Cancer Res Treat.
2020 Jan;52(1):31-40. 10.4143/crt.2018.624.
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy versus Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy in Definitive Chemoradiotherapy for Cervical Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Comparison of Survival Outcomes and Toxicities
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Guangzhou, China
- 3Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou, China
- KMID: 2501199
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.624
Abstract
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to compare the survival and toxicities in cervical esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (CESCC) treated by concurrent chemoradiothrapy with either three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) or intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) techniques.
Materials and Methods
A total of 112 consecutive CESCC patients were retrospectively reviewed. 3D-CRT and IMRT groups had been analyzed by propensity score matching method, with sex, age, Karnofsky performance status, induction chemotherapy, and tumor stage well matched. The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards model were used for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Toxicities were compared between two groups by Fisher exact test.
Results
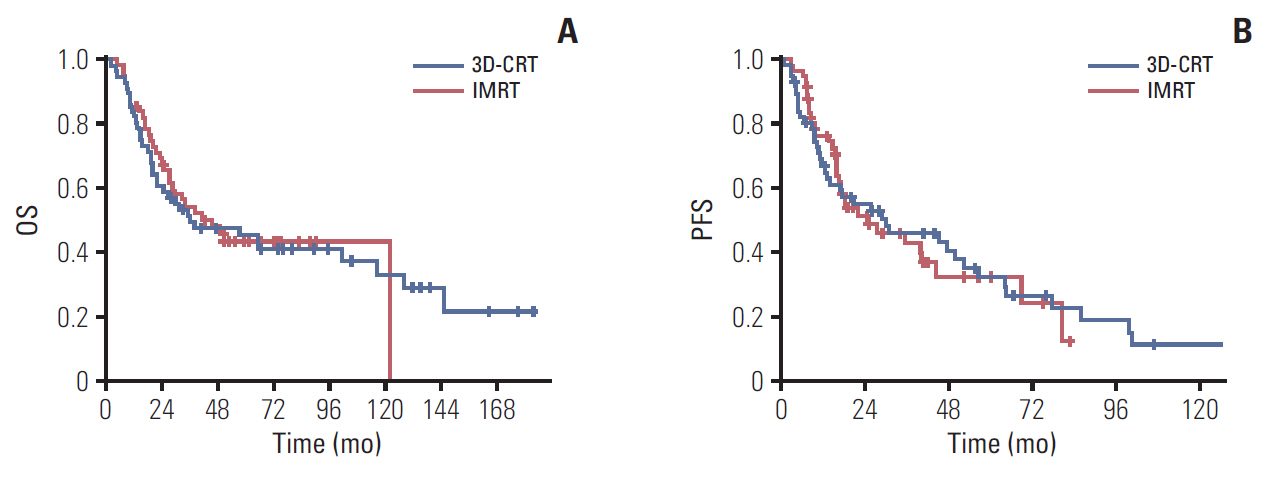
With a median follow-up time of 34.9 months, the 3-year OS (p=0.927) and PFS (p=0.859) rate was 49.6% and 45.8% in 3D-CRT group, compared with 54.4% and 42.8% in IMRT group. The rates of grade ≥ 3 esophagitis, grade ≥ 2 pneumonitis, esophageal stricture, and hemorrhage were comparable between two groups, while the rate of tracheostomy dependence was much higher in IMRT group than 3D-CRT group (14.3% vs.1.8%, p=0.032). Radiotherapy technique (hazard ratio [HR], 0.09; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01 to 0.79) and pretreatment hoarseness (HR, 0.12; 95% CI 0.02 to 0.70) were independently prognostic of tracheostomy dependence.
Conclusion
No survival benefits had been observed while comparing IMRT versus 3D-CRT in CESCC patients. IMRT with fraction dose escalation and pretreatment hoarseness were considered to be associated with a higher risk for tracheostomy dependence. Radiation dose escalation beyond 60 Gy should be taken into account carefully when using IMRT with hypofractionated regimen.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mendenhall WM, Sombeck MD, Parsons JT, Kasper ME, Stringer SP, Vogel SB. Management of cervical esophageal carcinoma. Semin Radiat Oncol. 1994; 4:179–91.
Article2. Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A, Macdonald JS, Martenson JA Jr, Al-Sarraf M, et al. Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. JAMA. 1999; 281:1623–7.
Article3. Minsky BD, Pajak TF, Ginsberg RJ, Pisansky TM, Martenson J, Komaki R, et al. INT 0123 (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 94-05) phase III trial of combined-modality therapy for esophageal cancer: high-dose versus standard-dose radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:1167–74.
Article4. Tong DK, Law S, Kwong DL, Wei WI, Ng RW, Wong KH. Current management of cervical esophageal cancer. World J Surg. 2011; 35:600–7.
Article5. Kim HJ, Suh YG, Lee YC, Lee SK, Shin SK, Cho BC, et al. Dose-response relationship between radiation dose and locoregional control in patients with stage II-III esophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Res Treat. 2017; 49:669–77.
Article6. Grass GD, Cooper SL, Armeson K, Garrett-Mayer E, Sharma A. Cervical esophageal cancer: a population-based study. Head Neck. 2015; 37:808–14.
Article7. Yamada K, Murakami M, Okamoto Y, Okuno Y, Nakajima T, Kusumi F, et al. Treatment results of radiotherapy for carcinoma of the cervical esophagus. Acta Oncol. 2006; 45:1120–5.
