Restor Dent Endod.
2020 May;45(2):e25. 10.5395/rde.2020.45.e25.
Influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments: a systematic review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endodontics, School of Dentistry, Grande Rio University (UNIGRANRIO), Duque de Caxias, RJ, Brazil
- 2Department of Endodontics, School of Dentistry, State University of Rio de Janeiro (UERJ), Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
- 3Department of Endodontics, School of Dentistry, Fluminense Federal University (UFF), Niterói, RJ, Brazil
- 4Department of Preventive and Community Dentistry, School of Dentistry, State University of Rio de Janeiro (UERJ), Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
- KMID: 2503520
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e25
Abstract
Objectives
This systematic review evaluated the influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments.
Materials and Methods
A systematic search without restrictions was conducted in the following electronic databases: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, and Open Grey. The hand search was also performed in the main endodontic journals. The eligible studies were submitted to the methodological assessment and data extraction.
Results
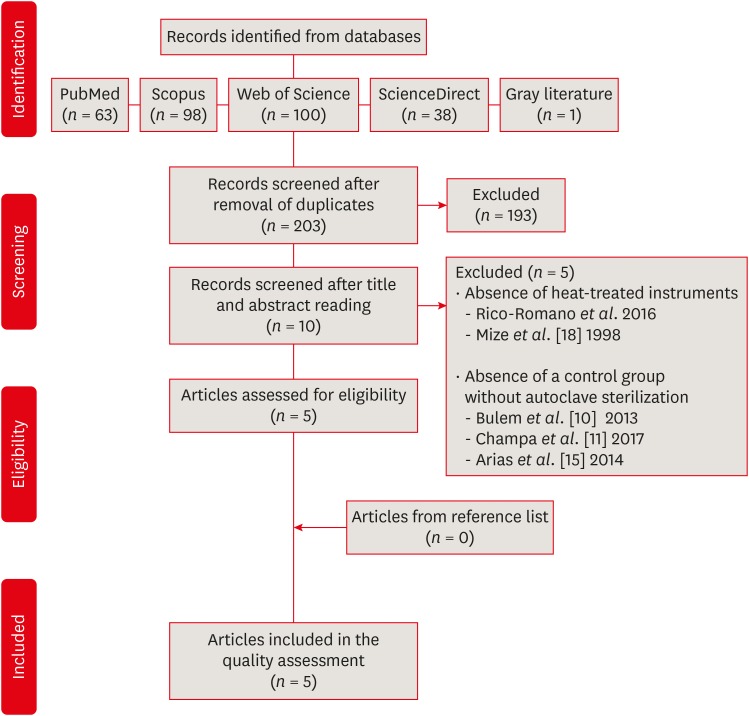
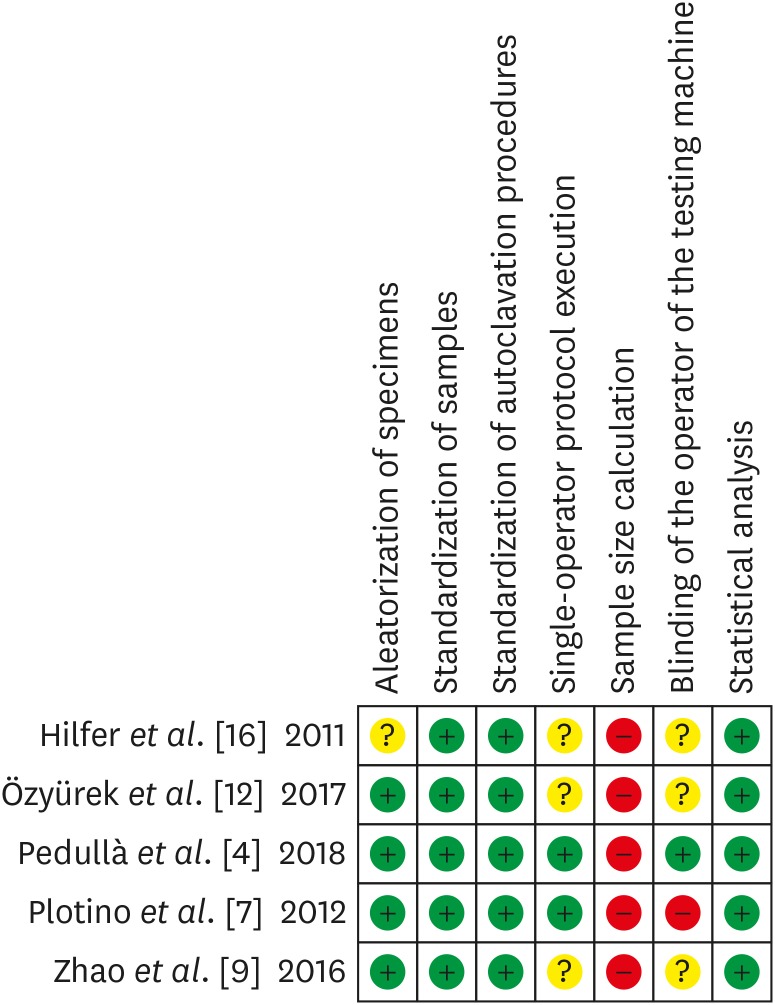
From 203 abstracts, a total of 10 articles matched the eligible criteria. After reading the full articles, 2 were excluded because of the absence of the heat-treated instruments in the experimental design and 3 due to the lack of a control group using heat-treated instruments without autoclave sterilization. From the 5 included studies, 1 presented a low risk of bias, 3 presented moderate and 1 high risk. It was observed heterogeneous findings in the included studies, with autoclave sterilization cycles increasing, decreasing or not affecting the cyclic fatigue life of heat-treated NiTi instruments. However, the retrieved studies evaluating the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments presented different protocols and assessing outcomes, this variability makes the findings less comparable within and also between groups and preclude the establishment of an unbiased scientific evidence base.
