Korean J Orthod.
2020 Nov;50(6):373-382. 10.4041/kjod.2020.50.6.373.
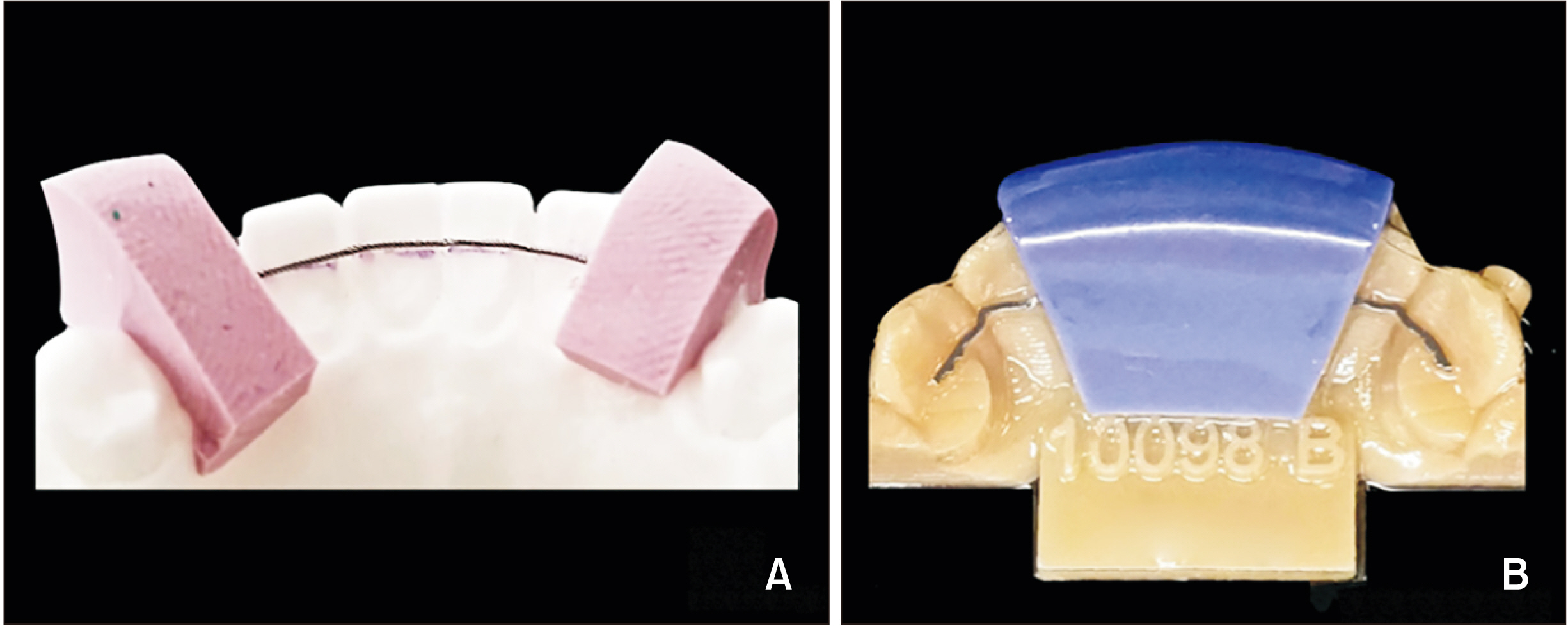
Innovative customized CAD/CAM nickel-titanium lingual retainer versus standard stainless-steel lingual retainer: A randomized controlled trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics, University Hospital of Liège, Liège, Belgium
- 2Department of Biostatistics and Medico-economic Information, University Hospital of Liège, University of Liège, Liège, Belgium
- KMID: 2508444
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2020.50.6.373
Abstract
Objective
To compare computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) customized nitinol retainers with standard stainlesssteel fixed retainers over a 12-month study period.
Methods
This randomized controlled trial (RCT) was conducted on 62 patients randomly allocated to a control group that received stainless-steel retainers or a test group that received customized CAD/CAM nickel-titanium retainers. Four time points were defined: retainer placement (T0) and 1-month (T1), 6-month (T2), and 12-month (T3) follow-up appointments. At each time point, Little’s irregularity index (LII) (primary endpoint) and dental stability measurements such as intercanine width were recorded in addition to assessment of periodontal parameters. Radiological measurements such as the incisor mandibular plane angle (IMPA) were recorded at T0 and T3. Failure events (wire integrity or debonding) were assessed at each time point.
