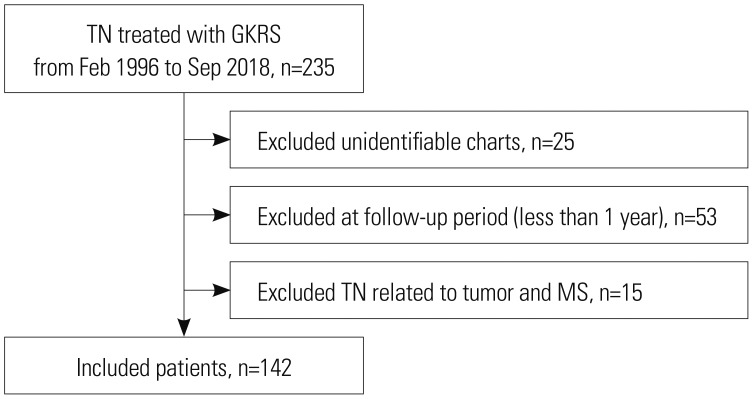
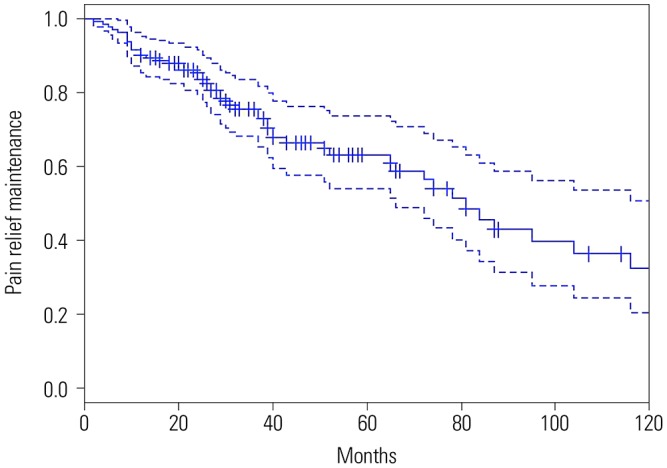
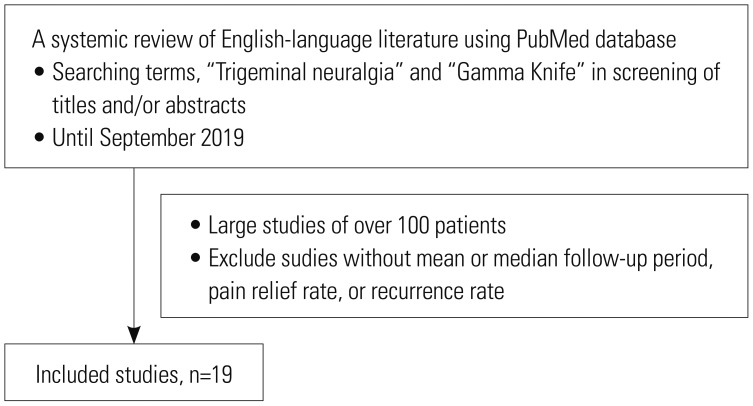
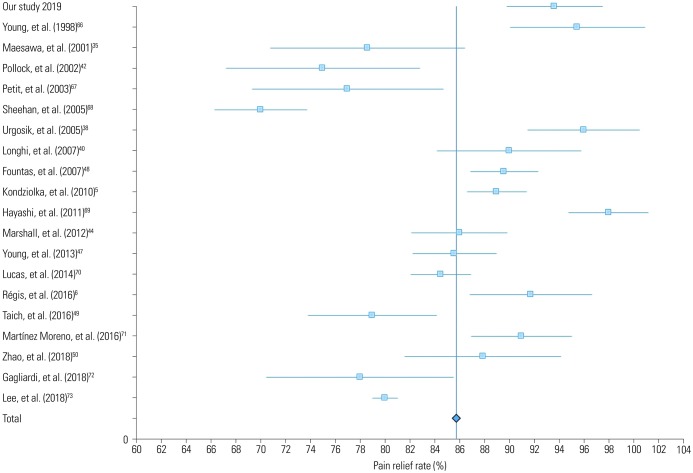
Yonsei Med J.
