Clin Endosc.
2020 Sep;53(5):519-524. 10.5946/ce.2020.222.
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Procedures: A Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1AW Morrow Gastroenterology and Liver Centre, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Sydney, Australia
- 2The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
- KMID: 2507584
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.222
Abstract
- Since the 1980s, endoscopic ultrasound has advanced from being purely diagnostic to an interventional modality. The gastrointestinal tract offers an exceptional window for assessing the vascular structures in the mediastinum and in the abdomen. This has led to a rapidly growing interest in endoscopic ultrasound-controlled vascular interventions as a minimally invasive alternative to surgical and radiological procedures.
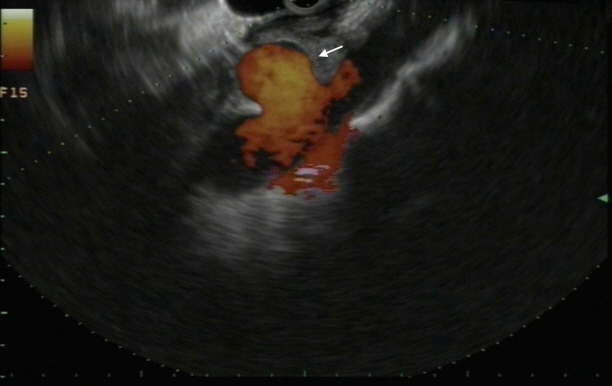
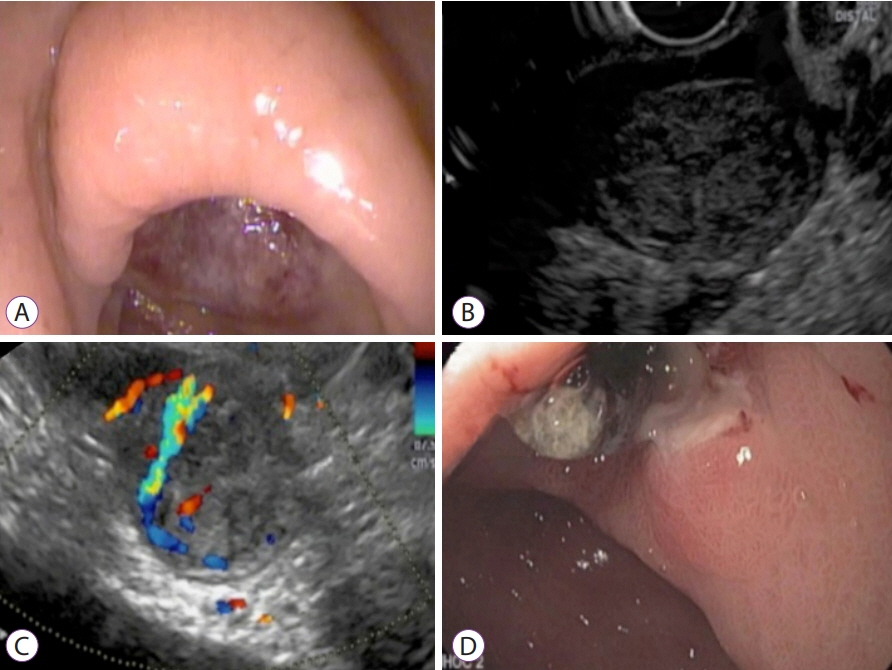
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weilert F, Binmoeller KF. EUS-guided vascular access and therapy. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2012; 22:303–314, x.
Article2. Saxena P, Lakhtakia S. Endoscopic ultrasound guided vascular access and therapy (with videos). Endosc Ultrasound. 2015; 4:168–175.
Article3. Abraldes JG, Bosch J. The treatment of acute variceal bleeding. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007; 41(Suppl 3):S312–S317.
Article4. Helmy A, Hayes PC. Review article: current endoscopic therapeutic options in the management of variceal bleeding. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001; 15:575–594.5. Irisawa A, Obara K, Bhutani MS, et al. Role of para-esophageal collateral veins in patients with portal hypertension based on the results of endoscopic ultrasonography and liver scintigraphy analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 18:309–314.
Article6. Hou MC, Lin HC, Lee FY, Chang FY, Lee SD. Recurrence of esophageal varices following endoscopic treatment and its impact on rebleeding: comparison of sclerotherapy and ligation. J Hepatol. 2000; 32:202–208.
Article7. Lahoti S, Catalano MF, Alcocer E, Hogan WJ, Geenen JE. Obliteration of esophageal varices using EUS-guided sclerotherapy with color Doppler. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51:331–333.
Article8. Weilert F, Binmoeller KF. New endoscopic technologies and procedural advances for endoscopic hemostasis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 14:1234–1244.
Article9. Goral V, Yılmaz N. Current approaches to the treatment of gastric varices: glue, coil application, TIPS, and BRTO. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019; 55:335.
Article10. Seewald S, Ang TL, Imazu H, et al. A standardized injection technique and regimen ensures success and safety of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate injection for the treatment of gastric fundal varices (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:447–454.
Article11. Romero-Castro R, Pellicer-Bautista FJ, Jimenez-Saenz M, et al. EUS-guided injection of cyanoacrylate in perforating feeding veins in gastric varices: results in 5 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:402–407.
Article12. Romero-Castro R, Ellrichmann M, Ortiz-Moyano C, et al. EUS-guided coil versus cyanoacrylate therapy for the treatment of gastric varices: a multicenter study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:711–721.