Results
From T0 to T3, LII and other dental measurements showed no significant differences between the two groups. The data for periodontal parameters remained stable over the study period, except for the gingival index, which was slightly, but significantly, higher in the test group at T3 (p = 0.039). The IMPA angle showed no intergroup difference. The two groups showed no significant difference in debonding events.
Conclusions
This RCT conducted over a 12-month period demonstrated no significant difference between customized CAD/CAM nickel-titanium lingual retainers and standard stainlesssteel lingual retainers in terms of dental anterior stability and retainer survival. Both retainers eventually appeared to be equally effective in maintaining periodontal health.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Three-dimensional evaluation of the transfer accuracy of a bracket jig fabricated using computer-aided design and manufacturing to the anterior dentition: An
in vitro study
Jae-Hyun Park, Jin-Young Choi, Seong-Hun Kim, Su-Jung Kim, Kee-Joon Lee, Gerald Nelson
Korean J Orthod. 2021;51(6):375-386. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2021.51.6.375.CAD/CAM 시스템을 이용하여 band 없이 공간유지 장치를 제작한 증례
Eun-Sook Kang
J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci. 2024;40(2):100-106. doi: 10.14368/jdras.2024.40.2.100.
Reference
-
1. Sadowsky C, Sakols EI. 1982; Long-term assessment of orthodontic relapse. Am J Orthod. 82:456–63. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9416(82)90312-8. PMID: 6961816.
Article2. Yu Y, Sun J, Lai W, Wu T, Koshy S, Shi Z. 2013; Interventions for managing relapse of the lower front teeth after orthodontic treatment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (9):CD008734. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008734.pub2. PMID: 24014170.
Article3. Wolf M, Schumacher P, Jäger F, Wego J, Fritz U, Korbmacher-Steiner H, et al. 2015; Novel lingual retainer created using CAD/CAM technology: evaluation of its positioning accuracy. J Orofac Orthop. 76:164–74. DOI: 10.1007/s00056-014-0279-8. PMID: 25744094.4. Kartal Y, Kaya B. 2019; Fixed orthodontic retainers: a review. Turk J Orthod. 32:110–4. DOI: 10.5152/TurkJOrthod.2019.18080. PMID: 31294414. PMCID: PMC6605884.
Article5. Kravitz ND, Shirck JM. 2015. Nov. Bonded lingual retainers [Internet]. Orthodontic Products;Available from: http://www.kravitzorthodontics.com/assets/pdfs/bonded-lingual-retainers.pdf. cited 2020 Jul.6. Kravitz ND, Grauer D, Schumacher P, Jo YM. 2017; Memotain: a CAD/CAM nickel-titanium lingual retainer. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 151:812–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.11.021. PMID: 28364905.
Article7. Renkema AM, Renkema A, Bronkhorst E, Katsaros C. 2011; Long-term effectiveness of canine-to-canine bonded flexible spiral wire lingual retainers. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 139:614–21. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2009.06.041. PMID: 21536204.
Article8. Knaup I, Wagner Y, Wego J, Fritz U, Jäger A, Wolf M. 2019; Potential impact of lingual retainers on oral health: comparison between conventional twistflex retainers and CAD/CAM fabricated nitinol retainers: a clinical in vitro and in vivo investigation. J Orofac Orthop. 80:88–96. DOI: 10.1007/s00056-019-00169-7. PMID: 30778609.9. Aycan M, Goymen M. 2019; Comparison of the different retention appliances produced using CAD/CAM and conventional methods and different surface roughening methods. Lasers Med Sci. 34:287–96. DOI: 10.1007/s10103-018-2585-7. PMID: 30084028.
Article10. Schumacher P. 2015. Jun. 11. CAD/CAM-fabricated lingual retainers made of nitinol. Dental Tribune [Internet]. Available from: https://www.dental-tribune.com/clinical/cadcam-fabricated-lingual-retainers-made-of-nitinol/. cited 2020 Jul 26.11. Andrews LF. 1972; The six keys to normal occlusion. Am J Orthod. 62:296–309. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9416(72)90268-0. PMID: 4505873.
Article12. Little RM. 1975; The irregularity index: a quantitative score of mandibular anterior alignment. Am J Orthod. 68:554–63. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9416(75)90086-X. PMID: 1059332.
Article13. Loe H, Silness J. 1963; Periodontal disease in pregnancy. I. Prevalence and severity. Acta Odontol Scand. 21:533–51. DOI: 10.3109/00016356309011240. PMID: 14121956.14. Silness J, Loe H. 1964; Periodontal disease in pregnancy. II. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condtion. Acta Odontol Scand. 22:121–35. DOI: 10.3109/00016356408993968. PMID: 14158464.15. Sullivan HC, Atkins JH. 1968; Freeutogenous gingival grafts. 1. Principles of successful grafting. Periodontics. 6:5–13. PMID: 4865672.16. Greene JC, Vermillion JR. 1960; The oral hygiene index: a method for classifying oral hygiene status. J Am Dent Assoc. 61:172–9. DOI: 10.14219/jada.archive.1960.0177.