2020 Feb;61(2):111-119. 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.2.111.
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery on the Trigeminal Root Entry Zone for Idiopathic Trigeminal Neuralgia: Results and a Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jchang@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2468485
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.2.111
Abstract
- Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a chronic disorder of the trigeminal nerve characterized by repeated electrical shock-like sensations on one side of the face. It can cause severe pain in the face and disrupt or impair quality of life in patients. Options for the management of TN consist of pharmacological and surgical treatments, including Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKRS). GKRS has been used for TN for a long time because of its low rate of complications and high success rate. Moreover, GKRS can be of use for drug-resistant TN patients who are poor surgical candidates due to medical comorbidities, patients of older age, or patients who refuse invasive therapy. We reviewed the rationale, effects, safety, and current treatment policies of GKRS for TN in view of our institution's results and a review of the literature to date.
MeSH Terms
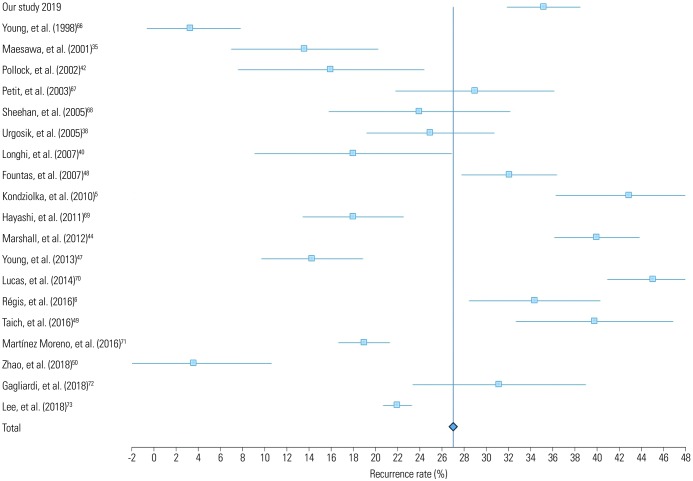
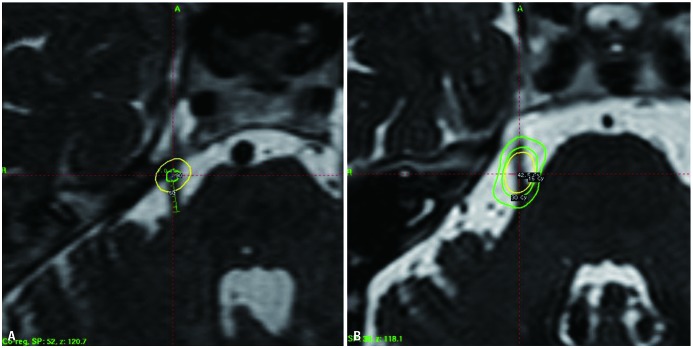
Figure
Reference
-
1. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia. 2013; 33:629–808. PMID: 23771276.2. McMillan R. Trigeminal Neuralgia—a debilitating facial pain. Rev Pain. 2011; 5:26–34.
Article3. Leksell L. The stereotactic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand. 1951; 102:316–319. PMID: 14914373.4. Lindquist C, Kihlström L, Hellstrand E. Functional neurosurgery--a future for the gamma knife? Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1991; 57:72–81. PMID: 1725560.5. Kondziolka D, Zorro O, Lobato-Polo J, Kano H, Flannery TJ, Flickinger JC, et al. Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2010; 112:758–765. PMID: 19747055.
Article6. Régis J, Tuleasca C, Resseguier N, Carron R, Donnet A, Gaudart J, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of Gamma Knife surgery in classical trigeminal neuralgia: a 497-patient historical cohort study. J Neurosurg. 2016; 124:1079–1087. PMID: 26339857.
Article7. Romanelli P, Heit G, Chang SD, Martin D, Pham C, Adler J. Cyberknife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2003; 81:105–109. PMID: 14742972.
Article8. Smith ZA, Gorgulho AA, Bezrukiy N, McArthur D, Agazaryan N, Selch MT, et al. Dedicated linear accelerator radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a single-center experience in 179 patients with varied dose prescriptions and treatment plans. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 81:225–231. PMID: 21236592.
Article9. Costa GMF, Leite CMdA. Trigeminal neuralgia: peripheral and central mechanisms. Revista Dor. 2015; 16:297–301.
Article10. Yadav YR, Nishtha Y, Sonjjay P, Vijay P, Shailendra R, Yatin K. Trigeminal neuralgia. Asian J Neurosurg. 2017; 12:585–597. PMID: 29114270.