Conclusions
Considering the little scientific evidence and considerable risk of bias, it is still possible to conclude that autoclave sterilization procedures appear to influence the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated NiTi instruments.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
Victor de Ornelas Peraça, Samantha Rodrigues Xavier, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Erick Miranda Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
Restor Dent Endod. 2021;46(2):e28. doi: 10.5395/rde.2021.46.e28.
Reference
-
1. Es-Souni M, Es-Souni M, Brandies HF. On the transformation behaviour, mechanical properties and biocompatibility of two niti-based shape memory alloys: NiTi42 and NiTi42Cu7. Biomaterials. 2001; 22:2153–2161. PMID: 11432595.2. Abu-Tahun IH, Kwak SW, Ha JH, Kim HC. Microscopic features of fractured fragment of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments by two different modes of torsional loading. Scanning. 2018; 2018:9467059. PMID: 29675119.
Article3. Thompson SA. An overview of nickel-titanium alloys used in dentistry. Int Endod J. 2000; 33:297–310. PMID: 11307203.
Article4. Pedullà E, Benites A, La Rosa GM, Plotino G, Grande NM, Rapisarda E, Generali L. Cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments after immersion in sodium hypochlorite and/or sterilization. J Endod. 2018; 44:648–653. PMID: 29397218.
Article5. Cheung GS, Peng B, Bian Z, Shen Y, Darvell BW. Defects in ProTaper S1 instruments after clinical use: fractographic examination. Int Endod J. 2005; 38:802–809. PMID: 16218972.
Article6. Peng B, Shen Y, Cheung GS, Xia TJ. Defects in ProTaper S1 instruments after clinical use: longitudinal examination. Int Endod J. 2005; 38:550–557. PMID: 16011774.
Article7. Plotino G, Costanzo A, Grande NM, Petrovic R, Testarelli L, Gambarini G. Experimental evaluation on the influence of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue of new nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J Endod. 2012; 38:222–225. PMID: 22244641.
