Infect Chemother.
2019 Sep;51(3):315-329. 10.3947/ic.2019.51.3.315.
Historical Review of Leptospirosis in the Korea (1945 – 2015)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. macropha@korea.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Emerging Infectious Diseases, Korea University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2459048
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2019.51.3.315
Abstract
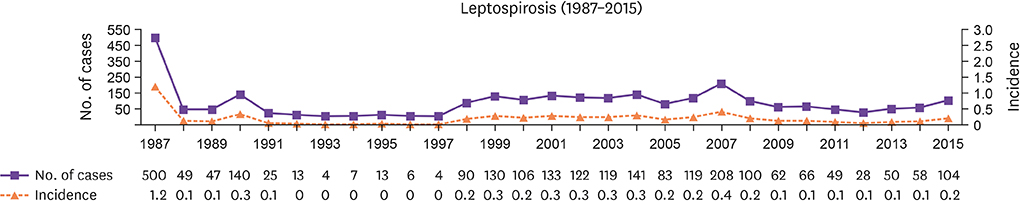
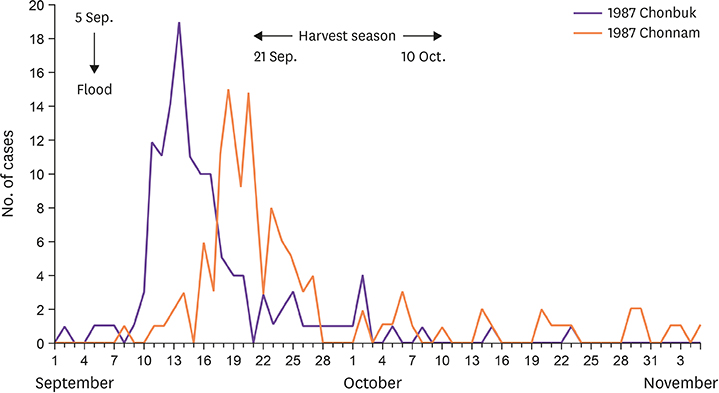
- Leptospirosis is a widespread worldwide zoonosis. Human leptospirosis was first identified in the Korea in 1984 as the cause of "epidemic pulmonary hemorrhagic fever of unknown etiology" that occurred sporadically or in outbreaks. The major outbreaks, leading to some deaths, mainly involved rice field farmers who worked in wet and muddy rice paddies following floods or heavy rainfalls. Leptospirosis was designated a nationally notifiable disease in 1987. The Korean government introduced a supplementary immunization program to control the disease from 1988 to 1997, which provided people at risk in endemic areas with the inactivated vaccine prepared from a local strain Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai. In addition, the continuous promotion of education and awareness in the media played a role in improving personal hygiene management. Since then, the reported incidence of leptospirosis has been low. Leptospirosis is currently considered in the differential diagnosis of acute febrile illnesses occurring in fall. This study historically reviews clinical and epidemiological publications, scientific reports, and public health policies for recognition, identification, and infection control of human leptospirosis in the Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Inada R, Ido Y, Hoki R, Kaneko R, Ito H. The etiology, mode of infection, and specific therapy of Weil's disease (Spirochaetosis icterohemorrhagica). J Exp Med. 1916; 23:377–402.