Article8. Wang S, Liao Z, Chen Y, Chang JY, Jeter M, Guerrero T, et al. Esophageal cancer located at the neck and upper thorax treated with concurrent chemoradiation: a single-institution experience. J Thorac Oncol. 2006; 1:252–9.
Article9. Huang SH, Lockwood G, Brierley J, Cummings B, Kim J, Wong R, et al. Effect of concurrent high-dose cisplatin chemotherapy and conformal radiotherapy on cervical esophageal cancer survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 71:735–40.
Article10. Zhang P, Xi M, Zhao L, Qiu B, Liu H, Hu YH, et al. Clinical efficacy and failure pattern in patients with cervical esophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2015; 116:257–61.
Article11. Cao C, Luo J, Gao L, Xu G, Yi J, Huang X, et al. Definitive radiotherapy for cervical esophageal cancer. Head Neck. 2015; 37:151–5.
Article12. Zhao L, Zhou Y, Mu Y, Chai G, Xiao F, Tan L, et al. Patterns of failure and clinical outcomes of definitive radiotherapy for cervical esophageal cancer. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:21852–60.
Article13. Gkika E, Gauler T, Eberhardt W, Stahl M, Stuschke M, Pottgen C. Long-term results of definitive radiochemotherapy in locally advanced cancers of the cervical esophagus. Dis Esophagus. 2014; 27:678–84.
Article14. Freilich J, Hoffe SE, Almhanna K, Dinwoodie W, Yue B, Fulp W, et al. Comparative outcomes for three-dimensional conformal versus intensity-modulated radiation therapy for esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2015; 28:352–7.
Article15. Haefner MF, Lang K, Verma V, Koerber SA, Uhlmann L, Debus J, et al. Intensity-modulated versus 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in the definitive treatment of esophageal cancer: comparison of outcomes and acute toxicity. Radiat Oncol. 2017; 12:131.
Article16. Nicolini G, Ghosh-Laskar S, Shrivastava SK, Banerjee S, Chaudhary S, Agarwal JP, et al. Volumetric modulation arc radiotherapy with flattening filter-free beams compared with static gantry IMRT and 3D conformal radiotherapy for advanced esophageal cancer: a feasibility study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 84:553–60.
Article17. Zhang WZ, Chen JZ, Li DR, Chen ZJ, Guo H, Zhuang TT, et al. Simultaneous modulated accelerated radiation therapy for esophageal cancer: a feasibility study. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:13973–80.
Article18. Fenkell L, Kaminsky I, Breen S, Huang S, Van Prooijen M, Ringash J. Dosimetric comparison of IMRT vs. 3D conformal radiotherapy in the treatment of cancer of the cervical esophagus. Radiother Oncol. 2008; 89:287–91.
Article19. Gao M, Li Q, Ning Z, Gu W, Huang J, Mu J, et al. Dosimetric comparison between step-shoot intensity-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric-modulated arc therapy for upper thoracic and cervical esophageal carcinoma. Med Dosim. 2016; 41:131–5.
Article20. Hoffman KE, Voong KR, Levy LB, Allen PK, Choi S, Schlembach PJ, et al. Randomized trial of hypofractionated, dose-escalated, intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) versus conventionally fractionated IMRT for localized prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:2943–9.
Article21. Kim JO, Chu KP, Fairchild A, Ghosh S, Butts C, Chu Q, et al. Dose-escalated hypofractionated intensity-modulated radiation therapy with concurrent chemotherapy for inoperable or unresectable non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2017; 40:294–9.
Article22. Freedman GM, Anderson PR, Bleicher RJ, Litwin S, Li T, Swaby RF, et al. Five-year local control in a phase II study of hypofractionated intensity modulated radiation therapy with an incorporated boost for early stage breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 84:888–93.
Article23. Li QQ, Liu MZ, Hu YH, Liu H, He ZY, Lin HX. Definitive concomitant chemoradiotherapy with docetaxel and cisplatin in squamous esophageal carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 2010; 23:253–9.24. Yang H, Feng C, Cai BN, Yang J, Liu HX, Ma L. Comparison of three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy, and volumetric-modulated arc therapy in the treatment of cervical esophageal carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 2017; 30:1–8.
Article25. Cao C, Luo J, Gao L, Xu G, Yi J, Huang X, et al. Definitive intensity-modulated radiotherapy compared with definitive conventional radiotherapy in cervical oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Radiol Med. 2015; 120:603–10.
Article26. Ito M, Kodaira T, Tachibana H, Tomita N, Makita C, Koide Y, et al. Clinical results of definitive chemoradiotherapy for cervical esophageal cancer: comparison of failure pattern and toxicities between intensity-modulated radiotherapy and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Head Neck. 2017; 39:2406–15.
Article27. Staton J, Robbins KT, Newman L, Samant S, Sebelik M, Vieira F. Factors predictive of poor functional outcome after chemoradiation for advanced laryngeal cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; 127:43–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dosimetric advantages and clinical outcomes of simultaneous integrated boost intensity-modulated radiotherapy for anal squamous cell carcinoma
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy: a review with a physics perspective
- Dosimetric comparison between modulated arc therapy and static intensity modulated radiotherapy in thoracic esophageal cancer: a single institutional experience
- Radiation therapy of cervical cancer: Current status in Korea and recent developments
- A Comparison of Gastrointestinal Toxicities between Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy and Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer