Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2020 Aug;24(3):243-251. 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.3.243.
Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Catholic Kwandong University International St. Mary’s Hospital, Incheon, Korea
- KMID: 2505336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.3.243
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
Although systemic therapy is recommended in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), treatment options for advanced HCC with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) are debatable. Recent studies have recommended other treatments, such as surgical resection (SR) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis of hazard ratio (HR) for overall survival (OS) between the two modalities using previous reports in order to compare the two treatment options.
Methods
A systematic review was performed on previously reported data that compared the survival benefits of SR and TACE in patients with advanced HCC with PVTT.Thereafter, the meta-analysis was performed to determine the cumulative HR between the two different treatment groups. We used the HR and 95% CI directly from the original data, when available; however, if these data were unavailable, reconstruction was performed with the secondary data from the original Kaplan-Meier survival curve.
Results
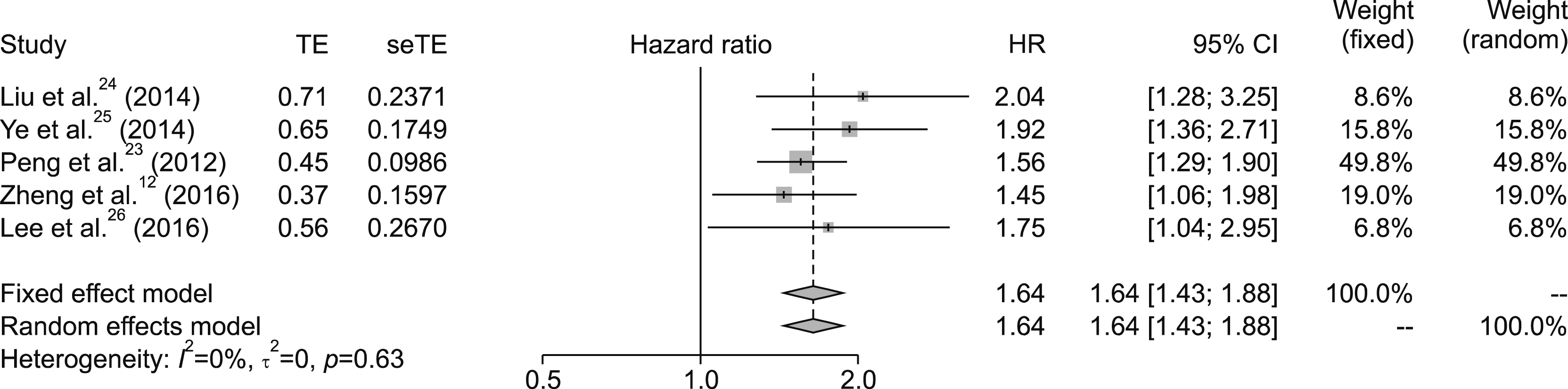
A total of seven studies were eligible; however, 2 were excluded from the meta-analysis. The remaining 5 studies that included 1422 patients (SR group=559, TACE group=863) were studied for the meta-analysis. The median OS was longer in the SR group (8.2-64 months in SR vs. 6.6-32 months in TACE), proving that SR offered survival benefits. Moreover, the HR for the OS in the TACE group was 1.64 (95% CI, 1.43-1.88) compared to SR group, depicting that TACE was a less favorable option compared to SR.
Conclusions
There is evidence that SR may be a better viable option for advanced HCC with PVTT.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. 2018; Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 391:1301–1314. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30010-2. PMID: 29307467.
Article2. Tunissiolli NM, Castanhole-Nunes MMU, Biselli-Chicote PM, Pavarino EC, da Silva RF, da Silva RC, et al. 2017; Hepatocellular carcinoma: a comprehensive review of biomarkers, clinical aspects, and therapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:863–872. DOI: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.4.863. PMID: 28545181. PMCID: PMC5494234.3. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. 2008; Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:378–390. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0708857. PMID: 18650514.
Article4. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. 2009; Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70285-7. PMID: 19095497.