Article2. Weil A. On a strange, acute infectious disease, accompanied by swelling of the spleen, icterus, and nephritis. [German]. Dtsch Arch Klin Med. 1886; 39:209–232.3. Fain S. Leptospira and leptospirosis. Boca Raton: CRC press;1994. p. 1–19.4. Chun C. An overview of acute infectious diseases in South Korea. Seoul: Newest Medical Publisher;1975. p. 155–156.5. Chun CH. Zoonotic contagious disease in Korea. Korean J Infect Dis. 1975; 7:37–42.6. Kang SY, Park SC, Bahk YW, Chun C, Choi I. Panel discussion: A pneumonitis-like disease epidemic during this autumn. J Korean Med Assoc. 1975; 18:1095–1102.7. Park SC, Lee JH, Kim M, Park HC, Min SH, Lee BH, Kim CS. An epidemiological study on the epidemic pneumonitis, occurred in Ryeo Ju and I Cheon, central area of Korea, 1975. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:263–268.8. Nam SD. Epidemiological pattern of acute endemic respiratory diseases. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:269–273.9. Kim KH, Hong SJ, Lee HS, Kang MW, Kim HY, Chung KW, Chung HY, Chun CH, Kim SM, Lee CM, Kim JJ. Clinical pictures of the hemorrhagic pneumonia like disease which occurred epidemically in the central area of Korea in autumn, 1975. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:274–286.10. Chae IS, Shim BS, Chin CJ, Shin KC, Choi KO. An epidemiological, clinical, and radiological study of the epidemic pneumonitis, occurred in the central area of Korea in autumn, 1975. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:287–292.11. Bahk YW, Kim CY, Park SH, Suk YK. Radiologic manifestation of pneumonia-like disease occurred in the central area of Korea in autumn, 1975. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:293–297.12. Kim KS. On the radiologic findings. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:298–302.13. Han WS, Kim DS. Autopsy and postmortem needle biopsy findings of pneumonitis-like disease. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:303–306.14. Moon GJ. The gross and histopathological findings. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:307–309.15. Ro YM, Yuk SJ, Yoon HJ, Choi JS, Cho HK, Hahn BS, Kim KS, Park CI, Han HS. Acute febrile hemorrhagic lung disease of unknown cause – A report of 20 cases in the epidemic of October through November in 1975. J Korean Med Assoc. 1976; 19:315–323.16. Choe KH, Kim DS, Shin KC, Lee KY, Ro SK, Kim JJ, Lee JT, Shim BS, Shim YH, Chai IS. Epidemic pulmonary hemorrhagic fever: II. Retrospective study (1970-1974). J Korean Med Assoc. 1980; 23:145–150.17. Shim YH, Shim BS, Choe KH, Kim DS, Shin KC, Lee KY, Lee YW, Kim YJ, Chin CJ, Lee JT, Chai IS. Epidemic pulmonary hemorrhagic fever: I. Epidemiological and clinical observation. J Korean Med Assoc. 1980; 23:131–144.18. Kim JS, Lee CW, Oh DK, In SD, Lee YH, Cho WH, Lee WY, Kim SO. An analytic epidemiological study to test the hypothesis, leptospirosis as the cause of epidemic pulmonary hemorrhagic fever in Korea. Korean J Epidemiol. 1984; 6:8–15.19. Cho MK, Paik SB, Oh HB, Song C. Bacteriological studies on leptospirosis in Korea (1984). Korean J Epidemiol. 1984; 6:16–26.20. Lee WY, Lee BK, Kim JD, Kim JS, Kim SO. Leptospira interrogans “Korea” isolated from patients with epidemic pulmonary hemorrhagic fever. Korean J Epidemiol. 1984; 6:36–46.21. Paik SB, Shin YO, Chung IB, Kim KH, Chai IS. Isolation and identification of pathogen for pneumonitis-like disease epidemic in South Korea. Korea National Institute of Health Annual Report. 1976. 13:p. 127–134.22. Kim MJ. Infectious diseases occurring in autumn season in South Korea: Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of leptospirosis. J Korean Med Assoc. 1994; 37:1408–1414.23. Choi BY, Kang SM, Lee SJ, Park HB, Kim DW, Oh SJ, Kim JS. The surveillance and management system of leptospirosis in a rural community of Korea, 1989 and 1990. Korean J Epidemiol. 1993; 15:74–84.24. Lee HW. Seroepidemiologic studies of acute hemorrhagic diseases in Korea from 1985 to 1987 (hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, leptospirosis and scrub typhus). J Korean Med Assoc. 1988; 31:581–593.25. National Institute of Health. Studies on the Epidemiology of Leptospirosis in Korea (I). Final report from year 1. 1986. p. 109–127.26. Cho MK. Characterization of Leptospira interrogans isolated in Korea and seroepidemiological study on leptospirosis (1984-1987). J Korean Med Assoc. 1988; 31:612–622.27. Cho MK, Min CH, Kim YW, Yoon CS. Serological studies on leptospirosis in Kangwondo area (1985). J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1986; 21:205–210.28. Chang WH, Choi MS, Park KH, Lee WK, Kim SY, Choi IH, Choe KW, Woo JH, Song YW, Choi DH, Lee JH, Kim WY, Kee JI, Park YS, Kang SK, Park SK, Yoon SY, Kim JW, Chung SS, Kim SY. Seroepidemiological study of leptospirosis in Korea, 1987. Korean J Infect Dis. 1988; 20:179–186.29. Chang WH, Choi MS, Kee SH, Kim IS, Park CS, Kim IJ, Choi SB, Choe KW, Woo JH, Kang JS, Choi DH, Kim JW, Kim SH, Lee JH, Kim SY, Kee JI, Kim SY, Park KH, Yoon SY, Kim MC, Kang SK, Lee YK, Lee WK, Choi IH, Kim BC. Seroepidemiological survey of leptospirosis in Korea, 1988 and 1989. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1990; 25:341–346.30. Kim YW, Cho MK, Kim HS, Yoon CS, Yoo KS, Lee JH, Min CH. Patterns of acute febrile illness (murine typhus, scrub typhus, leptospirosis and hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome) from 1986 to 1990 in Korea. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1991; 26:431–441.31. Chang WH, Kim IS, Choi MS, Kee SH, Hahn MJ, Seong SY, Uhm KH, Lee JH, Kang JS, Kim SY, Park KH, Kim IJ. Seroepidemiological survey of the leptospirosis in Korea, 1986-1991. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1993; 28:13–22.32. Dikken H, Kmety E. Serological typing method for leptospires. In : Bergan T, Norris Jr, editors. Methods in Microbiology. New York: Academic Press;1978. 11:p. 259–309.33. Kobayashi Y, Tamai T, Oyama T, Hasegawa H, Sada E, Kusaba T, Hamaji M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against etiological agents of Weil's disease. Microbiol Immunol. 1984; 28:359–370.
