Neurointervention.
2019 Sep;14(2):131-136. 10.5469/neuroint.2019.00094.
Alternative Transcarotid Approach for Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Case Series
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology, University Medical Center Goettingen, Goettingen, Germany. hanna.styczen@med.uni-goettingen.de
- 2Department of Neuroradiology, Clinic of Radiology, Neuroradiology and Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland.
- KMID: 2458493
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2019.00094
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Mechanical thrombectomy has become the standard of care for acute stroke caused by large vessel occlusion. As more patients are treated endovascularly, the number of older patients with tortuous vessels has risen. In these patients, catheterizing the internal carotid artery via a transfemoral approach can be very difficult or even impossible. Therefore, in selected patients, alternative strategies to the transfemoral approach have to be applied.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
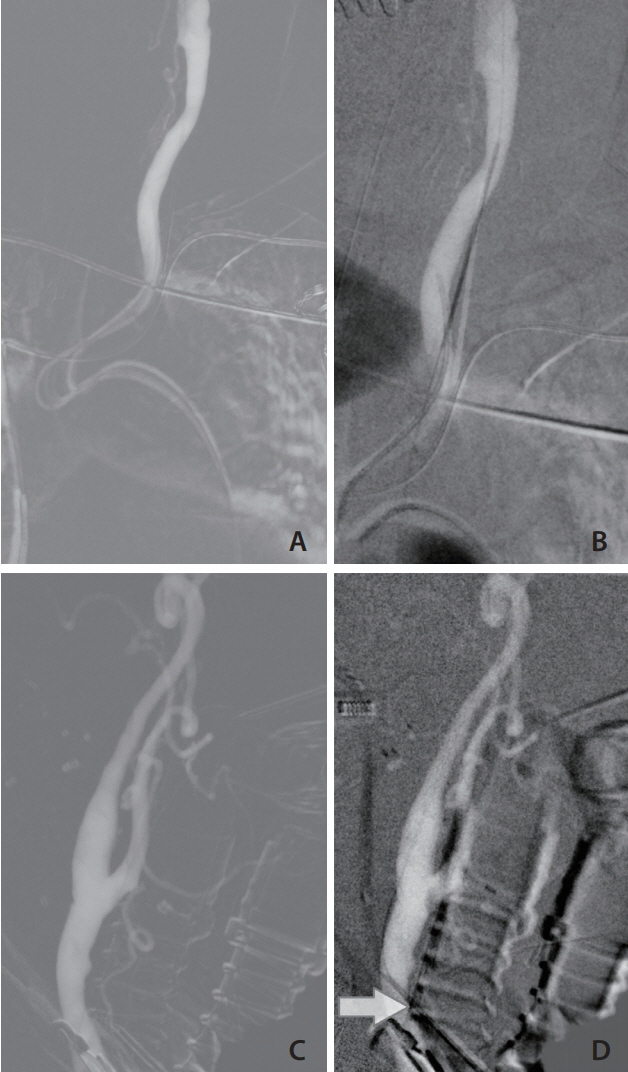
We report a case series of six patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy via a combined transfemoral and transcarotid approach. Puncture of the carotid artery was conducted using roadmap guidance after an unsuccessful transfemoral attempt. Technical aspects and outcomes with this alternative approach were analyzed.
RESULTS
Direct puncture of the carotid artery was achieved in five out of six patients (83%). In three out of six patients (50%), revascularization (modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction score ≥2b) was restored. No complications related to endovascular therapy were documented. One patient showed good neurological outcome (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] 5 at admission, mRS 1 at discharge).
CONCLUSION
A combined transfemoral/transcarotid approach can be an alternative vascular access in patients with problematic vessel anatomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Pull-Through Buddy Wire Technique for Endovascular Thrombectomy in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: Technical Note
Pin-Yi Chiang, Yen-Heng Lin, Yu-Cheng Huang, Chung-Wei Lee
Neurointervention. 2021;16(1):64-69. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2020.00409.
Reference
-
1. Jo KW, Park SM, Kim SD, Kim SR, Baik MW, Kim YW. Is transradial cerebral angiography feasible and safe? A single center’s experience. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 47:332–337.
