J Rheum Dis.
2021 Jan;28(1):4-16. 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.1.4.
Advances in Management of Intestinal Behçet’s Disease: A Perspective From Gastroenterologists
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2510337
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2021.28.1.4
Abstract
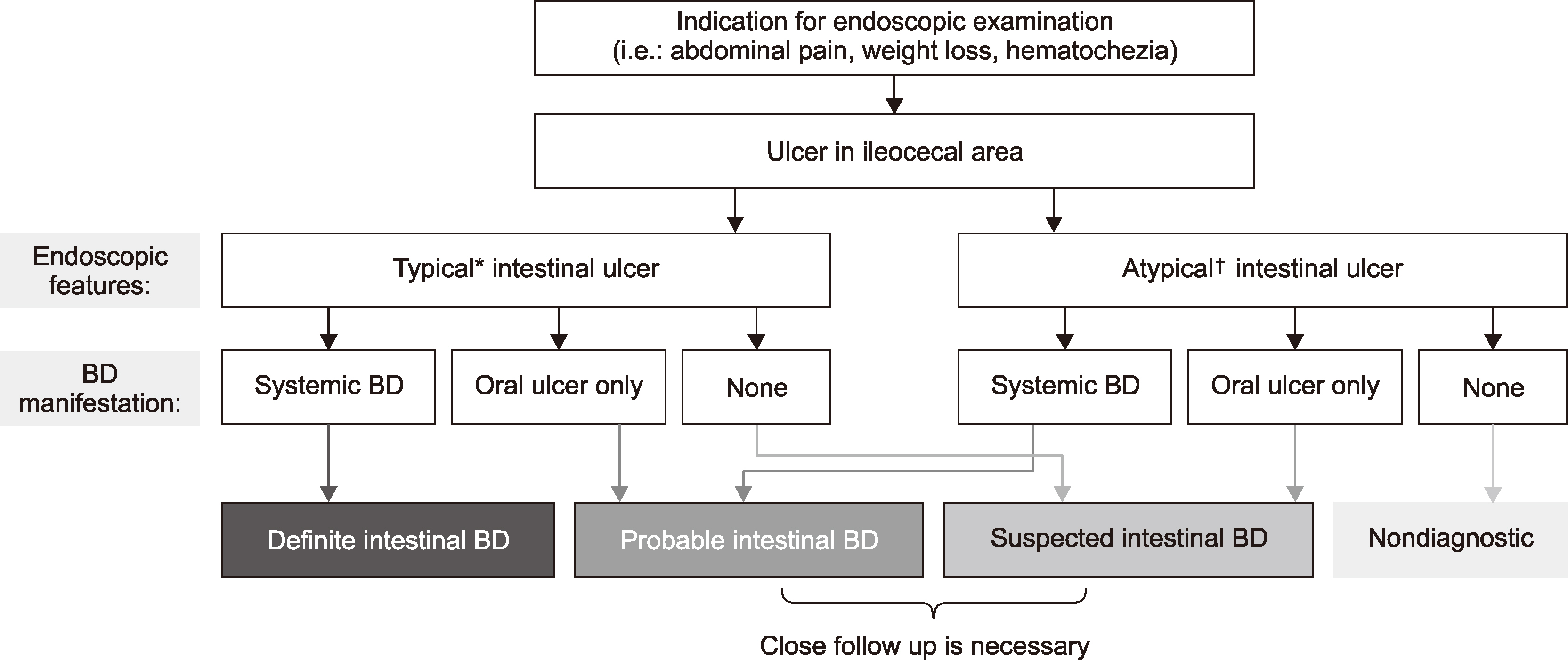
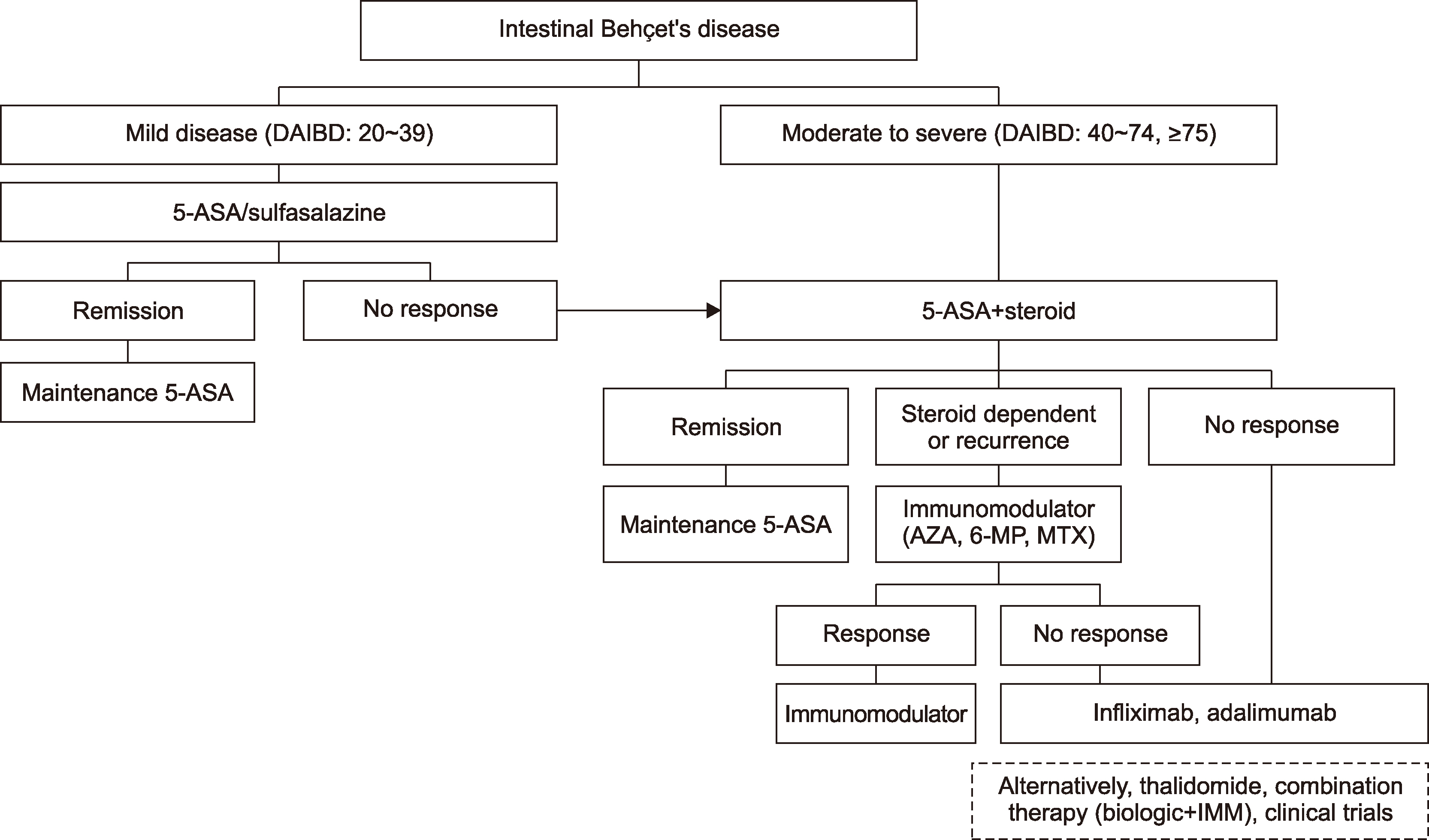
- Intestinal Behçet’s disease (intestinal BD) is a rare chronic inflammatory disorder of the intestine that is characterized by recurrent intestinal manifestations with other systemic features of BD. Intestinal BD is diagnosed when a typically shaped ulcer is observed in the gastrointestinal tract, and the clinical findings meet the diagnostic criteria for BD. Owing to the small number of patients, intestinal BD is easily underestimated. On the other hand, but it often requires surgical treatment because of severe complications, including intestinal perforations or massive bleeding. The same treatment strategies used for inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are used for intestinal BD. 5-Aminosalicylic acids, corticosteroids, and immunomodulators are considered conventional therapies, but a considerable number of patients eventually become unresponsive to these pharmaceutical treatments. Recently, biologic agents, such as anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors, have also been suggested as a new treatment option for intestinal BD. This article reviews the pathogenesis and diagnosis of intestinal BD and the current treatment strategies that are expected to be useful for rheumatologic specialists.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dilsen N. 1996; History and development of Behçet's disease. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 63:512–9. PMID: 8896069.2. Nakata K, Murakami T, Hashi N, Tsutsumi S. 1964; Neuro-Behçet's syndrome. Report of an autopsy case. Bull Osaka Med Sch. 10:105–19. PMID: 5828923.3. Kobayashi K, Ueno F, Bito S, Iwao Y, Fukushima T, Hiwatashi N, et al. 2007; Development of consensus statements for the diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet's disease using a modified Delphi approach. J Gastroeenterol. 42:737–45. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-007-2090-4. PMID: 17876543.
Article4. Cheon JH, Kim WH. 2015; An update on the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of intestinal Behçet's disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 27:24–31. DOI: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000125. PMID: 25405821.
