Cancer Res Treat.
2020 Oct;52(4):1059-1066. 10.4143/crt.2019.633.
Real-World Data of Pyrotinib-Based Therapy in Metastatic HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: Promising Efficacy in Lapatinib-Treated Patients and in Brain Metastasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Oncology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- KMID: 2507933
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2019.633
Abstract
- Purpose
Pyrotinib is a newly-developed irreversible pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. This study reported the first real-world data of pyrotinib-based therapy in metastatic human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer (BC), focusing on efficacy in lapatinib-treated patients and in brain metastasis.
Materials and Methods
One hundred thirteen patients with metastatic HER2-positive BC treated with pyrotinib-based therapy in Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center under non-clinical trial settings from September 1, 2018 to March 1, 2019 were included.
Results
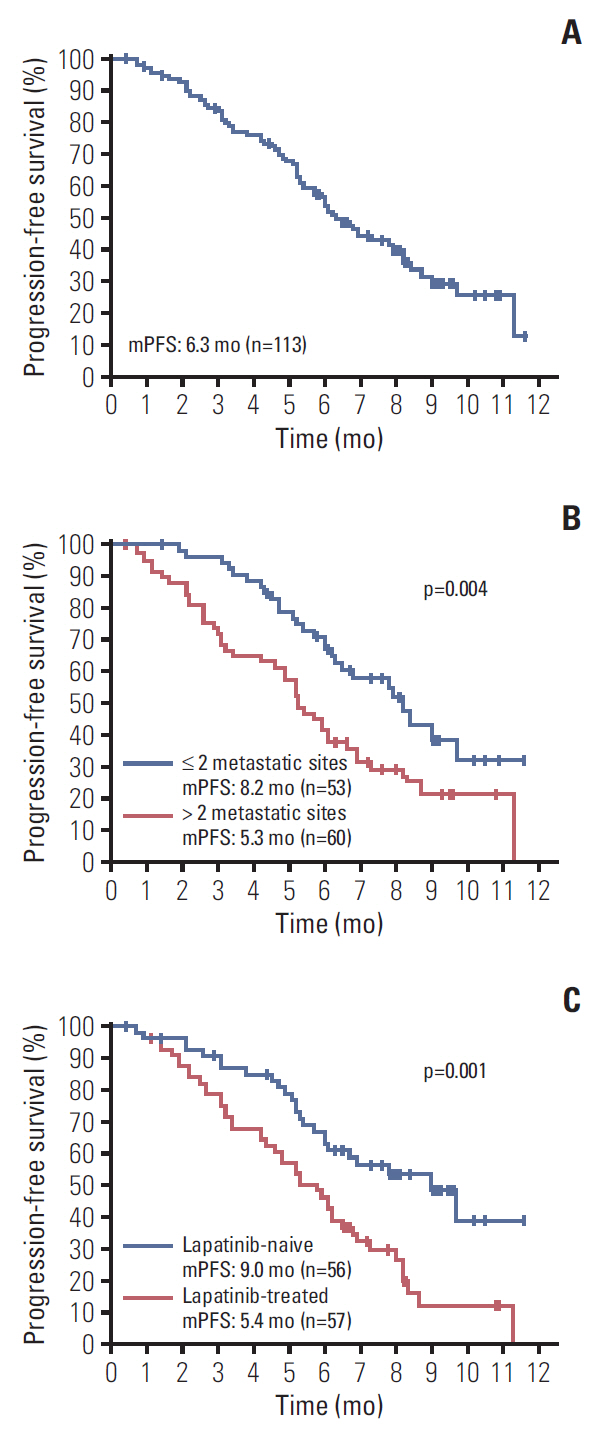
Over half patients have received more than two lines of systematic therapy and exposed to two or more kinds of anti-HER2 agents. Most patients received a combined therapy, commonly of pyrotinib plus capecitabine, or vinorelbine or trastuzumab. Median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.3 months (range, 5.54 to 7.06 months) and objective response rate (ORR) was 29.5%, with two patients (1.9%) achieving complete response. Lapatinib-naïve patients had significantly longer PFS than lapatinib-treated patients (9.0 months vs. 5.4 months, p=0.001). ORR for lapatinib-treated patients was 23.2%. Thirty-one of 113 patients have brain metastasis. Median PFS was 6.7 months and intracranial ORR was 28%. For patients without concurrent radiotherapy and/or brain surgery, the ORR was very low (6.3%). But for patients receiving concurrent radiotherapy and/or brain surgery, the ORR was 66.7%, and three patients achieved complete response. Most common adverse event was diarrhea.
