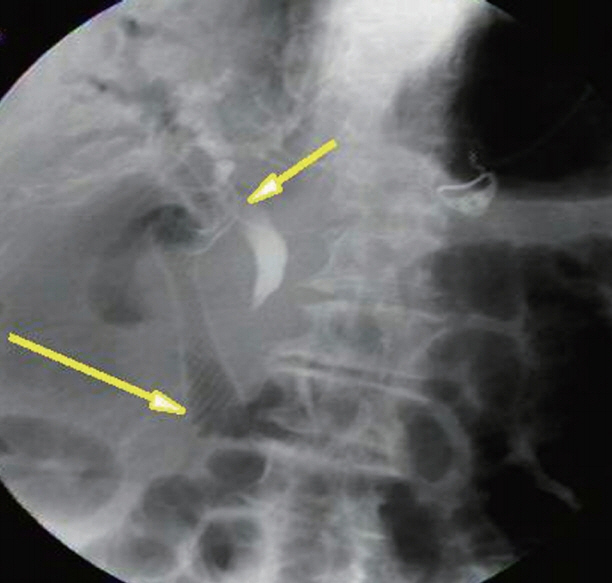
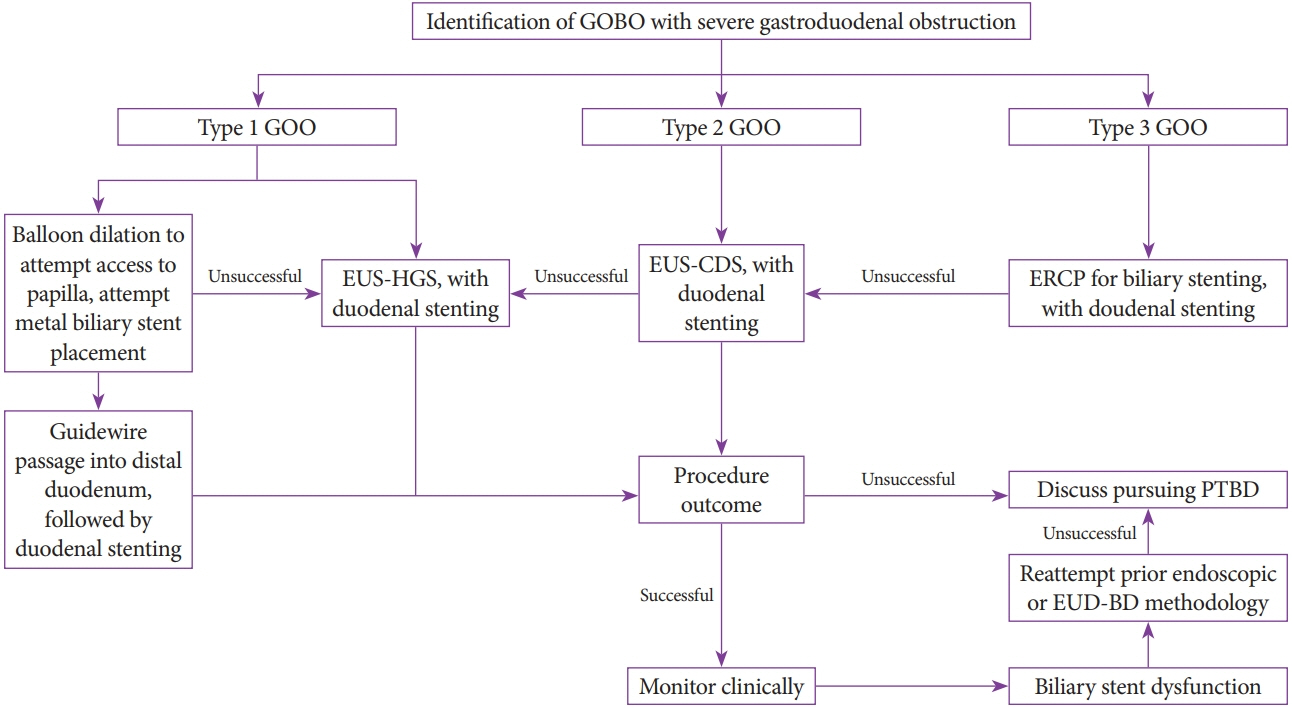
Clin Endosc.