Article5. Cerrito L, Annicchiarico BE, Iezzi R, Gasbarrini A, Pompili M, Ponziani FR. 2019; Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis: beyond the known frontiers. World J Gastroenterol. 25:4360–4382. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4360. PMID: 31496618. PMCID: PMC6710186.
Article6. Minagawa M, Makuuchi M. 2006; Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus. World J Gastroenterol. 12:7561–7567. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i47.7561. PMID: 17171782. PMCID: PMC4088035.
Article7. Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A, Vilana R, Ayuso Mdel C, Sala M, et al. 1999; Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology. 29:62–67. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510290145. PMID: 9862851.
Article8. Manzano-Robleda Mdel C, Barranco-Fragoso B, Uribe M, Méndez-Sánchez N. 2015; Portal vein thrombosis: what is new? Ann Hepatol. 14:20–27. DOI: 10.1016/S1665-2681(19)30797-5. PMID: 25536638.9. Suh SJ, Yim HJ, Lee DW, Hyun JJ, Jung YK, Kim JH, et al. 2017; Factors affecting prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: implications for future therapeutic strategies. J Liver Cancer. 17:60–71. DOI: 10.17998/jlc.17.1.60.10. Jarnagin W, Chapman WC, Curley S, D'Angelica M, Rosen C, Dixon E, et al. 2010; Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: expert consensus statement. HPB (Oxford). 12:302–310. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00182.x. PMID: 20590903. PMCID: PMC2951816.
Article11. Kudo M, Izumi N, Kokudo N, Matsui O, Sakamoto M, Nakashima O, et al. 2011; Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: Consensus-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines proposed by the Japan Society of Hepatology (JSH) 2010 updated version. Dig Dis. 29:339–364. DOI: 10.1159/000327577. PMID: 21829027.
Article12. Zheng N, Wei X, Zhang D, Chai W, Che M, Wang J, et al. 2016; Hepatic resection or transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e3959. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003959. PMID: 27367992. PMCID: PMC4937906.
Article13. Shi J, Lai EC, Li N, Guo WX, Xue J, Lau WY, et al. 2010; Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:2073–2080. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-010-0940-4. PMID: 20131013.
Article14. Liu L, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Qi X, Chen H, Bai W, et al. 2014; Transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: prognostic factors in a single-center study of 188 patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014:194278. DOI: 10.1155/2014/194278. PMID: 24800212. PMCID: PMC3996986.
Article15. Silva JP, Berger NG, Tsai S, Christians KK, Clarke CN, Mogal H, et al. 2017; Transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. HPB (Oxford). 19:659–666. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2017.04.016. PMID: 28552299.
Article16. Zhang XP, Wang K, Li N, Zhong CQ, Wei XB, Cheng YQ, et al. 2017; Survival benefit of hepatic resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 17:902. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3895-z. PMID: 29282010. PMCID: PMC5746018.
Article17. Zhang ZY, Dong KS, Zhang EL, Zhang LW, Chen XP, Dong HH. 2019; Resection might be a meaningful choice for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e18362. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018362. PMID: 31852141. PMCID: PMC6922393.18. Batson S, Greenall G, Hudson P. 2016; Review of the reporting of survival analyses within randomised controlled trials and the implications for meta-analysis. PLoS One. 11:e0154870. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154870. PMID: 27149107. PMCID: PMC4858202.
Article19. Guyot P, Ades AE, Ouwens MJ, Welton NJ. 2012; Enhanced secondary analysis of survival data: reconstructing the data from published Kaplan-Meier survival curves. BMC Med Res Methodol. 12:9. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-9. PMID: 22297116. PMCID: PMC3313891.
Article20. R Development Core Team. 2017. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing;Vienna: Available from: https://www.R-project.org/.21. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. 2003; Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 327:557–560. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. PMID: 12958120. PMCID: PMC192859.
Article22. Fan J, Zhou J, Wu ZQ, Qiu SJ, Wang XY, Shi YH, et al. 2005; Efficacy of different treatment strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J Gastroenterol. 11:1215–1219. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i8.1215. PMID: 15754408. PMCID: PMC4250717.