Article8. Rodrigues RC, Antunes HS, Neves MA, Siqueira JF Jr, Rôças IN. Infection control in retreatment cases: in vivo antibacterial effects of 2 instrumentation systems. J Endod. 2015; 41:1600–1605. PMID: 26234543.9. Zhao D, Shen Y, Peng B, Haapasalo M. Effect of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of thermally treated nickel-titanium instruments. Int Endod J. 2016; 49:990–995. PMID: 26372255.
Article10. Bulem UK, Kececi AD, Guldas HE. Experimental evaluation of cyclic fatigue resistance of four different nickel-titanium instruments after immersion in sodium hypochlorite and/or sterilization. J Appl Oral Sci. 2013; 21:505–510. PMID: 24473715.
Article11. Champa C, Divya V, Srirekha A, Karale R, Shetty A, Sadashiva P. An analysis of cyclic fatigue resistance of reciprocating instruments in different canal curvatures after immersion in sodium hypochlorite and autoclaving: an in vitro study. J Conserv Dent. 2017; 20:194–198. PMID: 29279625.12. Özyürek T, Yılmaz K, Uslu G. The effects of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium instruments. Restor Dent Endod. 2017; 42:301–308. PMID: 29142878.
Article13. Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA. PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015; 4:1. PMID: 25554246.
Article14. Aurélio IL, Marchionatti AM, Montagner AF, May LG, Soares FZ. Does air particle abrasion affect the flexural strength and phase transformation of Y-TZP? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dent Mater. 2016; 32:827–845. PMID: 27083253.
Article15. Arias A, Perez-Higueras JJ, de la Macorra JC. Influence of clinical usage of GT and GTX files on cyclic fatigue resistance. Int Endod J. 2014; 47:257–263. PMID: 23808563.
Article16. Hilfer PB, Bergeron BE, Mayerchak MJ, Roberts HW, Jeansonne BG. Multiple autoclave cycle effects on cyclic fatigue of nickel-titanium rotary files produced by new manufacturing methods. J Endod. 2011; 37:72–74. PMID: 21146081.
Article17. Khabiri M, Ebrahimi M, Saei MR. The effect of autoclave sterilization on resistance to cyclic fatigue of Hero endodontic file #642 (6%) at two artificial curvature. J Dent (Shiraz). 2017; 18:277–281. PMID: 29201971.18. Mize SB, Clement DJ, Pruett JP, Carnes DL Jr. Effect of sterilization on cyclic fatigue of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J Endod. 1998; 24:843–847. PMID: 10023267.
Article19. Parashos P, Gordon I, Messer HH. Factors influencing defects of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic instruments after clinical use. J Endod. 2004; 30:722–725. PMID: 15448468.
Article20. Peters OA. Current challenges and concepts in the preparation of root canal systems: a review. J Endod. 2004; 30:559–567. PMID: 15273636.
Article21. Plotino G, Grande NM, Cordaro M, Testarelli L, Gambarini G. A review of cyclic fatigue testing of nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J Endod. 2009; 35:1469–1476. PMID: 19840633.
Article22. de Hemptinne F, Slaus G, Vandendael M, Jacquet W, De Moor RJ, Bottenberg P. In vivo intracanal temperature evolution during endodontic treatment after the injection of room temperature or preheated sodium hypochlorite. J Endod. 2015; 41:1112–1115. PMID: 25814243.23. de Vasconcelos RA, Murphy S, Carvalho CA, Govindjee RG, Govindjee S, Peters OA. Evidence for reduced fatigue resistance of contemporary rotary instruments exposed to body temperature. J Endod. 2016; 42:782–787. PMID: 26993574.
Article24. Inan U, Keskin C, Sivas Yilmaz Ö, Baş G. Cyclic fatigue of Reciproc Blue and Reciproc instruments exposed to intracanal temperature in simulated severe apical curvature. Clin Oral Investig. 2019; 23:2077–2082.