2020 Mar;53(2):167-175. 10.5946/ce.2019.050.
Review of Simultaneous Double Stenting Using Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Techniques in Combined Gastric Outlet and Biliary Obstructions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX, USA
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX, USA
- 3Gastrointestinal Care Consultants, Houston, TX, USA
- KMID: 2500884
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.050
Abstract
- Concomitant malignant gastric outlet obstruction and biliary obstruction may occur in patients with advanced cancers affecting these anatomical regions. This scenario presents a unique challenge to the endoscopist in selecting an optimal management approach. We sought to determine the efficacy and safety of endoscopic techniques for treating simultaneous gastric outlet and biliary obstruction (GOBO) with endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guidance for biliary drainage. An extensive literature search for peer-reviewed published cases yielded 6 unique case series that either focused on or included the use of EUS-guided biliary drainage (EUS-BD) with simultaneous gastroduodenal stenting. In our composite analysis, a total of 51 patients underwent simultaneous biliary drainage through EUS, with an overall reported technical success rate of 100% for both duodenal stenting and biliary drainage. EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy or EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy was employed as the initial technique. In 34 cases in which clinical success was ascribed, 100% derived clinical benefit. The common adverse effects of double stenting included cholangitis, stent migration, bleeding, food impaction, and pancreatitis. We conclude that simultaneous double stenting with EUS-BD and gastroduodenal stenting for GOBO is associated with high success rates. It is a feasible and practical alternative to percutaneous biliary drainage or surgery for palliation in patients with associated advanced malignancies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nakai Y, Hamada T, Isayama H, Itoi T, Koike K. Endoscopic management of combined malignant biliary and gastric outlet obstruction. Dig Endosc. 2017; 29:16–25.
Article2. Sato T, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Type of combined endoscopic biliary and gastroduodenal stenting is significant for biliary route maintenance. Intern Med. 2016; 55:2153–2161.
Article3. Baron TH. Management of simultaneous biliary and duodenal obstruction: the endoscopic perspective. Gut Liver. 2010; 4(Suppl 1):S50–S56.
Article4. Akinci D, Akhan O, Ozkan F, et al. Palliation of malignant biliary and duodenal obstruction with combined metallic stenting. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007; 30:1173–1177.
Article5. Kaw M, Singh S, Gagneja H. Clinical outcome of simultaneous self-expandable metal stents for palliation of malignant biliary and duodenal obstruction. Surg Endosc. 2003; 17:457–461.
Article6. Potz BA, Miner TJ. Surgical palliation of gastric outlet obstruction in advanced malignancy. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2016; 8:545–555.
Article7. Riff BP, DiMaio CJ. Endoscopic treatment of simultaneous malignant biliary and gastric outlet obstruction. In : Adler DG, editor. Advanced pancreaticobiliary endoscopy. Cham: Springer International Publishing Switzerland;2016. p. 121–133.8. Kim KO, Kim TN, Lee HC. Effectiveness of combined biliary and duodenal stenting in patients with malignant biliary and duodenal obstruction. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012; 47:962–967.
Article9. Zhao L, Xu H, Zhang Y. Palliation double stenting for malignant biliary and duodenal obstruction. Exp Ther Med. 2016; 11:348–352.
Article10. Sharaiha RZ, Khan MA, Kamal F, et al. Efficacy and safety of EUS-guided biliary drainage in comparison with percutaneous biliary drainage when ERCP fails: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:904–914.
Article11. Maetani I, Tada T, Ukita T, Inoue H, Sakai Y, Nagao J. Comparison of duodenal stent placement with surgical gastrojejunostomy for palliation in patients with duodenal obstructions caused by pancreaticobiliary malignancies. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:73–78.
Article12. Matsumoto K, Kato H, Tsutsumi K, et al. Long-term outcomes and risk factors of biliary stent dysfunction after endoscopic double stenting for malignant biliary and duodenal obstructions. Dig Endosc. 2017; 29:617–625.
