J Pathol Transl Med.
2019 Mar;53(2):148-151. 10.4132/jptm.2019.01.15.
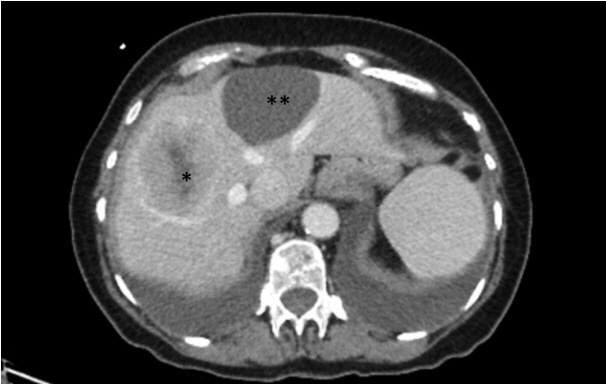
Metastatic Insulinoma Presenting as a Liver Cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY, USA. LeeH5@amc.edu
- 2Department of General Surgery, Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY, USA.
- KMID: 2465457
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.01.15
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Halfdanarson TR, Rubin J, Farnell MB, Grant CS, Petersen GM. Pancreatic endocrine neoplasms: epidemiology and prognosis of pancreatic endocrine tumors. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008; 15:409–27.
Article2. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2010. p. 322–6.3. Halfdanarson TR, Rabe KG, Rubin J, Petersen GM. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): incidence, prognosis and recent trend toward improved survival. Ann Oncol. 2008; 19:1727–33.
Article4. Zhang X, Song J, Liu P, et al. A modified M-stage classification based on the metastatic patterns of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: a population-based study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2018; 18:73.
Article5. Cloyd JM, Kopecky KE, Norton JA, et al. Neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas: degree of cystic component predicts prognosis. Surgery. 2016; 160:708–13.
Article6. Fiori S, Del Gobbo A, Gaudioso G, et al. Hepatic pseudocystic metastasis of well-differentiated ileal neuroendocrine tumor: a case report with review of the literature. Diagn Pathol. 2013; 8:148.
Article7. Isomura T, Kojiro M, Kawano Y, et al. Small multiple carcinoid tumors occurring in the ileum with a pseuodcystic liver metastasis. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1980; 30:137–43.8. Yoshioka M, Shibata S, Uchinami H, et al. The transformation of a nonfunctioning islet cell tumor of the pancreas into a proinsulinoma under conditions of lung metastasis. Intern Med. 2015; 54:785–90.
Article9. Bozkirli E, Bakiner O, Abali H, et al. A case of inoperable malignant insulinoma with resistant hypoglycemia who experienced the most significant clinical improvement with everolimus. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2013; 2013:636175.
Article10. Alexandraki K, Angelousi A, Boutzios G, Kyriakopoulos G, Rontogianni D, Kaltsas G. Management of neuroendocrine tumors of unknown primary. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2017; 18:423–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Correction of Ethics Statement: Metastatic Insulinoma Presenting as a Liver Cyst
- A Case of Malignant Insulinoma Resistant to Octreotide and Combination Chemotherapy
- A Case of Somatostatinoma which Manifested as Insulinoma when Metastasized to the Liver
- A case of hypoglycemia in a patient of hemangiopericytoma with hepatic metastasis
- Cystic Insulinoma of the Pancreas