Article25. Plotino G, Grande NM, Testarelli L, Gambarini G, Castagnola R, Rossetti A, Özyürek T, Cordaro M, Fortunato L. Cyclic fatigue of Reciproc and Reciproc Blue nickel-titanium reciprocating files at different environmental temperatures. J Endod. 2018; 44:1549–1552. PMID: 30144990.
Article26. Savage NW, Walsh LJ. The use of autoclaves in the dental surgery. Aust Dent J. 1995; 40:197–200. PMID: 7661768.
Article27. Viana AC, Gonzalez BM, Buono VT, Bahia MG. Influence of sterilization on mechanical properties and fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments. Int Endod J. 2006; 39:709–715. PMID: 16916360.
Article28. Zinelis S, Darabara M, Takase T, Ogane K, Papadimitriou GD. The effect of thermal treatment on the resistance of nickel-titanium rotary files in cyclic fatigue. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 103:843–847. PMID: 17428695.
Article29. Li XF, Zheng P, Xu L, Su Q. The influence of autoclave sterilization on surface characteristics and cyclic fatigue resistance of 3 nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2015; 24:690–695. PMID: 27063120.30. Shen Y, Huang X, Wang Z, Wei X, Haapasalo M. Low environmental temperature influences the fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium files. J Endod. 2018; 44:626–629. PMID: 29306534.
Article31. Aminsobhani M, Khalatbari MS, Meraji N, Ghorbanzadeh A, Sadri E. Evaluation of the fractured surface of five endodontic rotary instruments: a metallurgical study. Iran Endod J. 2016; 11:286–292. PMID: 27790257.32. Shim KS, Oh S, Kum K, Kim YC, Jee KK, Chang SW. Mechanical and metallurgical properties of various nickel-titanium rotary instruments. BioMed Res Int. 2017; 2017:4528601. PMID: 29318149.
Article33. Iacono F, Pirani C, Generali L, Bolelli G, Sassatelli P, Lusvarghi L, Gandolfi MG, Giorgini L, Prati C. Structural analysis of HyFlex EDM instruments. Int Endod J. 2017; 50:303–313. PMID: 26864081.
Article34. Shen Y, Zhou HM, Wang Z, Campbell L, Zheng YF, Haapasalo M. Phase transformation behavior and mechanical properties of thermomechanically treated K3XF nickel-titanium instruments. J Endod. 2013; 39:919–923. PMID: 23791264.35. Shen Y, Zhou HM, Zheng YF, Campbell L, Peng B, Haapasalo M. Metallurgical characterization of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J Endod. 2011; 37:1566–1571. PMID: 22000465.
Article36. Braga LC, Faria Silva AC, Buono VT, de Azevedo Bahia MG. Impact of heat treatments on the fatigue resistance of different rotary nickel-titanium instruments. J Endod. 2014; 40:1494–1497. PMID: 25146041.
Article37. Shen Y, Zhou H, Coil JM, Aljazaeri B, Buttar R, Wang Z, Zheng YF, Haapasalo M. ProFile Vortex and Vortex Blue nickel-titanium rotary instruments after clinical use. J Endod. 2015; 41:937–942. PMID: 25841958.
Article38. Tsujimoto M, Irifune Y, Tsujimoto Y, Yamada S, Watanabe I, Hayashi Y. Comparison of conventional and new-generation nickel-titanium files in regard to their physical properties. J Endod. 2014; 40:1824–1829. PMID: 25266465.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium instruments
- The effect of heat sterilization on the surface topography and the tensile properties in various nickel titanium wires including a Korean product
- Cyclic fatigue of the sodium hypochlorite treated and/or steam autoclaved nickel-titanium endodontic files
- Cyclic fatigue resistance of the WaveOne Gold Glider, ProGlider, and the One G glide path instruments in double-curvature canals
- Effect of adaptive motion on cyclic fatigue resistance of a nickel titanium instrument designed for retreatment