Article23. Peng ZW, Guo RP, Zhang YJ, Lin XJ, Chen MS, Lau WY. 2012; Hepatic resection versus transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Cancer. 118:4725–4736. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.26561. PMID: 22359112.
Article24. Liu PH, Lee YH, Hsia CY, Hsu CY, Huang YH, Chiou YY, et al. 2014; Surgical resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a propensity score analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 21:1825–1833. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-014-3510-3. PMID: 24499831.
Article25. Ye JZ, Zhang YQ, Ye HH, Bai T, Ma L, Xiang BD, et al. 2014; Appropriate treatment strategies improve survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with portal vein tumor thrombus. World J Gastroenterol. 20:17141–17147. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17141. PMID: 25493028. PMCID: PMC4258584.
Article26. Lee JM, Jang BK, Lee YJ, Choi WY, Choi SM, Chung WJ, et al. 2016; Survival outcomes of hepatic resection compared with transarterial chemoembolization or sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Clin Mol Hepatol. 22:160–167. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2016.22.1.160. PMID: 27044767. PMCID: PMC4825165.
Article27. Wang K, Guo WX, Chen MS, Mao YL, Sun BC, Shi J, et al. 2016; Multimodality treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a large-scale, multicenter, propensity mathching score analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e3015. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003015. PMID: 26986115. PMCID: PMC4839896.28. Lee ET, Go OT. 1997; Survival analysis in public health research. Annu Rev Public Health. 18:105–134. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.18.1.105. PMID: 9143714.
Article29. Schober P, Vetter TR. 2018; Survival analysis and interpretation of time-to-event data: the tortoise and the hare. Anesth Analg. 127:792–798. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000003653. PMID: 30015653. PMCID: PMC6110618.30. Tanaka A, Morimoto T, Yamaoka Y. 1996; Implications of surgical treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the portal vein. Hepatogastroenterology. 43:637–643. PMID: 8799408.31. Chok KS, Cheung TT, Chan SC, Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM. 2014; Surgical outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J Surg. 38:490–496. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-013-2290-4. PMID: 24132826.
Article32. Wu CC, Hsieh SR, Chen JT, Ho WL, Lin MC, Yeh DC, et al. 2000; An appraisal of liver and portal vein resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi extending to portal bifurcation. Arch Surg. 135:1273–1279. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.135.11.1273. PMID: 11074879.
Article33. Song MJ, Bae SH. 2014; Newer treatments for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Intern Med. 29:149–155. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2014.29.2.149. PMID: 24648795. PMCID: PMC3956982.
Article34. Cheng AL, Guan Z, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. 2012; Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma according to baseline status: subset analyses of the phase III Sorafenib Asia-Pacific trial. Eur J Cancer. 48:1452–1465. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.12.006. PMID: 22240282.
Article35. Kudo M. 2011; Signaling pathway and molecular-targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis. 29:289–302. DOI: 10.1159/000327562. PMID: 21829020.
Article36. Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P, Villanueva A, Llovet JM, Lynch M. 2008; Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3129–3140. DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0013. PMID: 18852116.
Article37. Mazzaferro V, Sposito C, Bhoori S, Romito R, Chiesa C, Morosi C, et al. 2013; Yttrium-90 radioembolization for intermediate-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase 2 study. Hepatology. 57:1826–1837. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26014. PMID: 22911442.
Article38. Kim DY, Park BJ, Kim YH, Han KH, Cho SB, Cho KR, et al. 2015; Radioembolization with yttrium-90 resin microspheres in hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter prospective study. Am J Clin Oncol. 38:495–501. DOI: 10.1097/COC.0b013e3182a78dba. PMID: 24064753.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of surgical resection versus transarterial chemoembolization with additional radiation therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion
- A Case of Successful Hepatic Resection after Insufficient Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiation Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Invasion
- Comparing efficacies of different treatment regimens in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus using network meta-analysis
- Reappraisal of transarterial radioembolization for liver-confined hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: Editorial on “Transarterial radioembolization versus tyrosine kinase inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis”
- Ultraselective conventional transarterial chemoembolization: When and how?