Article13. Itoi T, Yamao K. EUS 2008 Working Group document: evaluation of EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(2 Suppl):S8–S12.
Article14. Savides TJ, Varadarajulu S, Palazzo L. EUS 2008 Working Group document: evaluation of EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(2 Suppl):S3–S7.
Article15. Tyberg A, Desai AP, Kumta NA, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage after failed ERCP: a novel algorithm individualized based on patient anatomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 84:941–946.
Article16. Ogura T, Higuchi K. Technical tips of endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:820–828.
Article17. Ogura T, Higuchi K. Technical tips for endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:3945–3951.
Article18. Khashab MA, Valeshabad AK, Modayil R, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage by using a standardized approach for malignant biliary obstruction: rendezvous versus direct transluminal techniques (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:734–741.
Article19. Belletrutti PJ, DiMaio CJ, Gerdes H, Schattner MA. Endoscopic ultrasound guided biliary drainage in patients with unapproachable ampullae due to malignant duodenal obstruction. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2011; 42:137–142.
Article20. Ogura T, Chiba Y, Masuda D, et al. Comparison of the clinical impact of endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy and hepaticogastrostomy for bile duct obstruction with duodenal obstruction. Endoscopy. 2016; 48:156–163.
Article21. Paik WH, Lee TH, Park DH, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage versus ERCP for the primary palliation of malignant biliary obstruction: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018; 113:987–997.
Article22. Iwamuro M, Kawamoto H, Harada R, et al. Combined duodenal stent placement and endoscopic ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage for malignant duodenal obstruction with biliary stricture. Dig Endosc. 2010; 22:236–240.
Article23. Kawakubo K, Isayama H, Nakai Y, et al. Simultaneous duodenal metal stent placement and EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy for unresectable pancreatic cancer. Gut Liver. 2012; 6:399–402.
Article24. Rebello C, Bordini A, Yoshida A, et al. A one-step procedure by using linear echoendoscope to perform EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy and duodenal stenting in patients with irresectable periampullary cancer. Endosc Ultrasound. 2012; 1:156–161.
Article25. Artifon EL, Frazão MS, Wodak S, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy and duodenal stenting in patients with unresectable periampullary cancer: one-step procedure by using linear echoendoscope. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:374–379.
Article26. Tonozuka R, Itoi T, Sofuni A, Itokawa F, Moriyasu F. Endoscopic double stenting for the treatment of malignant biliary and duodenal obstruction due to pancreatic cancer. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25(Suppl 2):100–108.
Article27. Giovannini M, Moutardier V, Pesenti C, Bories E, Lelong B, Delpero JR. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided bilioduodenal anastomosis: a new technique for biliary drainage. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:898–900.
Article28. Rimbaş M, Larghi A, Kunda R. EUS-guided biliary drainage: is it ready for prime time? Endosc Ultrasound. 2017; 6(Suppl 3):S122–S126.
Article29. Belletrutti PJ, Gerdes H, Schattner MA. Successful endoscopic ultrasound-guided transduodenal biliary drainage through a pre-existing duodenal stent. JOP. 2010; 11:234–236.30. Yamao K, Bhatia V, Mizuno N, et al. EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy for palliative biliary drainage in patients with malignant biliary obstruction: results of long-term follow-up. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:340–342.
Article31. Bang JY, Navaneethan U, Hasan M, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Stent placement by EUS or ERCP for primary biliary decompression in pancreatic cancer: a randomized trial (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 88:9–17.32. Maetani I, Ogawa S, Hoshi H, et al. Self-expanding metal stents for palliative treatment of malignant biliary and duodenal stenoses. Endoscopy. 1994; 26:701–704.
Article33. Wang K, Zhu J, Xing L, Wang Y, Jin Z, Li Z. Assessment of efficacy and safety of EUS-guided biliary drainage: a systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:1218–1227.34. Anderloni A, Fugazza A, Troncone E, et al. Single-stage EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy using a lumen-apposing metal stent for malignant distal biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 89:69–76.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage in malignant distal biliary obstruction
- Endoscopic Management of Combined Biliary and Duodenal Obstruction
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage for Benign Biliary Diseases
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage in malignant hilar obstruction
- Recent development of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage