Ann Lab Med.
2020 Nov;40(6):500-503. 10.3343/alm.2020.40.6.500.
Late Diagnosis of Wilson Disease, Initially Presenting as Cerebellar Atrophy Mimicking Spinocerebellar Ataxia, by Multigene Panel Testing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Laboratory Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Departments of Neurology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2507798
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2020.40.6.500
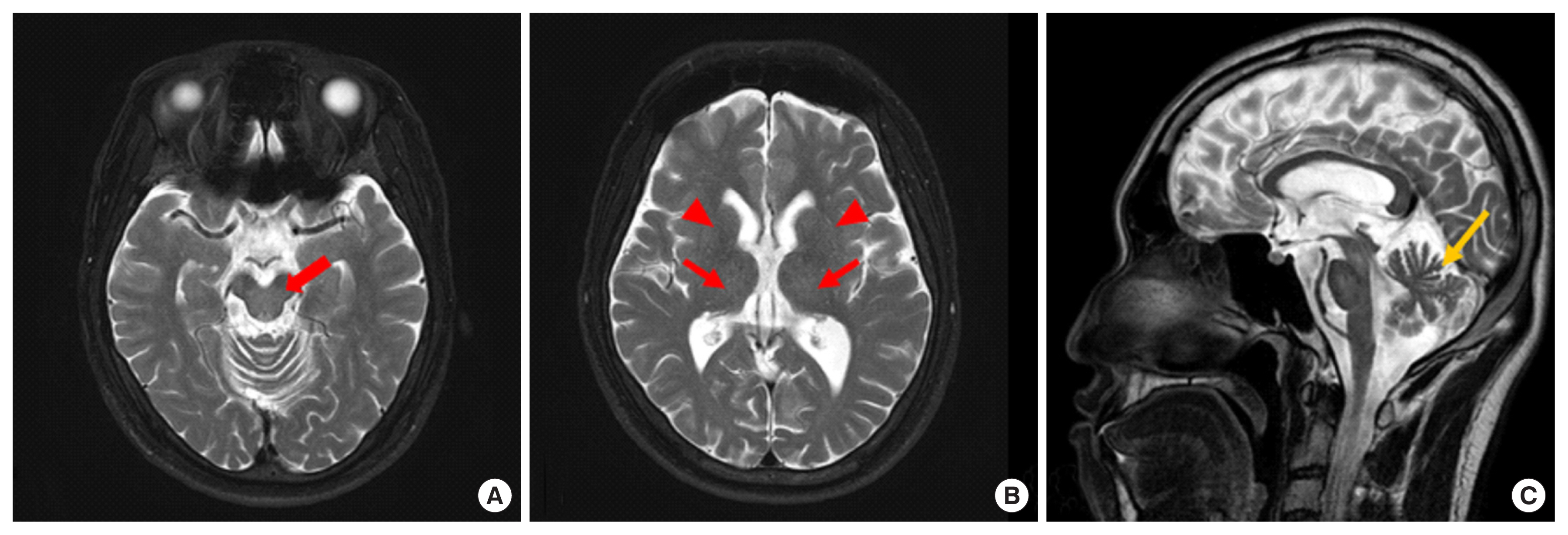
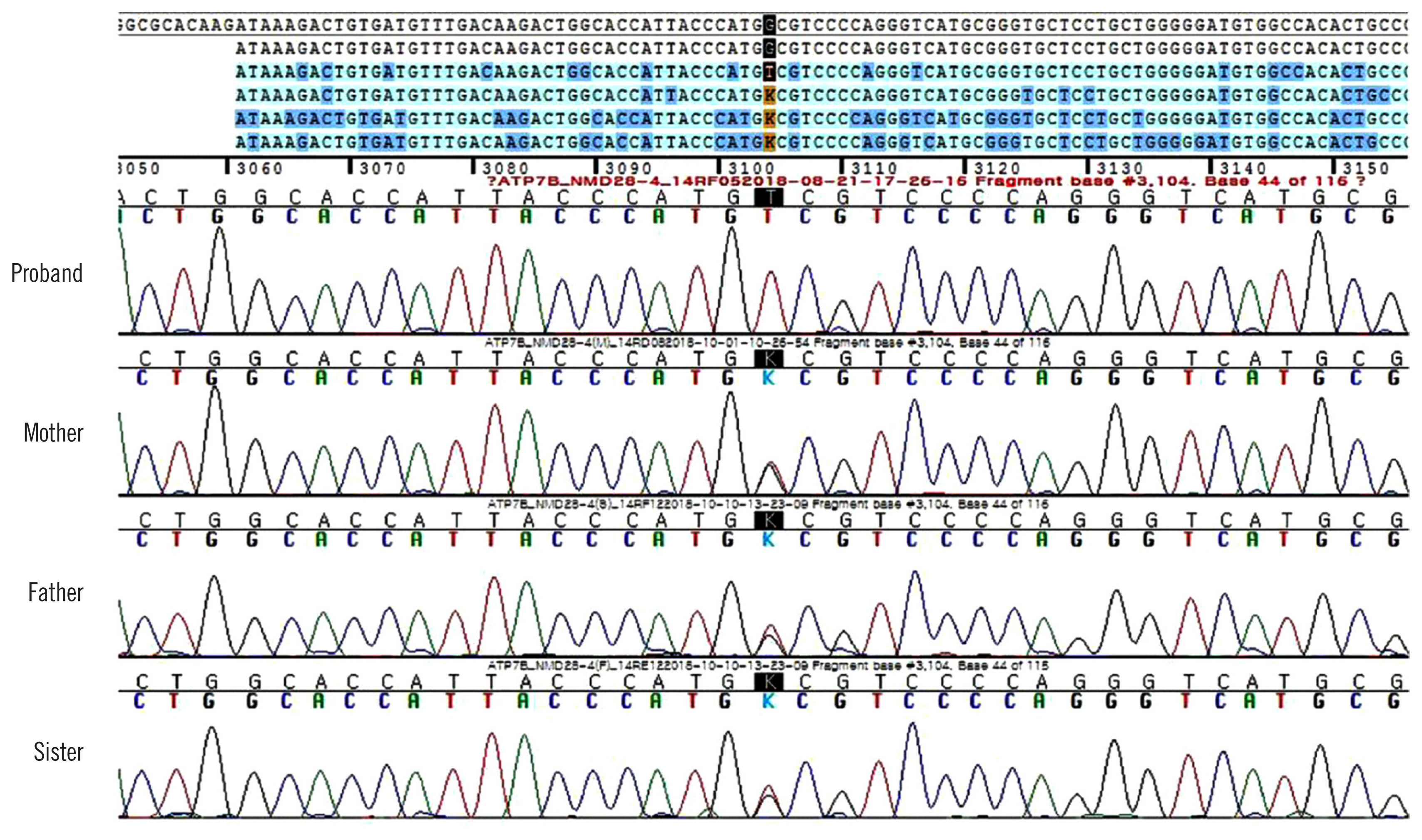
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tanzi RE, Petrukhin K, Chernov I, Pellequer JL, Wasco W, Ross B, et al. The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993; 5:344–50.
Article2. Rosencrantz R, Schilsky M. Wilson disease: pathogenesis and clinical considerations in diagnosis and treatment. Semin Liver Dis. 2011; 31:245–59.
Article3. Prashanth LK, Taly AB, Sinha S, Arunodaya GR, Swamy HS. Wilson’s disease: diagnostic errors and clinical implications. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75:907–9.
Article4. Poujois A, Woimant F. Challenges in the diagnosis of Wilson disease. Ann Transl Med. 2019; 7(S2):S67.