Article11. Kumar S, Rastogi S, Kumar S, Mahendra P, Bansal M, Chandra L. Pain in trigeminal neuralgia: neurophysiology and measurement: a comprehensive review. J Med Life. 2013; 6:383–388. PMID: 24701256.12. Love S, Coakham HB. Trigeminal neuralgia: pathology and pathogenesis. Brain. 2001; 124:2347–2360. PMID: 11701590.
Article13. Marinković S, Gibo H, Todorović V, Antić B, Kovacević D, Milisavljević M, et al. Ultrastructure and immunohistochemistry of the trigeminal peripheral myelinated axons in patients with neuralgia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009; 111:795–800. PMID: 19836877.
Article14. Burchiel KJ. A new classification for facial pain. Neurosurgery. 2003; 53:1164–1166. PMID: 14580284.
Article15. Wiffen PJ, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Carbamazepine for acute and chronic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; CD005451. PMID: 16034977.16. Montano N, Conforti G, Di Bonaventura R, Meglio M, Fernandez E, Papacci F. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015; 11:289–299. PMID: 25750533.17. Cruccu G, Gronseth G, Alksne J, Argoff C, Brainin M, Burchiel K, et al. AAN-EFNS guidelines on trigeminal neuralgia management. Eur J Neurol. 2008; 15:1013–1028. PMID: 18721143.
Article18. Barker FG, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD. The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:1077–1084. PMID: 8598865.
Article19. Burchiel KJ, Clarke H, Haglund M, Loeser JD. Long-term efficacy of microvascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1988; 69:35–38. PMID: 2454303.
Article20. Sekula RF Jr, Frederickson AM, Jannetta PJ, Quigley MR, Aziz KM, Arnone GD. Microvascular decompression for elderly patients with trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective study and systematic review with meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. 2011; 114:172–179. PMID: 20653393.
Article21. Yang DB, Wang ZM, Jiang DY, Chen HC. The efficacy and safety of microvascular decompression for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia in patients older than 65 years. J Craniofac Surg. 2014; 25:1393–1396. PMID: 24816027.
Article22. Parmar M, Sharma N, Modgill V, Naidu P. Comparative evaluation of surgical procedures for trigeminal neuralgia. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2013; 12:400–409. PMID: 24431878.
Article23. Park SS, Lee MK, Kim JW, Jung JY, Kim IS, Ghang CG. Percutaneous balloon compression of trigeminal ganglion for the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: experience in 50 patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 43:186–189. PMID: 19096641.24. Asplund P, Blomstedt P, Bergenheim AT. Percutaneous balloon compression vs percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy for the primary treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 2016; 78:421–428. PMID: 26465639.
Article25. Pollock BE. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizotomy for patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective analysis of factors related to pain relief. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102:223–228. PMID: 15739548.
Article26. Yoon KB, Wiles JR, Miles JB, Nurmikko TJ. Long-term outcome of percutaneous thermocoagulation for trigeminal neuralgia. Anaesthesia. 1999; 54:803–808. PMID: 10460537.
Article27. Wu CY, Meng FG, Xu SJ, Liu YG, Wang HW. Selective percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: report on 1860 cases. Chin Med J (Engl). 2004; 117:467–470. PMID: 15043796.28. Fouad W. Management of trigeminal neuralgia by radiofrequency thermocoagulation. Alex J Med. 2011; 47:79–86.
Article29. Tuleasca C, Régis J, Sahgal A, De Salles A, Hayashi M, Ma L, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review: International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society Practice Guidelines. J Neurosurg. 2018; 130:733–757. PMID: 29701555.30. Tang YZ, Wu BS, Yang LQ, Yue JN, He LL, Li N, et al. The longterm effective rate of different branches of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia after single radiofrequency thermocoagulation: a cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e1994. PMID: 26559288.31. Keep MF, DeMare PA, Ashby LS. Gamma knife surgery for refractory postherpetic trigeminal neuralgia: targeting in one session both the retrogasserian trigeminal nerve and the centromedian nucleus of the thalamus. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102:276–282.
Article32. Tuleasca C, Carron R, Resseguier N, Donnet A, Roussel P, Gaudart J, et al. Multiple sclerosis-related trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective series of 43 patients treated with gamma knife surgery with more than one year of follow-up. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2014; 92:203–210. PMID: 25011487.