Article5. Han M, Jung YS, Kim WH, Cheon JH, Park S. 2017; Incidence and clinical outcomes of intestinal Behçet's disease in Korea, 2011-2014: a nationwide population-based study. J Gastro-enterol. 52:920–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-016-1300-3. PMID: 28028610.
Article6. Mizushima Y. 1988; Recent research into Behçet's disease in Japan. Int J Tissue React. 10:59–65. PMID: 3053482.7. International Study Group for Behçet's Disease. 1990; Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet's disease. Lancet. 335:1078–80. PMID: 1970380.8. Lee CR, Kim WH, Cho YS, Kim MH, Kim JH, Park IS, et al. 2001; Colonoscopic findings in intestinal Behçet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 7:243–9. DOI: 10.1097/00054725-200108000-00010. PMID: 11515851.
Article9. Jung HC, Rhee PL, Song IS, Choi KW, Kim CY. 1991; Temporal changes in the clinical type or diagnosis of Behçet's colitis in patients with aphthoid or punched-out colonic ulcerations. J Korean Med Sci. 6:313–8. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.1991.6.4.313. PMID: 1844639. PMCID: PMC3049715.10. Cheon JH, Kim ES, Shin SJ, Kim TI, Lee KM, Kim SW, et al. 2009; Development and validation of novel diagnostic criteria for intestinal Behçet's disease in Korean patients with ileocolonic ulcers. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:2492–9. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2009.331. PMID: 19532129.
Article11. Cheon JH, Shin SJ, Kim SW, Lee KM, Kim JS, Kim WH. IBD Study Group of the Korean Association of the Study of Intestinal Diseases. 2009; Diagnosis of intestinal Behçet's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 53:187–93. PMID: 19835220.12. Choi IJ, Kim JS, Cha SD, Jung HC, Park JG, Song IS, et al. 2000; Long-term clinical course and prognostic factors in intestinal Behçet's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 43:692–700. DOI: 10.1007/BF02235590. PMID: 10826433.
Article13. Kim JS, Lim SH, Choi IJ, Moon H, Jung HC, Song IS, et al. 2000; Prediction of the clinical course of Behçet's colitis according to macroscopic classification by colonoscopy. Endoscopy. 32:635–40. DOI: 10.1055/s-2000-9012. PMID: 10935793.
Article14. Shepherd NA. 1991; Pathological mimics of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Pathol. 44:726–33. DOI: 10.1136/jcp.44.9.726. PMID: 1918397. PMCID: PMC496717.
Article15. Ebert EC. 2009; Gastrointestinal manifestations of Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 54:201–7. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-008-0337-4. PMID: 18594975.
Article16. Lawton G, Bhakta BB, Chamberlain MA, Tennant A. 2004; The Behcet's disease activity index. Rheumatology (Oxford). 43:73–8. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg453. PMID: 12890862.
Article17. Cheon JH, Han DS, Park JY, Ye BD, Jung SA, Park YS, et al. Korean IBD Study Group. 2011; Development, validation, and responsiveness of a novel disease activity index for intestinal Behçet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:605–13. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.21313. PMID: 20848515.18. Lee HJ, Kim YN, Jang HW, Jeon HH, Jung ES, Park SJ, et al. 2012; Correlations between endoscopic and clinical disease activity indices in intestinal Behcet's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 18:5771–8. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i40.5771. PMID: 23155319. PMCID: PMC3484347.
Article19. Medzhitov R, Shevach EM, Trinchieri G, Mellor AL, Munn DH, Gordon S, et al. 2011; Highlights of 10 years of immunology in Nature Reviews Immunology. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:693–702. DOI: 10.1038/nri3063. PMID: 21941295. PMCID: PMC3703536.
Article20. Karasneh J, Gül A, Ollier WE, Silman AJ, Worthington J. 2005; Whole-genome screening for susceptibility genes in multicase families with Behçet's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 52:1836–42. DOI: 10.1002/art.21060. PMID: 15934084.
Article21. Remmers EF, Cosan F, Kirino Y, Ombrello MJ, Abaci N, Satorius C, et al. 2010; Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the MHC class I, IL10, and IL23R-IL12RB2 regions associated with Behçet's disease. Nat Genet. 42:698–702. DOI: 10.1038/ng.625. PMID: 20622878. PMCID: PMC2923807.
Article22. Mizuki N, Meguro A, Ota M, Ohno S, Shiota T, Kawagoe T, et al. 2010; Genome-wide association studies identify IL23R- IL12RB2 and IL10 as Behçet's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 42:703–6. DOI: 10.1038/ng.624. PMID: 20622879.23. Direskeneli H. 2001; Behçet's disease: infectious aetiology, new autoantigens, and HLA-B51. Ann Rheum Dis. 60:996–1002. DOI: 10.1136/ard.60.11.996. PMID: 11602462. PMCID: PMC1753405.24. Ohno S, Ohguchi M, Hirose S, Matsuda H, Wakisaka A, Aizawa M. 1982; Close association of HLA-Bw51 with Behçet's disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 100:1455–8. DOI: 10.1001/archopht.1982.01030040433013. PMID: 6956266.25. Franke A, McGovern DP, Barrett JC, Wang K, Radford-Smith GL, Ahmad T, et al. 2010; Genome-wide meta-analysis increases to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 42:1118–25. DOI: 10.1038/ng.717. PMID: 21102463. PMCID: PMC3299551.26. Kim ES, Kim SW, Moon CM, Park JJ, Kim TI, Kim WH, et al. 2012; Interactions between IL17A, IL23R, and STAT4 polymorphisms confer susceptibility to intestinal Behcet's disease in Korean population. Life Sci. 90:740–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.03.017. PMID: 22483685.
Article27. Sayinalp N, Ozcebe OI, Ozdemir O, Haznedaroğlu IC, Dündar S, Kirazli S. 1996; Cytokines in Behçet's disease. J Rheumatol. 23:321–2. PMID: 8882039.28. Suzuki Y, Hoshi K, Matsuda T, Mizushima Y. 1992; Increased peripheral blood gamma delta+ T cells and natural killer cells in Behçet's disease. J Rheumatol. 19:588–92. PMID: 1534375.29. Sugi-Ikai N, Nakazawa M, Nakamura S, Ohno S, Minami M. 1998; Increased frequencies of interleukin-2- and interferon-gamma-producing T cells in patients with active Behçet's disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 39:996–1004. PMID: 9579479.30. Direskeneli H, Eksioglu-Demiralp E, Kibaroglu A, Yavuz S, Ergun T, Akoglu T. 1999; Oligoclonal T cesl expansions in patients with Behçet's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 117:166–70. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00931.x. PMID: 10403931. PMCID: PMC1905484.31. Freysdottir J, Lau S, Fortune F. 1999; Gammadelta T cells in Behçet's disease (BD) and recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS). Clin Exp Immunol. 118:451–7. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.01069.x. PMID: 10594567. PMCID: PMC1905456.32. Na SY, Park MJ, Park S, Lee ES. 2013; Up-regulation of Th17 and related cytokines in Behçet's disease corresponding to disease activity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 31(3 Suppl 77):32–40. PMID: 24064012.33. Abraham C, Cho JH. 2009; Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 361:2066–78. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra0804647. PMID: 19923578. PMCID: PMC3491806.
Article34. Sartor RB. 2006; Mechanisms of disease: pathogenesis of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:390–407. DOI: 10.1038/ncpgasthep0528. PMID: 16819502.
Article35. Lee HW, Chung SH, Moon CM, Che X, Kim SW, Park SJ, et al. 2016; The correlation of serum IL-12B expression with disease activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e3772. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003772. PMID: 27281077. PMCID: PMC4907655.
Article36. Lee HJ, Kim JH, Kim SW, Joo HA, Lee HW, Kim YS, et al. 2017; Proteomic analysis of serum amyloid a as a potential marker in intestinal Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 62:1953–62. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-017-4606-y. PMID: 28523576.
Article37. Hisamatsu T, Ueno F, Matsumoto T, Kobayashi K, Koganei K, Kunisaki R, et al. 2014; The 2nd edition of consensus statements for the diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet's disease: indication of anti-TNFα monoclonal antibodies. J Gastroenterol. 49:156–62. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-013-0872-4. PMID: 23955155. PMCID: PMC3895195.
Article38. Watanabe K, Tanida S, Inoue N, Kunisaki R, Kobayashi K, Nagahori M, et al. 2020; Evidence-based diagnosis and clinical practice guidelines for intestinal Behçet's disease 2020 edited by Intractable Diseases, the Health and Labour Sciences Research Grants. J Gastroenterol. 55:679–700. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-020-01690-y. PMID: 32377946. PMCID: PMC7297851.
Article39. Lee HW, Kim WH, Cheon JH. 2013; The medical treatments of intestinal Behçet's disease: an update. Intest Res. 11:155–60. DOI: 10.5217/ir.2013.11.3.155.
Article40. Baert F, Caprilli R, Angelucci E. 2007; Medical therapy for Crohn's disease: top-down or step-up? Dig Dis. 25:260–6. DOI: 10.1159/000103897. PMID: 17827952.
Article41. Stolfi C, Pellegrini R, Franze E, Pallone F, Monteleone G. 2008; Molecular basis of the potential of mesalazine to prevent colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 14:4434–9. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.4434. PMID: 18680220. PMCID: PMC2731267.
Article42. Stolfi C, Fina D, Caruso R, Caprioli F, Sarra M, Fantini MC, et al. 2008; Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent and -independent inhibition of proliferation of colon cancer cells by 5-aminosalicylic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 75:668–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.09.020. PMID: 17981262.
Article43. Choi CH, Moon W, Kim YS, Kim ES, Lee BI, Jung Y, et al. IBD Study Group of the Korean Association for the Study of the Intestinal Diseases. 2017; Second Korean guideline for the management of ulcerative colitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 69:1–28. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2017.69.1.1. PMID: 28135789.
Article44. Yoo HM, Han KH, Kim PS, Kim WH, Kang JK, Park IS, et al. 1997; Clinical features of intestinal Behoet's disease and therapeutic effects of sulfasalazine. Korean J Gastroenterol. 29:465–72.45. Jung YS, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH, Cheon JH. 2012; Long-term clinical outcomes and factors predictive of relapse after 5-aminosalicylate or sulfasalazine therapy in patients with intestinal Behcet disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 46:e38–45. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182431d56. PMID: 22298088.
Article46. Kinoshita H, Nishioka H, Ikeda A, Ikoma K, Sameshima Y, Ohi H, et al. 2019; Remission induction, maintenance, and endoscopic outcome with oral 5-aminosalicylic acid in intestinal Behçet's disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 34:1929–39. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14690. PMID: 31017728.
Article47. Karadag O, Bolek EC. 2020; Management of Behcet's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 59(Supple 3):iii108–17. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa086. PMID: 32348509.
Article48. Park JJ, Yang SK, Ye BD, Kim JW, Park DI, Yoon H, et al. IBD Study Group of the Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases. 2017; Second Korean guidelines for the management of Crohn's disease. Intest Res. 15:38–67. DOI: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.1.38. PMID: 28239314. PMCID: PMC5323307.
Article49. Choi CH, Moon W, Kim YS, Kim ES, Lee BI, Jung Y, et al. IBD Study Group of the Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases. 2017; Second Korean guidelines for the management of ulcerative colitis. Intest Res. 15:7–37. DOI: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.1.7. PMID: 28239313. PMCID: PMC5323310.
Article50. Park JJ, Kim WH, Cheon JH. 2013; Outcome predictors for intestinal Behçet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 54:1084–90. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1084. PMID: 23918555. PMCID: PMC3743188.
Article51. Narum S, Westergren T, Klemp M. 2014; Corticosteroids and risk of gastrointestinal bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 4:e004587. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004587. PMID: 24833682. PMCID: PMC4025450.
Article52. Park J, Cheon JH, Park YE, Lee YJ, Lee HJ, Park SJ, et al. 2017; Risk factors and outcomes of acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding in intestinal Behçet's disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 32:745–51. DOI: 10.1007/s00384-016-2728-x. PMID: 27924367.
Article53. Elion GB. 1989; The purine path to chemotherapy. Science. 244:41–7. DOI: 10.1126/science.2649979. PMID: 2649979.
Article54. González-Lama Y, Gisbert JP. 2016; Monitoring thiopurine metabolites in inflammatory bowel disease. Frontline Gastro-enterol. 7:301–7. DOI: 10.1136/flgastro-2015-100681. PMID: 28839871. PMCID: PMC5369498.
Article55. Dubinsky MC. 2004; Azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine in inflammatory bowel disease: pharmacology, efficacy, and safety. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:731–43. DOI: 10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00344-1. PMID: 15354273.
Article56. Derijks LJ, Gilissen LP, Engels LG, Bos LP, Bus PJ, Lohman JJ, et al. 2006; Pharmacokinetics of 6-thioguanine in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Ther Drug Monit. 28:45–50. DOI: 10.1097/01.ftd.0000179839.71138.6d. PMID: 16418693.
Article57. Chang JY, Cheon JH. 2019; Thiopurine therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a focus on metabolism and pharmacogenetics. Dig Dis Sci. 64:2395–403. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-019-05720-5. PMID: 31290039.
Article58. Lee HW, Cheon JH, Lee HJ, Park SJ, Hong SP, Kim TI, et al. 2015; Postoperative effects of thiopurines in patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 60:3721–7. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-015-3799-1. PMID: 26199149.
Article59. Jung YS, Cheon JH, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. 2012; Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for thiopurine maintenance therapy in patients with intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 18:750–7. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.21757. PMID: 21618352.
