J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2019 Dec;60(12):1269-1274. 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.12.1269.
Long-term Outcome of a Muscle Union Procedure in Patients with Horizontal Paralytic Strabismus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lethe22@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2466181
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2019.60.12.1269
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the long-term surgical outcomes of a muscle union procedure in patients with paralytic strabismus.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 20 patients who underwent muscle union procedure for paralytic strabismus from September 2010 to March 2018. We analyzed the clinical results before and at the final visit after surgery. We also compared the outcomes of the first year after surgery between patients with sixth cranial nerve palsy, with third cranial nerve palsy and with medial rectus muscle rupture after endoscopic sinus surgery.
RESULTS
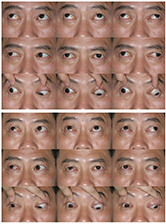
The mean follow-up duration was 42 ± 20 months (12-79 months). The mean age at surgery was 40 ± 19 years (7-65 years). Eleven patients underwent surgery for sixth cranial nerve palsy, six patients underwent surgery for third cranial nerve palsy, and three patients underwent surgery for medial rectus rupture after endoscopic sinus surgery. The mean horizontal deviation at the primary eye position was 58 ± 19 prism diopters before surgery and decreased to 14 ± 17 prism diopters at the final visit. The success rate at the last visit was 60%. The mean horizontal deviation at postoperative 1 year was 4 ± 9 prism diopters in the sixth nerve palsy group and 26 ± 16 prism diopters in the third nerve palsy group (p = 0.002). The success rate was 91% in the sixth nerve palsy group and 33% in the third nerve palsy group at postoperative 1 year (p = 0.017). There were no complications during surgery or anterior segment ischemia for any of the patients.
CONCLUSIONS
A muscle union procedure had good long-term surgical outcomes in patients with paralytic strabismus, especially in patients with sixth cranial nerve palsy. However, in the case of third cranial nerve palsy or rupture of the medial rectus muscle, the effects were limited.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clark RA, Demer JL. Rectus extraocular muscle pulley displacement after surgical transposition and posterior fixation for treatment of paralytic strabismus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 133:119–128.2. Foster RS. Vertical muscle transposition augmented with lateral fixation. J AAPOS. 1997; 1:20–30.3. Hussein MA, Coats DK. Limitation of opposing ductions following augmented horizontal rectus muscle transposition. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 136:947–949.4. Jensen CD. Rectus muscle union: a new operation for paralysis of the rectus muscles. Trans Pac Coast Otoophthalmol Soc Annu Meet. 1964; 45:359–387.5. Park KA, Oh SY. Muscle union procedure with medial rectus recession for unilateral abducens palsy. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2013; 50:e11–e14. Accessed May 1, 2019. https://www.healio.com/ophthalmology/journals/jpos/%7Bfcc1ab72-5f0b-4316-8a09-a408cf8b01fd%7D/muscle-union-procedure-with-medial-rectus-recession-for-unilateralabducens-palsy.6. Park KA, Lyu I, Yoon J, et al. Muscle union procedure in patients with paralytic strabismus. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0129035.7. Scott AB, Kraft SP. Botulinum toxin injection in the management of lateral rectus paresis. Ophthalmology. 1985; 92:676–683.8. Wright KW. Color atlas of strabismus surgery: strategies and techniques. 4th ed. New York: Springer;2007. p. 161–165.9. Selezinka W, Sandall GS, Henderson JW. Rectus muscle union in sixth nerve paralysis. Jensen rectus muscle union. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974; 92:382–386.10. Maruo T, Iwashige H, Kubota N, et al. Results of surgery for paralytic esotropia due to abducens palsy. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1996; 40:229–234.11. Muraki S, Nishida Y, Ohji M. Surgical results of a muscle transposition procedure for abducens palsy without tenotomy and muscle splitting. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 156:819–824.12. Rosenbaum AL, Kushner BJ, Kirschen D. Vertical rectus muscle transposition and botulinum toxin (Oculinum) to medial rectus for abducens palsy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:820–823.13. Simon JW, Price EC, Krohel GB, et al. Anterior segment ischemia following strabismus surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984; 21:179–185.14. Saunders RA, Phillips MS. Anterior segment ischemia after three rectus muscle surgery. Ophthalmology. 1988; 95:533–537.15. von Noorden GK. Anterior segment ischemia following the Jensen procedure. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976; 94:845–847.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Botulinum Toxin Chemodenervation in Chronic Paralytic Strabismus
- Simulation of Paralytic Strabismus and Its Surgical Management Using a Mathematical Model of the Eye
- Recession-Resection Surgery Augmented with Botulinum Toxin A Chemodenervation for Paralytic Horizontal Strabismus
- Effect of Vertical Transposition of the Horizontal Muscles on Vertical Strabismus Associated with Exotropia
- Strabismus Surgery on Congenital Oculomotor Nerve Palsied Eye