Article17. Steinnes J, Johnsen G, Kerosuo H. 2017; Stability of orthodontic treatment outcome in relation to retention status: an 8-year follow-up. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 151:1027–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.10.032. PMID: 28554448.
Article18. Egli F, Bovali E, Kiliaridis S, Cornelis MA. 2017; Indirect vs direct bonding of mandibular fixed retainers in orthodontic patients: comparison of retainer failures and posttreatment stability. follow-up A 2-year of a single-center randomized controlled trial. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 151:15–27. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.09.009. PMID: 28024770.19. Swidi AJ, Griffin AE, Buschang PH. 2019; Mandibular alignment changes after full-fixed orthodontic treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthod. 41:609–21. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjz004. PMID: 30788505.
Article20. Gunay F, Oz AA. 2018; Clinical effectiveness of 2 orthodontic retainer wires on mandibular arch retention. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 153:232–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2017.06.019. PMID: 29407500.
Article21. Möhlhenrich SC, Jäger F, Jäger A, Schumacher P, Wolf M, Fritz U, et al. 2018; Biomechanical properties of CAD/CAM-individualized nickel-titanium lingual retainers: an in vitro study. J Orofac Orthop. 79:309–19. DOI: 10.1007/s00056-018-0144-2. PMID: 30014179.
Article22. Zinelis S, Pandis N, Al Jabbari YS, Eliades G, Eliades T. 2018; Does long-term intraoral service affect the mechanical properties and elemental composition of multistranded wires of lingual fixed retainers? Eur J Orthod. 40:126–31. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjx045. PMID: 28633359.
Article23. Al-Nimri K, Al Habashneh R, Obeidat M. 2009; Gingival health and relapse tendency: a prospective study of two types of lower fixed retainers. Aust Orthod J. 25:142–6. PMID: 20043549.24. Schneider E, Ruf S. 2011; Upper bonded retainers: survival and failure rates. Angle Orthod. 81:1050–6. DOI: 10.2319/022211-132.1. PMID: 21657830.25. Arn ML, Dritsas K, Pandis N, Kloukos D. 2020; The effects of fixed orthodontic retainers on periodontal health: a systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 157:156–64.e17. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2019.10.010. PMID: 32005466.
Article26. Wouters C, Lamberts TA, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM, Renkema AM. 2019; Development of a clinical practice guideline for orthodontic retention. Orthod Craniofac Res. 22:69–80. DOI: 10.1111/ocr.12302. PMID: 30771260. PMCID: PMC6850190.
Article27. Doldo T, Di Vece L, Ferrari Cagidiaco E, Nuti N, Parrini S, Ferrari M, et al. 2018; A New Generation of Orthodontic retainer using 3d printing technology: clinical cases report. J Osseointegration. 10:142–8.28. Macauley D, Garvey TM, Dowling AH, Fleming GJ. 2012; Using Little's Irregularity Index in orthodontics: outdated and inaccurate? J Dent. 40:1127–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2012.09.010. PMID: 23000526.
Article29. Forde K, Storey M, Littlewood SJ, Scott P, Luther F, Kang J. 2018; Bonded versus vacuum-formed retainers: a randomized controlled trial. Part 1: stability, retainer survival, and patient satisfaction outcomes after 12 months. Eur J Orthod. 40:387–98. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjx058. PMID: 29059289.
Article30. Hu X, Ling J, Wu X. 2019; The CAD/CAM method is more efficient and stable in fabricating of lingual retainer compared with the conventional method. Biomed J Sci Tech Res. 18:13609–12. DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2019.18.003157.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Accuracy of lingual fixed retainers fabricated using a CAD/CAM bending machine
- Orthodontic appliances and MR image artefacts: An exploratory in vitro and in vivo study using 1.5-T and 3-T scanners
- ANALYSIS OF STRESS DEVELOPED WITHIN THE SUPPORTING TISSUE OF ABUTMENT TOOTH WITH INDIRECT RETAINER ACCORDING TO VARIOUS DESIGNS OF DIRECT RETAINER AND DEGREE OF BONE RESORPTION
- Mechanical properties of nickel titanium and steel alloys under stress- strain test
- Canal preparation with nickel-titanium or stainless steel instruments without the risk of instrument fracture: preliminary observations