Article13. Wang X, Yu S, Chen X, Duan L. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided injection of coils and cyanoacrylate glue for the treatment of gastric fundal varices with abnormal shunts: a series of case reports. J Int Med Res. 2019; 47:1802–1809.
Article14. Bhat YM, Weilert F, Fredrick RT, et al. EUS-guided treatment of gastric fundal varices with combined injection of coils and cyanoacrylate glue: a large U.S. experience over 6 years (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:1164–1172.
Article15. Hosking SW, Smart HL, Johnson AG, Triger DR. Anorectal varices, haemorrhoids, and portal hypertension. Lancet. 1989; 1:349–352.
Article16. Chawla Y, Dilawari JB. Anorectal varices--their frequency in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Gut. 1991; 32:309–311.
Article17. Boregowda U, Umapathy C, Halim N, et al. Update on the management of gastrointestinal varices. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2019; 10:1–21.
Article18. Sato T, Yamazaki K, Akaike J, Toyota J, Karino Y, Ohmura T. Retrospective analysis of endoscopic injection sclerotherapy for rectal varices compared with band ligation. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2010; 3:159–163.19. Sharma M, Somasundaram A. Massive lower GI bleed from an endoscopically inevident rectal varices: diagnosis and management by EUS (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:1106–1108.20. Mukkada RJ, Mathew PG, Francis Jose V, Paul Chettupuzha A, Antony R, Koshy A. EUS-guided coiling of rectal varices. VideoGIE. 2017; 2:208–210.
Article21. Weilert F, Shah JN, Marson FP, Binmoeller KF. EUS-guided coil and glue for bleeding rectal varix. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:915–916.
Article22. Levy MJ, Wong Kee Song LM, Farnell MB, Misra S, Sarr MG, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided angiotherapy of refractory gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:352–359.23. Law R, Fujii-Lau L, Wong Kee Song LM, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided hemostatic interventions for resistant nonvariceal bleeding. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:808–812.e1.
Article24. Naseer M, Lambert K, Hamed A, Ali E. Endoscopic advances in the management of non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding: a review. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 12:1–16.
Article25. Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, García-Pagan JC. The clinical use of HVPG measurements in chronic liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 6:573–582.
Article26. Sarin SK, Khanna R. Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Clin Liver Dis. 2014; 18:451–476.
Article27. Lai L, Poneros J, Santilli J, Brugge W. EUS-guided portal vein catheterization and pressure measurement in an animal model: a pilot study of feasibility. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:280–283.
Article28. Brugge WR. EUS is an important new tool for accessing the portal vein. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:343–344.
Article29. Giday SA, Clarke JO, Buscaglia JM, et al. EUS-guided portal vein catheterization: a promising novel approach for portal angiography and portal vein pressure measurements. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:338–342.
Article30. Magno P, Ko CW, Buscaglia JM, et al. EUS-guided angiography: a novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the vascular system. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:587–591.
Article31. Huang JY, Samarasena JB, Tsujino T, et al. EUS-guided portal pressure gradient measurement with a simple novel device: a human pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:996–1001.
Article32. Buscaglia JM, Dray X, Shin EJ, et al. A new alternative for a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: EUS-guided creation of an intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:941–947.
Article33. Schulman AR, Popov V, Thompson CC. Randomized sham-controlled trials in endoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of adverse events. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86:972–985.e3.
Article34. Bosch J. EUS-guided intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a real alternative to transjugular intrahepatic portalsystemic shunt? Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:248–249.
Article35. Pommergaard HC, Rostved AA, Adam R, et al. Vascular invasion and survival after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a study from the European Liver Transplant Registry. HPB (Oxford). 2018; 20:768–775.
Article36. Michael H, Lenza C, Gupta M, Katz DS. Endoscopic ultrasound -guided fine-needle aspiration of a portal vein thrombus to aid in the diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011; 7:124–129.37. Kayar Y, Turkdogan KA, Baysal B, Unver N, Danalioglu A, Senturk H. EUS-guided FNA of a portal vein thrombus in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pan Afr Med J. 2015; 21:86.
Article38. Ting DT, Wittner BS, Ligorio M, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies extracellular matrix gene expression by pancreatic circulating tumor cells. Cell Rep. 2014; 8:1905–1918.
Article39. Chapman CG, Waxman I. EUS-guided portal venous sampling of circulating tumor cells. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019; 21:68.
Article40. Faigel DO, Kachaamy T, Lake D, et al. Safety and toxicity of EUS-guided portal injection chemotherapy (EPIC) using drug-eluting microbeads. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83(5 Suppl):AB150.41. Fritscher-Ravens A, Ganbari A, Mosse CA, Swain P, Koehler P, Patel K. Transesophageal endoscopic ultrasound-guided access to the heart. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:385–389.
Article42. Somani P, Sharma M, Patil A, Kumar A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of a pericardial mass. Endoscopy. 2016; 48(Suppl 1):E45–E46.
Article43. Romero-Castro R, Rios-Martin JJ, Gallego-Garcia de Vinuesa P, et al. Pericardial tumor diagnosed by EUS-guided FNA (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(3 Pt 1):562–563.
Article44. Gornals JB, de la Hera M, de Albert M, Claver E, Catala I. EUS cardiac puncture-guided right atrial tumor. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:165.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent development of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided vascular interventions: An overview of current and emerging techniques
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Hepaticogastrostomy: Technical Review and Tips to Prevent Adverse Events
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Pancreatic Duct Intervention
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided celiac plexus neurolysis for managing abdominal pain related with advanced cancer