Article34. Marshall RB, Wilton BE, Robinson AJ. Identification of leptospira serovars by restriction-endonuclease analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1981; 14:163–166.
Article35. Oh HB, Park KS, Cho MK. Serological analysis of Leptospira interrogans isolated in Korea by cross-agglutinin adsorption method (1985). J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1986; 21:337–343.36. Kim MJ. Serovar identification of Korean leptospiral strains with monoclonal antibodies. Korean J Med. 1987; 32:571–579.37. Kim MJ, Park SC, Oh HB. Clinical features of serologically proven leptospirosis in Korea and changes in leptospiral agglutinin titer. Korean J Med. 1987; 32:188–197.38. Chen T. Development and present status of leptospiral vaccine and technology of vaccine production in China. Jpn J Bacteriol. 1985; 40:755–762.
Article39. Chang WH, Kim SY, Seo JS. Restriction endonuclease DNA analysis of leptospiral field isolates from Korea. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1987; 22:463–471.40. Chang WH, Park KH, Lee JB. Serological analysis of Leptospira interrogans isolated in Korea by monoclonal antibodies. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1988; 23:277–292.41. Chang WH, Kim SY, Chun SW, Kee SH, Park KH, Kim IS. Restriction endonuclease DNA analysis and monoclonal antibody analysis of Leptospira interrogans isolated in Korea. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1989; 24:71–79.42. Cho MK, Kim YW, Min CH, Oh HB. Serovar Determination of Leptospira interrogans isolated in Korea by cross-agglutinin absorption method (1984-1987). J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1988; 23:169–177.43. Cho MK, Lee JH, Yoon CS, Kim YW, Min CH, Kim YS, Park KS, Oh HB. Serological analysis of Leptospira Interrogans in Korea using monoclonal antibodies and cross-agglutinin absorption test. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1989; 24:539–548.44. Oh HB, Chang WH, Cho MK, Seong WK, Park KS. Identification of new serovar yeonchon and hongchon belonging to Leptospira interrogans icterohemorragiae seogroup. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1991; 26:253–262.45. Sekiguchi I. Leptospirosis on Kyonsang-buck-do. [Japaness]. Saikingaku Zasshi. 1942; 553:164–172.46. Cha Y, Lee T. Study on leptospirosis, I. Seroepidemiological investigation of cattle. Domestic Animal Farming Hygiene Reports. 1959; 6:53–59.47. National Institute of Health. Studies on the Epidemiology of Leptospirosis in Korea (II). Final report from year 2. 1987. p. 110–147.48. Faine S. World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for the control of leptospirosis. Geneva: WHO;1982. 67:p. 21–23.49. Kim JS, Lee JW, Oh DK, In SD, Lee YH, Cho WH. An epidemiological study on identification of cause for epidemic pulmonary hemorrhagic fever. J Korean Med Assoc. 1985; 28:77–78.50. Chun HJ, Kim TY, Choi BK, Ahn CH, Oh JH, Kim YO, Lee WG, Kim JY, Byun HG, Lee HC, Park YJ. Clinical, roentgenological and pathological evaluation of hemorrhagic pulmonary fever. J Korean Military Med Assoc. 1985; 16:154–166.51. Choi BY, Chung DE, Lee SJ, Park HB, Park JB, Lee KH, Kim JS. An epidemiologic study on the leptospiral infection in the period of an anticipated epidemic - for soldiers stationed in a rural area. Korean J Epidemiol. 1992; 14:91–101.52. Lee HJ. A sero-epidemiologic study on leptospiros is among military personnel mobilized for harvesting in ricefield after flood [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University;1993.53. Kim MJ, Kang SK, Choi IS. Kobayashi YZ. Leptospirosis in Korea: clinical and epidemiologic study. In : Proceedings of Leptospirosis Research Conference 1990, Japanese Leptospirosis Research Society; Tokyo: Hokusen-sha pub;1991. p. 88–103.54. Chang WG, Song MJ, Cha YH, Kim KG, Paik UH, Kim YK, Kim SY, Kim YJ, Cho MK, Lee GJ. An epidemiological and clinical study of leptospirosis acquired by twelves combat policemen in september, 2000. Korean J Med. 2001; 61:553–561.55. Choi KW. Clinical characteristics of epidemic pulmonary hemorrhagic fever summarized from papers published. Korean J Epidemiol. 1984; 6:3–7.56. Kim MJ. Clinical characteristics of leptospirosis in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 1988; 31:623–627.57. Silva JJ, Dalston MO, Carvalho JE, Setúbal S, Oliveira JM, Pereira MM. Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features of the severe pulmonary form of leptospirosis. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2002; 35:395–399.
Article58. Seijo A, Coto H, San Juan J, Videla J, Deodato B, Cernigoi B, Messina OG, Collia O, de Bassadoni D, Schtirbu R, Olenchuk A, de Mazzonelli GD, Parma A. Lethal leptospiral pulmonary hemorrhage: an emerging disease in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002; 8:1004–1005.
Article59. Yersin C, Bovet P, Mérien F, Wong T, Panowsky J, Perolat P. Human leptospirosis in the Seychelles (Indian Ocean): a population-based study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998; 59:933–940.
Article60. Dolhnikoff M, Mauad T, Bethlem EP, Carvalho CR. Pathology and pathophysiology of pulmonary manifestations in leptospirosis. Braz J Infect Dis. 2007; 11:142–148.
Article61. Kang SJ, Lee KJ, Park KH, Jung SI. Clinical features of leptospirosis experienced in a university hospital between 2001 and 2007. Korean J Med. 2009; 77:453–460.62. Kim MJ. Clinical relevance of pulmonary involvement in leptospirosis. Korean J Med. 2009; 77:450–452.63. Chang W, Kim I, Lee W, Park K, Lee J, Chi J, Lee J. Microbiological and pathological features of experimentally induced leptospirosis in guinea pigs. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1986; 21:211–226.64. Woo JH. An experimental study of the pathogenesis of pulmonary hemorrhagic lesions in leptospirosis. Korean J Med. 1990; 38:644–655.65. Lee SH, Kim KA, Park YG, Seong IW, Kim MJ, Lee YJ. Identification and partial characterization of a novel hemolysin from Leptospira interrogans serovar lai. Gene. 2000; 254:19–28.
Article66. Lee SH, Kim S, Park SC, Kim MJ. Cytotoxic activities of Leptospira interrogans hemolysin SphH as a pore-forming protein on mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 2002; 70:315–322.
Article67. Lee JS, Yoon SC, Lee HY, Ahn KR, Kim SK, Chi JK. Clinical features of the case identified as leptospirosis. Korean J Epidemiol. 1984; 6:47–51.68. Lee JS, Ahn C, Oh HY, Kim S, Choi KW, Lee M, Chi JG, Kim YI, Sul DS, Park JM, Park YH. Clinical studies on leptospirosis in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 1986; 29:537–547.69. Kim SY, Yoon SJ, Kim JO, Lee BH. The leptospirosis associated with fever and rash. Korean J Infect Dis. 1986; 18:19–23.70. Kim SJ, Kim JM, Hyun CO, Hong SY, Song BS, Rhu HK, Park SC. A clinical study of leptospirosis in Chung Nam area. Korean J Infect Dis. 1987; 19:33–37.71. Kim WY, Han SY, Kim SK, Suh JE, Joo SA, Kim KM. The 16 cases of leptospirosis in Chuncheon area. Korean J Med. 1986; 30:745–750.72. Lee YC, Lee SH, Kwak ST, Hong KI, Choi MK, Kim YK, Kim KM, Kim YW, Cho MK. The 13 cases of confirmed leptospirosis in Chun Cheon area, by the culture and isolation of leptospira, in 1986. Korean J Med. 1987; 32:580–587.73. Park SK, Lee SH, Rhee YK, Kang SK, Kim KJ, Kim MC, Kim KW, Chang WH. Leptospirosis in Chonbuk Province of Korea in 1987: a study of 93 patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989; 41:345–351.
Article