Article60. Connell WR, Kamm MA, Ritchie JK, Lennard-Jones JE. 1993; Bone marrow toxicity caused by azathioprine in inflammatory bowel disease: 27 years of experience. Gut. 34:1081–5. DOI: 10.1136/gut.34.8.1081. PMID: 8174958. PMCID: PMC1374358.
Article61. Feuerstein JD, Nguyen GC, Kupfer SS, Falck-Ytter Y, Singh S. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. 2017; American Gastroentero-logical Association Institute guideline on therapeutic drug monitoring in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 153:827–34. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.032. PMID: 28780013.
Article62. Chang JY, Park SJ, Jung ES, Jung SA, Moon CM, Chun J, et al. 2020; Genotype-based treatment with thiopurine reduces incidence of myelosuppression in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:2010–8.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.034. PMID: 31446180.
Article63. Bannwarth B, Labat L, Moride Y, Schaeverbeke T. 1994; Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. An update. Drugs. 47:25–50. DOI: 10.2165/00003495-199447010-00003. PMID: 7510620.
Article64. Malaviya AN. 2020; Does methotrexate cause interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: what is the evidence? Int J Rheum Dis. 23:713–6. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.13828. PMID: 32573124.
Article65. Borhani-Haghighi A, Kardeh B, Banerjee S, Yadollahikhales G, Safari A, Sahraian MA, et al. 2019; Neuro-Behcet's disease: an update on diagnosis, differential diagnoses, and treatment. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 39:101906. DOI: 10.1016/j.msard.2019.101906. PMID: 31887565.
Article66. Khalil HE, El Gendy HA, Youssef HA, Haroun HE, Gheita TA, Bakir HM. 2016; The effectiveness of intraocular methotrexate in the treatment of posterior uveitis in Behçet's disease patients compared to retrobulbar steroids injection. J Ophthalmol. 2016:1678495. DOI: 10.1155/2016/1678495. PMID: 28070412. PMCID: PMC5187492.
Article67. Feagan BG, McDonald JW, Panaccione R, Enns RA, Bernstein CN, Ponich TP, et al. 2014; Methotrexate in combination with infliximab is no more effective than infliximab alone in patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 146:681–8.e1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.11.024. PMID: 24269926.
Article68. Wessels JA, Huizinga TW, Guchelaar HJ. 2008; Recent insights in the pharmacological actions of methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:249–55. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem279. PMID: 18045808.
Article69. Iwata S, Saito K, Yamaoka K, Tsujimura S, Nawata M, Hanami K, et al. 2011; Efficacy of combination therapy of anti-TNF-α antibody infliximab and methotrexate in refractory entero-Behçet's disease. Mod Rheumatol. 21:184–91. DOI: 10.3109/s10165-010-0370-y. PMID: 21052764.
Article70. Park J, Cheon JH, Park Y, Park SJ, Kim TI, Kim WH. 2018; Efficacy and tolerability of methotrexate therapy for refractory intestinal Behçet's disease: a single center experience. Intest Res. 16:315–8. DOI: 10.5217/ir.2018.16.2.315. PMID: 29743847. PMCID: PMC5934607.
Article71. Matsuda S, Koyasu S. 2000; Mechanisms of action of cyclo-sporine. Immunopharmacology. 47:119–25. DOI: 10.1016/S0162-3109(00)00192-2. PMID: 10878286.
Article72. Hatemi G, Silman A, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Chamberlain AM, Gul A, et al. EULAR Expert Committee. 2008; EULAR recommendations for the management of Behçet disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 67:1656–62. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.080432. PMID: 18245110.73. Ozdal PC, Ortaç S, Taskintuna I, Firat E. 2002; Long-term therapy with low dose cyclosporin A in ocular Behçet's disease. Doc Ophthalmol. 105:301–12. DOI: 10.1023/A:1021227019915. PMID: 12539855.74. Hatemi G, Christensen R, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Celik AF, Fortune F, et al. 2018; 2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of Behçet's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 77:808–18. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213225. PMID: 29625968.
Article75. Bayraktar Y, Ozaslan E, Van Thiel DH. 2000; Gastrointestinal manifestations of Behcet's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 30:144–54. DOI: 10.1097/00004836-200003000-00006. PMID: 10730919.
Article76. Venkataramanan R, Swaminathan A, Prasad T, Jain A, Zuckerman S, Warty V, et al. 1995; Clinical pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus. Clin Pharmacokinet. 29:404–30. DOI: 10.2165/00003088-199529060-00003. PMID: 8787947.
Article77. Schutte-Nutgen K, Tholking G, Suwelack B, Reuter S. 2018; Tacrolimus - pharmacokinetic considerations for clinicians. Curr Drug Metab. 19:342–50. DOI: 10.2174/1389200219666180101104159. PMID: 29298646.
