J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2020 Oct;46(5):348-352. 10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.5.348.
High grade carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- KMID: 2508260
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.5.348
Abstract
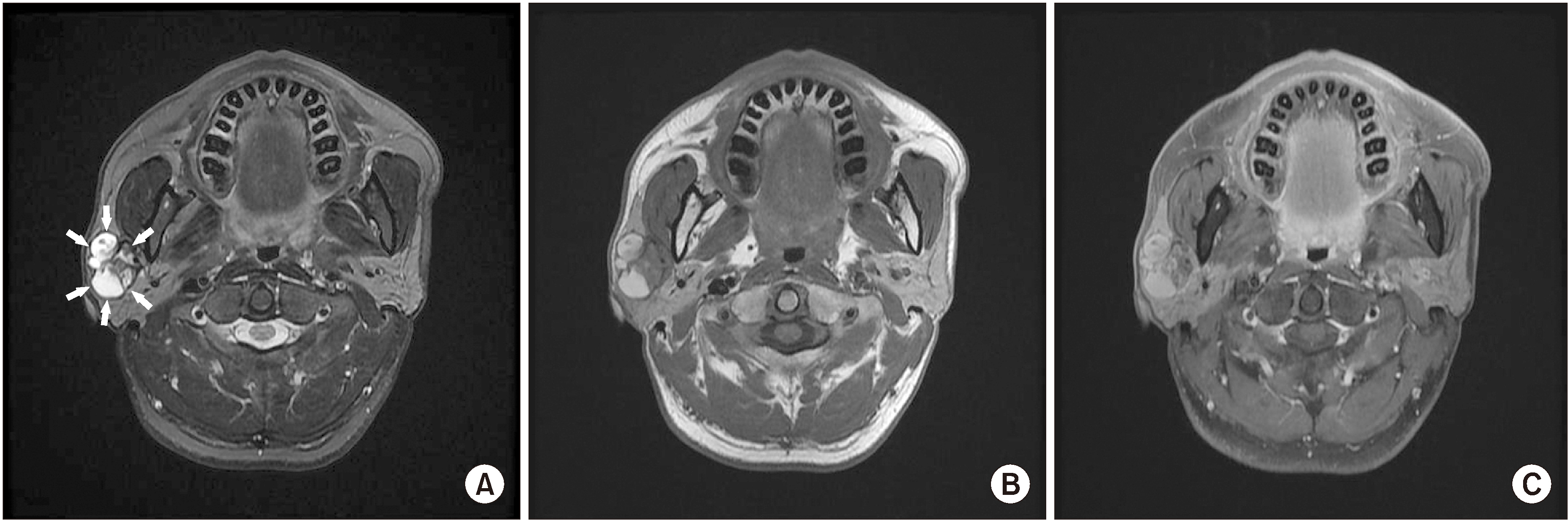
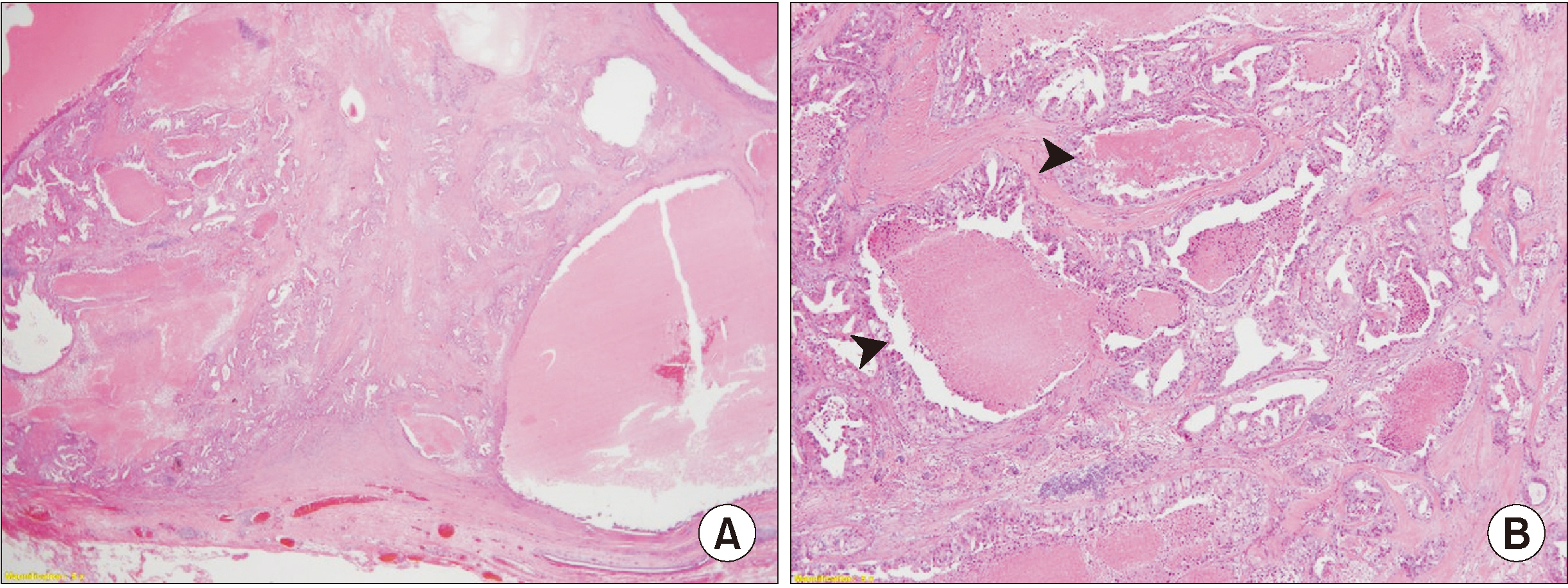
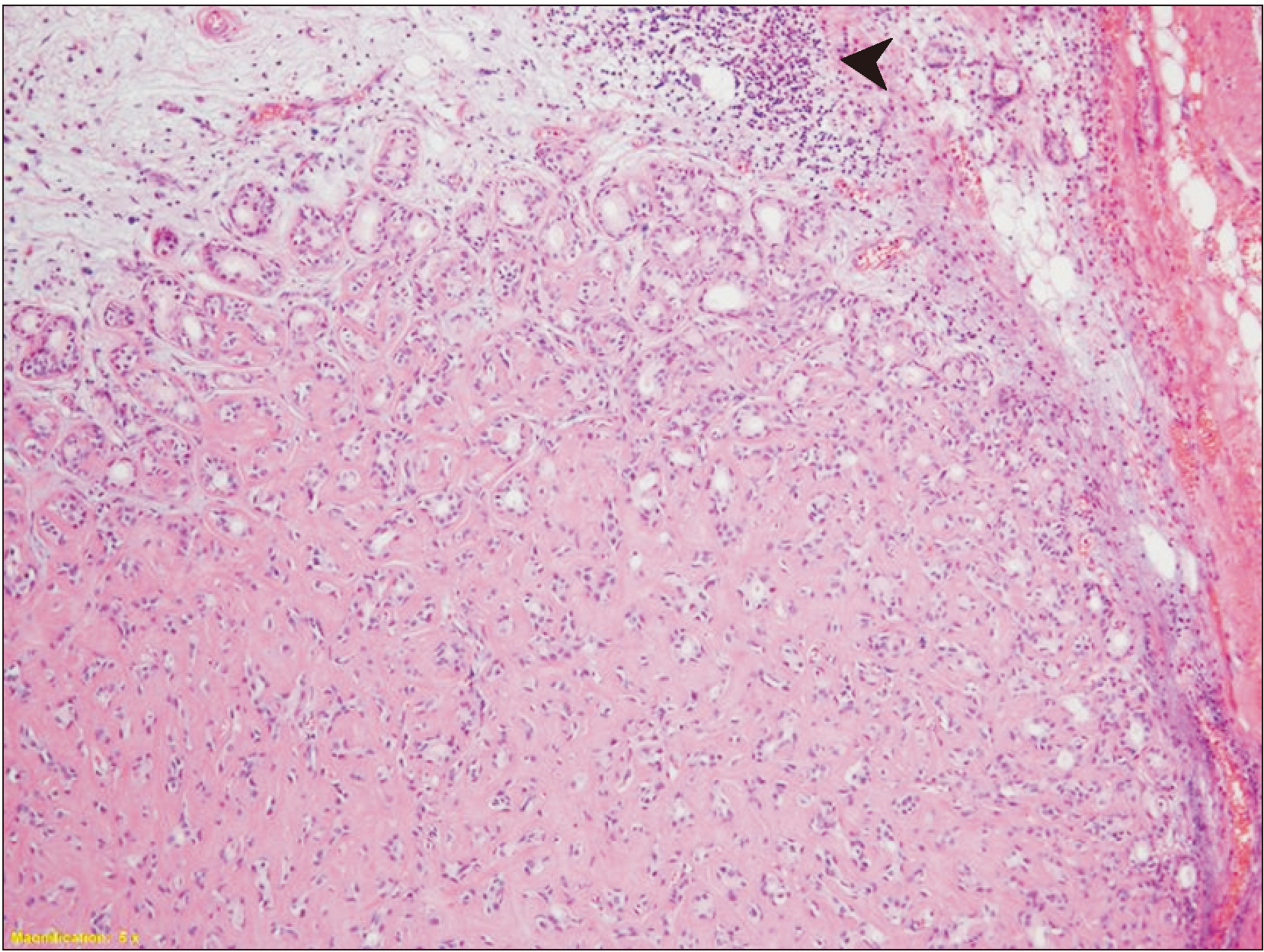
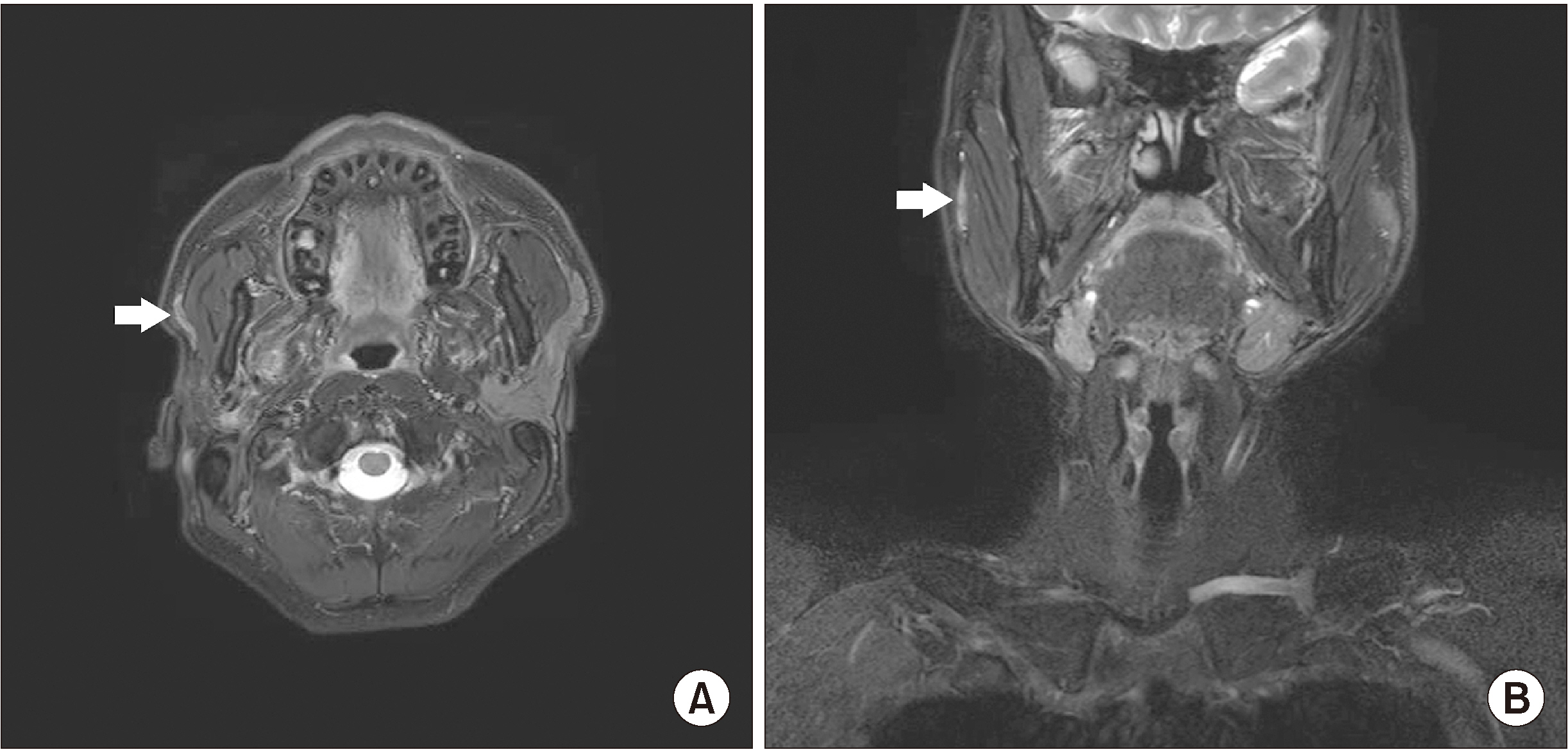
- Pleomorphic adenoma is the most prevalent benign tumor of the parotid gland, and shows potential malignancy. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma (CXPA) can occur in 3%-15% of pleomorphic adenoma cases. Owing to its clinical similarity to benign tumors, critical information related to CXPA can be easily overlooked, leading to frequent misdiagnosis of the condition. In this article, we report a rare case of CXPA found in the 55-year-old male patient with characteristic clinical, radiographic, and histological features, and subsequent treatment.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Gnepp DR, Brandwein-Gensler MS, El-Naggar AK, Nagao T. Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D, editors. 2005. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. IARC Press;Lyon: p. 242–3.2. Spiro RH, Huvos AG, Strong EW. 1977; Malignant mixed tumor of salivary origin: a clinicopathologic study of 146 cases. Cancer. 39:388–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(197702)39:2<388::aid-cncr2820390204>3.0.co;2-d . DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(197702)39:2<388::AID-CNCR2820390204>3.0.CO;2-D. PMID: 189890.