Article33. Schwarz W, Fox JM. Effects of monochromatic X-radiation on the membrane of nodes of Ranvier under voltage and current clamp conditions. Experientia. 1979; 35:1200–1201. PMID: 314907.
Article34. Szeifert GT, Salmon I, Lorenzoni J, Massager N, Levivier M. Pathological findings following trigeminal neuralgia radiosurgery. Prog Neurol Surg. 2007; 20:244–248. PMID: 17317993.
Article35. Maesawa S, Salame C, Flickinger JC, Pirris S, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. Clinical outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2001; 94:14–20. PMID: 11147887.
Article36. Gronseth G, Cruccu G, Alksne J, Argoff C, Brainin M, Burchiel K, et al. Practice parameter: the diagnostic evaluation and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the European Federation of Neurological Societies. Neurology. 2008; 71:1183–1190. PMID: 18716236.
Article37. Little AS, Shetter AG, Shetter ME, Bay C, Rogers CL. Long-term pain response and quality of life in patients with typical trigeminal neuralgia treated with gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 2008; 63:915–924. PMID: 19005382.
Article38. Urgosik D, Liscak R, Novotny J Jr, Vymazal J, Vladyka V. Treatment of essential trigeminal neuralgia with gamma knife surgery. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102:29–33.
Article39. Rogers CL, Shetter AG, Fiedler JA, Smith KA, Han PP, Speiser BL. Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: the initial experience of The Barrow Neurological Institute. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 47:1013–1019. PMID: 10863073.
Article40. Longhi M, Rizzo P, Nicolato A, Foroni R, Reggio M, Gerosa M. Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: results and potentially predictive parameters--part I: idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:1254–1261. PMID: 18162905.41. Guo S, Chao ST, Reuther AM, Barnett GH, Suh JH. Review of the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with gamma knife radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2008; 86:135–146. PMID: 18334855.
Article42. Pollock BE, Phuong LK, Gorman DA, Foote RL, Stafford SL. Stereotactic radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:347–353. PMID: 12186463.
Article43. Maher CO, Pollock BE. Radiation induced vascular injury after stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: case report. Surg Neurol. 2000; 54:189–193. PMID: 11077103.
Article44. Marshall K, Chan MD, McCoy TP, Aubuchon AC, Bourland JD, McMullen KP, et al. Predictive variables for the successful treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 2012; 70:566–573. PMID: 21849918.
Article45. Tang X, Wu H, Wang B, Zhang N, Dong Y, Ding J, et al. A new classification and clinical results of Gamma Knife radiosurgery for cavernous sinus hemangiomas: a report of 53 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2015; 157:961–969. PMID: 25862173.
Article46. McNatt SA, Yu C, Giannotta SL, Zee C-S, Zelman V, Apuzzo ML, et al. Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 2005; 56:1295–1303. PMID: 15918946.
Article47. Young B, Shivazad A, Kryscio RJ, St Clair W, Bush HM. Long-term outcome of high-dose γ knife surgery in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2013; 119:1166–1175. PMID: 23600932.48. Fountas KN, Smith JR, Lee GP, Jenkins PD, Cantrell RR, Sheils WC. Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: long-term outcome and complications. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 23:E8.
Article49. Taich ZJ, Goetsch SJ, Monaco E, Carter BS, Ott K, Alksne JF, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: clinical outcomes and prognostic factors. World Neurosurg. 2016; 90:604–612.e11. PMID: 26915701.
Article50. Zhao H, Shen Y, Yao D, Xiong N, Abdelmaksoud A, Wang H. Outcomes of two-isocenter gamma knife radiosurgery for patients with typical trigeminal neuralgia: pain response and quality of life. World Neurosurg. 2018; 109:e531–e538. PMID: 29038085.
Article51. Nicol B, Regine WF, Courtney C, Meigooni A, Sanders M, Young B. Gamma knife radiosurgery using 90 Gy for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93:152–154.
Article52. Massager N, Nissim O, Murata N, Devriendt D, Desmedt F, Vanderlinden B, et al. Effect of beam channel plugging on the outcome of gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 65:1200–1205. PMID: 16682146.
Article53. Pollock BE, Foote RL, Stafford SL, Link MJ, Gorman DA, Schomberg PJ. Results of repeated gamma knife radiosurgery for medically unresponsive trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93:162–164.