Article78. Matsumura K, Nakase H, Chiba T. 2010; Efficacy of oral tacrolimus on intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 16:188–9. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.20970. PMID: 19504615.
Article79. Cantarini L, Stromillo ML, Vitale A, Lopalco G, Emmi G, Silvestri E, et al. 2016; Efficacy and safety of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in refractory Behcet's disease with different organ involvement: a case series. Isr Med Assoc J. 18:238–42. PMID: 27228652.80. Alpsoy E, Durusoy C, Yilmaz E, Ozgurel Y, Ermis O, Yazar S, et al. 2002; Interferon alfa-2a in the treatment of Behçet disease: a randomized placebo-controlled and double-blind study. Arch Dermatol. 138:467–71. DOI: 10.1001/archderm.138.4.467. PMID: 11939808.
Article81. Georgiou S, Monastirli A, Pasmatzi E, Gartaganis S, Goerz G, Tsambaos D. 1998; Efficacy and safety of systemic recombinant interferon-alpha in Behçet's disease. J Intern Med. 243:367–72. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.1998.00159.x. PMID: 9651559.82. Beales IL. 1998; Gastrointestinal involvement in Behçet's syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 93:2633. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.02633.x. PMID: 9860455.
Article83. Lenz W. 1988; A short history of thalidomide embryopathy. Teratology. 38:203–15. DOI: 10.1002/tera.1420380303. PMID: 3067415.
Article84. Collins TF. 2006; History and evolution of reproductive and developmental toxicology guidelines. Curr Pharm Des. 12:1449–65. DOI: 10.2174/138161206776389813. PMID: 16611128.
Article85. Paine MF. 2017; Therapeutic disasters that hastened safety testing of new drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 101:430–4. DOI: 10.1002/cpt.613. PMID: 28318023.
Article86. Singhal S, Mehta J, Desikan R, Ayers D, Roberson P, Eddlemon P, et al. 1999; Antitumor activity of thalidomide in refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 341:1565–71. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199911183412102. PMID: 10564685.
Article87. Hamza MH. 1986; Treatment of Behçet's disease with thalidomide. Clin Rheumatol. 5:365–71. DOI: 10.1007/BF02054255. PMID: 3780143.
Article88. Gutiérrez-Rodríguez O. 1984; Thalidomide. A promising new treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 27:1118–21. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780271006. PMID: 6237660.89. Hamuryudan V, Mat C, Saip S, Ozyazgan Y, Siva A, Yurdakul S, et al. 1998; Thalidomide in the treatment of the mucocutaneous lesions of the Behçet syndrome. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 128:443–50. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-128-6-199803150-00004. PMID: 9499327.90. Yasui K, Uchida N, Akazawa Y, Nakamura S, Minami I, Amano Y, et al. 2008; Thalidomide for treatment of intestinal involvement of juvenile-onset Behçet disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 14:396–400. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.20317. PMID: 17973303.
Article91. Sayarlioglu M, Kotan MC, Topcu N, Bayram I, Arslanturk H, Gul A. 2004; Treatment of recurrent perforating intestinal ulcers with thalidomide in Behçet's disease. Ann Pharmacother. 38:808–11. DOI: 10.1345/aph.1D524. PMID: 15010523.
Article92. Lee HJ, Cheon JH, Lee KJ, Jang HW, Jung KS, Jung ES, et al. 2010; Clinical experience of thalidomide in the treatment of Korean patients with intestinal BehcӇet's disease: pilot experience in a single center. Intest Res. 8:63–9. DOI: 10.5217/ir.2010.8.1.63.93. Bariol C, Meagher AP, Vickers CR, Byrnes DJ, Edwards PD, Hing M, et al. 2002; Early studies on the safety and efficacy of thalidomide for symptomatic inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:135–9. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02564.x. PMID: 11966942.
Article94. Moreira AL, Sampaio EP, Zmuidzinas A, Frindt P, Smith KA, Kaplan G. 1993; Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory action on tumor necrosis factor alpha by enhancing mRNA degradation. J Exp Med. 177:1675–80. DOI: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1675. PMID: 8496685. PMCID: PMC2191046.
Article95. Hatemi I, Hatemi G, Pamuk ON, Erzin Y, Celik AF. 2015; TNF-alpha antagonists and thalidomide for the management of gastrointestinal Behçet's syndrome refractory to the conventional treatment modalities: a case series and review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 33(6 Suppl 94):S129–37. PMID: 26486925.96. Frassanito MA, Dammacco R, Cafforio P, Dammacco F. 1999; Th1 polarization of the immune response in Behçet's disease: a putative pathogenetic role of interleukin-12. Arthritis Rheum. 42:1967–74. DOI: 10.1002/1529-0131(199909)42:9<1967::AID-ANR24>3.0.CO;2-Z. PMID: 10513814.
