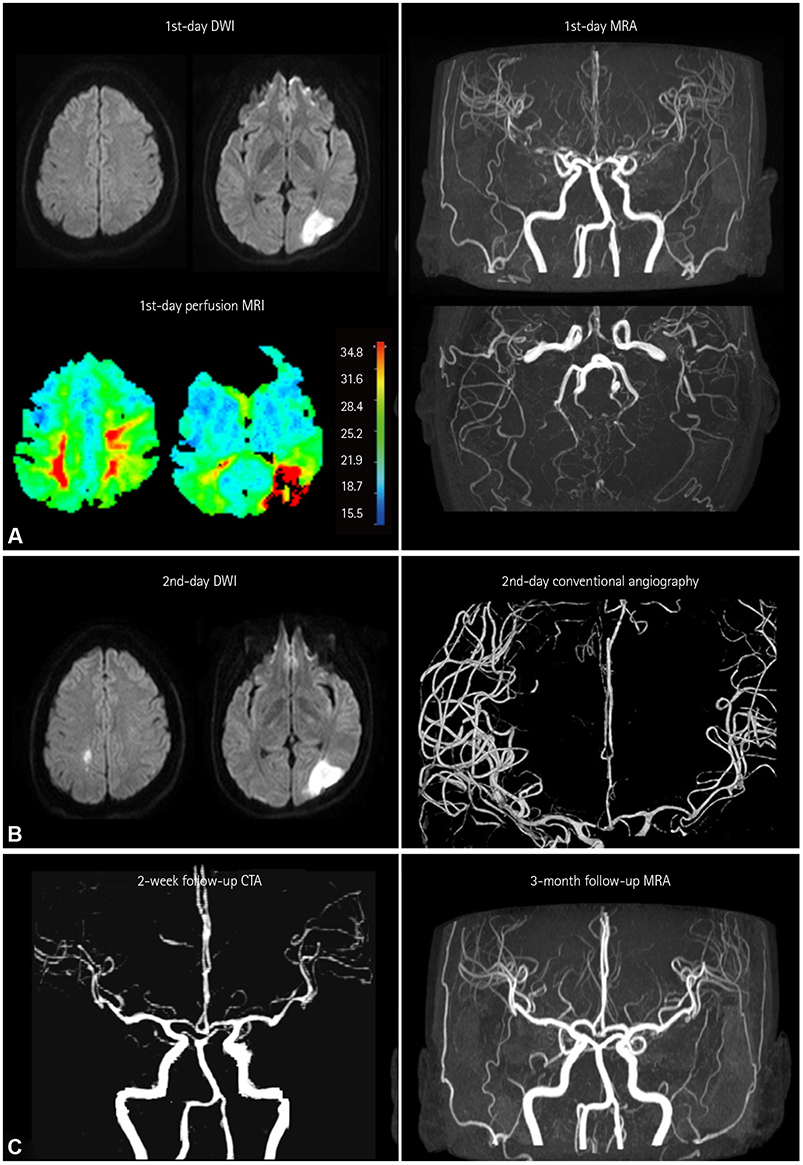
J Clin Neurol.
2019 Oct;15(4):588-590. 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.4.588.
Is the Presence of Headache Indispensable in Diagnosing Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Daejin Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea. gggbs@naver.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Daejin Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2467776
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2019.15.4.588
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Calabrese LH, Dodick DW, Schwedt TJ, Singhal AB. Narrative review: reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Intern Med. 2007; 146:34–44.
Article2. Wolff V, Ducros A. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome without typical thunderclap headache. Headache. 2016; 56:674–687.
Article3. Wolff V, Armspach JP, Lauer V, Rouyer O, Ducros A, Marescaux C, et al. Ischaemic strokes with reversible vasoconstriction and without thunderclap headache: a variant of the reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome? Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015; 39:31–38.
Article4. Chen SP, Fuh JL, Wang SJ. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: an under-recognized clinical emergency. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2010; 3:161–171.
Article5. Ducros A. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2012; 11:906–917.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Report Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome with Thunderclap Headache During Swimming
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Induced by Blood Transfusion
- Bilateral Anterior Cerebral Artery Infarction Associated with Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome
- Dynamic Arterial Change of Cerebral Vasoconstriction in Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Diagnosed by Visual Symptoms and Changes in Headache Patterns in a Patient with Chronic Migraine