Article54. Hasegawa T, Kondziolka D, Spiro R, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. Repeat radiosurgery for refractory trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 2002; 50:494–500. PMID: 11841716.
Article55. Pollock BE, Foote RL, Link MJ, Stafford SL, Brown PD, Schomberg PJ. Repeat radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 61:192–195. PMID: 15629611.
Article56. Aubuchon AC, Chan MD, Lovato JF, Balamucki CJ, Ellis TL, Tatter SB, et al. Repeat gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 81:1059–1065. PMID: 20932665.
Article57. Rand RW, Jacques DB, Melbye RW, Copcutt BG, Levenick MN, Fisher MR. Leksell Gamma Knife treatment of tic douloureux. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1993; 61:93–102. PMID: 8115760.
Article58. Xu Z, Schlesinger D, Moldovan K, Przybylowski C, Sun X, Lee CC, et al. Impact of target location on the response of trigeminal neuralgia to stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg. 2014; 120:716–724. PMID: 24313616.
Article59. Matsuda S, Serizawa T, Nagano O, Ono J. Comparison of the results of 2 targeting methods in Gamma Knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2008; 109:185–189. PMID: 19123907.
Article60. Park SH, Hwang SK, Kang DH, Park J, Hwang JH, Sung JK. The retrogasserian zone versus dorsal root entry zone: comparison of two targeting techniques of gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010; 152:1165–1170. PMID: 20204664.
Article61. Shaya M, Jawahar A, Caldito G, Sin A, Willis BK, Nanda A. Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a study of predictors of success, efficacy, safety, and outcome at LSUHSC. Surg Neurol. 2004; 61:529–534. PMID: 15165787.
Article62. Zhao ZF, Yang LZ, Jiang CL, Zheng YR, Zhang JW. Gamma Knife irradiation-induced histopathological changes in the trigeminal nerves of rhesus monkeys. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:39–44.
Article63. Shrivastava A, Mohammed N, Hung YC, Xu Z, Schlesinger D, Heinrichs T, et al. Impact of integral dose on the maintenance of pain relief in patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia treated with upfront Gamma knife radiosurgery. World Neurosurg. 2019; 129:e375–e380. PMID: 31132503.
Article64. Morbidini-Gaffney S, Chung CT, Alpert TE, Newman N, Hahn SS, Shah H, et al. Doses greater than 85 Gy and two isocenters in Gamma Knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia: updated results. J Neurosurg. 2006; 105:107–111.
Article65. Kim YH, Kim DG, Kim JW, Kim YH, Han JH, Chung HT, et al. Is it effective to raise the irradiation dose from 80 to 85 Gy in gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia? Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2010; 88:169–176. PMID: 20431328.
Article66. Young RF, Vermulen S, Posewitz A. Gamma knife radiosurgery for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1998; 70 Suppl 1:192–199. PMID: 9782251.
Article67. Petit JH, Herman JM, Nagda S, DiBiase SJ, Chin LS. Radiosurgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: evaluating quality of life and treatment outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 56:1147–1153. PMID: 12829153.
Article68. Sheehan J, Pan HC, Stroila M, Steiner L. Gamma knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia: outcomes and prognostic factors. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102:434–441. PMID: 15796376.
Article69. Hayashi M, Chernov M, Tamura N, Taira T, Izawa M, Yomo S, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery of essential trigeminal neuralgia using Leksell Gamma Knife model C with automatic positioning system: technical nuances and evaluation of outcome in 130 patients with at least 2 years follow-up after treatment. Neurosurg Rev. 2011; 34:497. PMID: 21701866.70. Lucas JT Jr, Nida AM, Isom S, Marshall K, Bourland JD, Laxton AW, et al. Predictive nomogram for the durability of pain relief from gamma knife radiation surgery in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014; 89:120–126. PMID: 24613811.
Article71. Martínez Moreno NE, Gutiérrez-Sárraga J, Rey-Portolés G, Jiménez-Huete A, Martínez Álvarez R. Long-term outcomes in the treatment of classical trigeminal neuralgia by Gamma Knife radiosurgery: a retrospective study in patients with minimum 2-year follow-up. Neurosurgery. 2016; 79:879–888. PMID: 27560193.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia: Case Report
- Anatomical Considerations in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Idiopathic Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Epidermoid Tumor in the Cerebellopontine Angle
- Outcome of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia
- The Role of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Essential and Secondary Trigeminal Neuralgia: vs Microsurgery