Article3. Antony J, Gopalan V, Smith RA, Lam AK. 2012; Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma: a comprehensive review of clinical, pathological and molecular data. Head Neck Pathol. 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-011-0281-z . DOI: 10.1007/s12105-011-0281-z. PMID: 21744105. PMCID: PMC3311945.
Article4. Beahrs OH, Woolner LB, Kirklin JW, Devine KD. 1957; Carcinomatous transformation of mixed tumors of the parotid gland. AMA Arch Surg. 75:605–13. discussion 613–4. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1957.01280160115015 . DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1957.01280160115015. PMID: 13457639.
Article5. Seifert G. 1992; Histopathology of malignant salivary gland tumours. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol. 28B:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0964-1955(92)90013-q . DOI: 10.1016/0964-1955(92)90013-Q. PMID: 1330147.
Article6. Olsen KD, Lewis JE. 2001; Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma: a clinicopathologic review. Head Neck. 23:705–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.1100 . DOI: 10.1002/hed.1100. PMID: 11505478.
Article7. Kato H, Kanematsu M, Mizuta K, Ito Y, Hirose Y. 2008; Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: radiologic-pathologic correlation with MR imaging including diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 29:865–7. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0974 . DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A0974. PMID: 18272554.
Article8. Tortoledo ME, Luna MA, Batsakis JG. 1984; Carcinomas ex pleomorphic adenoma and malignant mixed tumors. Histomorphologic indexes. Arch Otolaryngol. 110:172–6. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1984.00800290036008 . DOI: 10.1001/archotol.1984.00800290036008. PMID: 6322732.
Article9. Lewis JE, Olsen KD, Sebo TJ. 2001; Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma: pathologic analysis of 73 cases. Hum Pathol. 32:596–604. https://doi.org/10.1053/hupa.2001.25000 . DOI: 10.1053/hupa.2001.25000. PMID: 11431714.
Article10. Altemani A, Martins MT, Freitas L, Soares F, Araújo NS, Araújo VC. 2005; Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma (CXPA): immunoprofile of the cells involved in carcinomatous progression. Histopathology. 46:635–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02157.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02157.x. PMID: 15910594.
Article11. Nouraei SA, Hope KL, Kelly CG, McLean NR, Soames JV. 2005; Carcinoma ex benign pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Plast Reconstr Surg. 116:1206–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000181654.68120.0f . DOI: 10.1097/01.prs.0000181654.68120.0f. PMID: 16217459.
Article12. Chen AM, Garcia J, Bucci MK, Quivey JM, Eisele DW. 2007; The role of postoperative radiation therapy in carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 67:138–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.07.1380 . DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.07.1380. PMID: 17049183.
Article13. Thompson L. 2006; World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. Ear Nose Throat J. 85:74. DOI: 10.1177/014556130608500201. PMID: 16579185.
Article14. Gnepp DR. 1993; Malignant mixed tumors of the salivary glands: a review. Pathol Annu. 28 Pt 1:279–328. PMID: 8380049.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High-Grade Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Ex Metastasizing Pleomorphic Adenomas in the Parotid Gland and Parapharyngeal Space: a Case Report and Literature Review
- A Case of Salivary Duct Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma of Parotid Gland
- Lumpectomy as a Surgical Treatment of Primary Benign Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland
- Case Report: Intracapsular Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma of Parotid Gland
- Ectopic pleomorphic adenoma on subcutaneous plane of the cheek