pearson M. 2002; Average length of stay, delayed discharge, and hospital congestion. BMJ. 325:610–1. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.325.7365.610 . DOI: 10.1136/bmj.325.7365.610. PMID: 12242160. PMCID: PMC1124147.
Article24. Jarab F, Omar E, Bhayat A, Mansuri S, Ahmed S. 2012; Duration of hospital stay following orthognathic surgery at the Jordan University Hospital. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 11:314–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-011-0327-5 . DOI: 10.1007/s12663-011-0327-5. PMID: 23997483. PMCID: PMC3428448.
Article25. Peters ES, Fong B, Wormuth DW, Sonis ST. 1996; Risk factors affecting hospital length of stay in patients with odontogenic maxillofacial infections. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 54:1386–91. discussion 1391–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-2391(96)90249-9 . DOI: 10.1016/s0278-2391(96)90249-9. PMID: 8957116.
Article26. Nordin R, Abdul Rahman N, Rashdi MF, Yusoff A, Abdul Rahman R, Sulong S, et al. 2015; Oral and maxillofacial trauma caused by road traffic accident in two university hospitals in Malaysia: a cross-sectional study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 27:166–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajoms.2014.01.001 .
Article27. Aldrete JA. 1994; Discharge criteria. Baillières Clin Anaesthesiol. 8:763–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-3501(05)80109-6 . DOI: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000784,. PMID: 31425193.
Article28. Uzumcugil F, Ankay Yilbas A, Akca B, Ozkaragoz DB, Adiloğlu S, Tuz HH, et al. 2020; Overnight hospital stay and/or extended recovery period may allow long-duration oral and maxillofacial surgeries in the operating room of a dental hospital in an outpatient setting: a single-center experience. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 46:125–32. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.2.125 . DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.2.125. PMID: 32364352. PMCID: PMC7222620.
Article29. Vytla S, Gebauer D. 2017; Clinical guideline for the management of odontogenic infections in the tertiary setting. Aust Dent J. 62:464–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/adj.12538 . DOI: 10.1111/adj.12538. PMID: 28621799.
Article30. 1982. Fees (Medical) Order 1982 (Amendment 2017) [Internet]. The Official Portal of Parliament of Malaysia;Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: Available from: https://parlimen.gov.my/ipms/eps/2019-07-02/ST.84.2019 -84 -MOH.pdf . cited 2019 Jul 2.31. Galvão-Moreira LV, Cantanhede ALC, de Sousa Neto AC, da Cruz MCFN. 2017; Factors affecting hospital discharge in maxillofacial trauma patients: a retrospective study. Braz J Oral Sci. 16:e17026. https://doi.org/10.20396/bjos.v16i0.8650491 .
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors associated with treatment outcomes of patients hospitalized with severe maxillofacial infections at a tertiary center
- Management of velopharyngeal dysfunction: what is the role of oral and maxillofacial surgeons?
- A case of multiple facial gunshot wounds
- Understanding of oral potentially malignant disorders and epithelial dysplasia among oral and maxillofacial surgeons
- Advanced scope of Korean oral and maxillofacial surgery