Conclusion
Pyrotinib-based therapy demonstrated promising effects in metastatic HER2-positive BC and showed activity in lapatinib-treated patients. For patients with brain metastasis, pyrotinib-based regimen without radiotherapy showed limited efficacy, but when combined with radiotherapy it showed promising intracranial control.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Waks AG, Winer EP. Breast cancer treatment: a review. JAMA. 2019; 321:288–300.2. Jiang Z, Yan M, Hu X, Zhang Q, Ouyang Q, Feng J, et al. Pyrotinib combined with capecitabine in women with HER2+ metastatic breast cancer previously treated with trastuzumab and taxanes: a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37(15 Suppl):1001.
Article3. Li X, Yang C, Wan H, Zhang G, Feng J, Zhang L, et al. Discovery and development of pyrotinib: a novel irreversible EGFR/HER2 dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor with favorable safety profiles for the treatment of breast cancer. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017; 110:51–61.
Article4. Ma F, Li Q, Chen S, Zhu W, Fan Y, Wang J, et al. Phase I study and biomarker analysis of pyrotinib, a novel irreversible pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:3105–12.
Article5. Ma F, Ouyang Q, Li W, Jiang Z, Tong Z, Liu Y, et al. Pyrotinib or lapatinib combined with capecitabine in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer with prior taxanes, anthracyclines, and/or trastuzumab: a randomized, phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:2610–9.
Article6. Saura C, Oliveira M, Feng YH, Dai MS, Hurvitz SA, Kim SB, et al. Neratinib + capecitabine versus lapatinib + capecitabine in patients with HER2+ metastatic breast cancer previously treated with ≥ 2 HER2-directed regimens: findings from the multinational, randomized, phase III NALA trial. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37(15 Suppl):1002.
Article7. Awada A, Colomer R, Inoue K, Bondarenko I, Badwe RA, Demetriou G, et al. Neratinib plus paclitaxel vs trastuzumab plus paclitaxel in previously untreated metastatic ERBB2-positive breast cancer: the NEfERT-T randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2016; 2:1557–64.8. Gourd E. Pyrotinib versus lapatinib in HER2-positive breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:e562.
Article9. Freedman RA, Gelman RS, Anders CK, Melisko ME, Parsons HA, Cropp AM, et al. TBCRC 022: a phase II trial of neratinib and capecitabine for patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer and brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:1081–9.10. Martin AM, Cagney DN, Catalano PJ, Warren LE, Bellon JR, Punglia RS, et al. Brain metastases in newly diagnosed breast cancer: a population-based study. JAMA Oncol. 2017; 3:1069–77.11. Costa R, Carneiro BA, Wainwright DA, Santa-Maria CA, Kumthekar P, Chae YK, et al. Developmental therapeutics for patients with breast cancer and central nervous system metastasis: current landscape and future perspectives. Ann Oncol. 2017; 28:44–56.
Article12. Brufsky AM, Mayer M, Rugo HS, Kaufman PA, Tan-Chiu E, Tripathy D, et al. Central nervous system metastases in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: incidence, treatment, and survival in patients from registHER. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:4834–43.
Article13. Krop IE, Lin NU, Blackwell K, Guardino E, Huober J, Lu M, et al. Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) versus lapatinib plus capecitabine in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer and central nervous system metastases: a retrospective, exploratory analysis in EMILIA. Ann Oncol. 2015; 26:113–9.
Article14. Swain SM, Baselga J, Miles D, Im YH, Quah C, Lee LF, et al. Incidence of central nervous system metastases in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer treated with pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel: results from the randomized phase III study CLEOPATRA. Ann Oncol. 2014; 25:1116–21.
Article15. Petrelli F, Ghidini M, Lonati V, Tomasello G, Borgonovo K, Ghilardi M, et al. The efficacy of lapatinib and capecitabine in HER-2 positive breast cancer with brain metastases: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2017; 84:141–8.
Article16. Kim JM, Miller JA, Kotecha R, Chao ST, Ahluwalia MS, Peereboom DM, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent HER2-directed therapy is associated with improved objective response for breast cancer brain metastasis. Neuro Oncol. 2019; 21:659–68.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effective Treatment of Solitary Pituitary Metastasis with Panhypopituitarism in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer by Lapatinib
- Combination Therapy of Pyrotinib and Metronomic Vinorelbine in HER2+ Advanced Breast Cancer after Trastuzumab Failure (PROVE): A Prospective Phase 2 Study
- Brain metastasis in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: from biology to treatment
- Diagnosis and Treatment of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
- Personalized therapy for advanced breast cancer using molecular signatures