Article97. Gül A. 2001; Behçet's disease: an update on the pathogenesis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 19(5 Suppl 24):S6–12. PMID: 11760403.98. Lee CK, Kim HJ. 2007; Pathogenesis and treatment of intestinal Behçet's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 50:3–8. PMID: 18172353.99. Hassard PV, Binder SW, Nelson V, Vasiliauskas EA. 2001; Anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody therapy for gastrointestinal Behçet's disease: a case report. Gastroenterology. 120:995–9. DOI: 10.1053/gast.2001.22556. PMID: 11231954.
Article100. Lee JH, Kim TN, Choi ST, Jang BI, Shin KC, Lee SB, et al. 2007; Remission of intestinal Behçet's disease treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody (Infliximab). Korean J Intern Med. 22:24–7. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2007.22.1.24. PMID: 17427642. PMCID: PMC2687604.101. Naganuma M, Sakuraba A, Hisamatsu T, Ochiai H, Hasegawa H, Ogata H, et al. 2008; Efficacy of infliximab for induction and maintenance of remission in intestinal Behçet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 14:1259–64. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.20457. PMID: 18393375.
Article102. Lee JH, Cheon JH, Jeon SW, Ye BD, Yang SK, Kim YH, et al. 2013; Efficacy of infliximab in intestinal Behçet's disease: a Korean multicenter retrospective study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 19:1833–8. DOI: 10.1097/MIB.0b013e31828f19c9. PMID: 23702810.103. Hibi T, Hirohata S, Kikuchi H, Tateishi U, Sato N, Ozaki K, et al. 2016; Infliximab therapy for intestinal, neurological, and vascular involvement in Behcet disease: efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics in a multicenter, prospective, open-label, single-arm phase 3 study. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e3863. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003863. PMID: 27310969. PMCID: PMC4998455.104. Ooi CJ, Hilmi I, Banerjee R, Chuah SW, Ng SC, Wei SC, et al. Asia-Pacific Association of Gastroenterology (APAGE) Working Group on Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Asian Organization for Crohn's and Colitis. 2019; Best practices on immunomodulators and biologic agents for ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease in Asia. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 34:1296–315. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14648. PMID: 30848854.
Article105. Tanida S, Inoue N, Kobayashi K, Naganuma M, Hirai F, Iizuka B, et al. 2015; Adalimumab for the treatment of Japanese patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:940–8.e3. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.08.042. PMID: 25245624.
Article106. De Cassan C, De Vroey B, Dussault C, Hachulla E, Buche S, Colombel JF. 2011; Successful treatment with adalimumab in a familial case of gastrointestinal Behcet's disease. J Crohns Colitis. 5:364–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.crohns.2011.03.006. PMID: 21683309.
Article107. Kimura M, Tsuji Y, Iwai M, Inagaki M, Madian A, Yoshino T, et al. 2015; Usefulness of adalimumab for treating a case of intestinal Behçet's disease with trisomy 8 myelodysplastic syndrome. Intest Res. 13:166–9. DOI: 10.5217/ir.2015.13.2.166. PMID: 25932002. PMCID: PMC4414759.
Article108. Inoue N, Kobayashi K, Naganuma M, Hirai F, Ozawa M, Arikan D, et al. 2017; Long-term safety and efficacy of adalimumab for intestinal Behçet's disease in the open label study following a phase 3 clinical trial. Intest Res. 15:395–401. DOI: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.395. PMID: 28670237. PMCID: PMC5478765.
Article109. Vitale A, Emmi G, Lopalco G, Gentileschi S, Silvestri E, Fabiani C, et al. 2017; Adalimumab effectiveness in Behçet's disease: short and long-term data from a multicenter retrospective observational study. Clin Rheumatol. 36:451–5. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-016-3417-4. PMID: 27679471.
Article110. Miyagawa I, Nakano K, Iwata S, Nakayamada S, Saito K, Hanami K, et al. 2019; Comparative study of corticosteroid monotherapy, and TNF inhibitors with or without corticosteroid in patients with refractory entero-Behcet's disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 21:151. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-1933-8. PMID: 31228955. PMCID: PMC6589167.
Article111. Sugimura N, Mizoshita T, Sugiyama T, Togawa S, Miyaki T, Suzuki T, et al. 2019; Real-world efficacy of adalimumab and infliximab for refractory intestinal Behçet's disease. Dig Liver Dis. 51:967–71. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.10.024. PMID: 30872086.
Article