Article5. Ye S, Dai T, Leng B, Tang L, Jin L, Cao L. Genotype and clinical course in 2 Chinese Han siblings with Wilson disease presenting with isolated disabling premature osteoarthritis: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:e8641.6. Kim TJ, Kim IO, Kim WS, Cheon JE, Moon SG, Kwon JW, et al. MR imaging of the brain in Wilson disease of childhood: findings before and after treatment with clinical correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1373–8.7. McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010; 20:1297–303.
Article8. Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, Mieli-Vergani G, Tanner S, Sternlieb I, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2003; 23:139–42.9. Ala A, Walker AP, Ashkan K, Dooley JS, Schilsky ML. Wilson’s disease. Lancet. 2007; 369:397–408.
Article10. Jang JH, Lee T, Bang S, Kim YE, Cho EH. Carrier frequency of Wilson’s disease in the Korean population: a DNA-based approach. J Hum Genet. 2017; 62:815–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 8 Presenting as Ataxia without Definite Cerebellar Atrophy
- Dentatorubropallidoluysian Atrophy (DRPLA) With Comitant Esotropia
- A Patient with Spinocerebellar Ataxia 2 Presenting with Multiple System Atrophy
- Craniocervical Segmental Dystonia in the Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 2
- MRI in Movement Disorder Patients: "Hot cross bun" sign