Article2. Goland J, Doroszuk GF, Garbugino SL, Ypa MP. Transradial approach to treating endovascular cerebral aneurysms: case series and technical note. Surg Neurol Int. 2017; 8:73.
Article3. Montorsi P, Galli S, Ravagnani PM, Tresoldi S, Teruzzi G, Caputi L, et al. Carotid artery stenting with proximal embolic protection via a transradial or transbrachial approach: pushing the boundaries of the technique while maintaining safety and efficacy. J Endovasc Ther. 2016; 23:549–560.4. Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:1019–1030.5. Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:2296–2306.
Article6. Ribo M, Flores A, Rubiera M, Pagola J, Mendonca N, Rodriguez-Luna D, et al. Difficult catheter access to the occluded vessel during endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke is associated with worse clinical outcome. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013; 5 Suppl 1:i70–i73.
Article7. Wiesmann M, Kalder J, Reich A, Brockmann MA, Othman A, Greiner A, et al. Feasibility of combined surgical and endovascular carotid access for interventional treatment of ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016; 8:571–575.
Article8. Jadhav AP, Ribo M, Grandhi R, Linares G, Aghaebrahim A, Jovin TG, et al. Transcervical access in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014; 6:652–657.
Article9. Castaño C, Remollo S, García MR, Hidalgo C, Hernández-Perez M, Ciorba M. Mechanical thrombectomy with “ADAPT” technique by transcervical access in acute ischemic stroke. Neuroradiol J. 2015; 28:617–622.
Article10. Alvarez B, Matas M, Ribo M, Maeso J, Yugueros X, Alvarez-Sabin J. Transcervical carotid stenting with flow reversal is a safe technique for high-risk patients older than 70 years. J Vasc Surg. 2012; 55:978–984.
Article11. Maus V, Henkel S, Riabikin A, Riedel C, Behme D, Tsogkas I, et al. The SAVE technique: large-scale experience for treatment of intracranial large vessel occlusions. Clin Neuroradiol. 2018; Jul. 19. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-018-0702-4.
Article12. Mokin M, Snyder KV, Levy EI, Hopkins LN, Siddiqui AH. Direct carotid artery puncture access for endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke: technical aspects, advantages, and limitations. J NeuroInterv Surg. 2015; 7:108–113.
Article13. Roche A, Griffin E, Looby S, Brennan P, O’Hare A, Thornton J, et al. Direct carotid puncture for endovascular thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019; 11:647–652.
Article14. Fjetland L, Roy S. Transcarotid endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018; 29:1006–1010.
Article15. Psychogios MN, Behme D, Schregel K, Tsogkas I, Maier IL, Leyhe JR, et al. One-stop management of acute stroke patients: minimizing door-to-reperfusion times. Stroke. 2017; 48:3152–3155.16. Kaymaz ZO, Nikoubashman O, Brockmann MA, Wiesmann M, Brockmann C. Influence of carotid tortuosity on internal carotid artery access time in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Interv Neuroradiol. 2017; 23:583–588.
Article17. Blanc R, Piotin M, Mounayer C, Spelle L, Moret J. Direct cervical arterial access for intracranial endovascular treatment. Neuroradiology. 2006; 48:925–929.
Article18. Blanc R, Mounayer C, Piotin M, Sadik JC, Spelle L, Moret J. Hemostatic closure device after carotid puncture for stent and coil placement in an intracranial aneurysm: technical note. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:978–981.19. Massiere B, von Ristow A, Cury JM, Gress M, Vescovi A, Pedron C, et al. Closure of carotid artery puncture site with a percutaneous device. Ann Vasc Surg. 2009; 23:256.e5–e7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intravenous Thrombolysis and Endovascular Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke with Minor Symptom
- Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Emergency Microsurgical Embolectomy for the Treatment of Acute Intracranial Artery Occlusion: Report of Two Cases
- Endovascular recanalization therapy for patients with acute ischemic stroke with hidden aortic dissection: A case series
- Endovascular Treatment May Be Effective in Preventing Recurrence of Ischemic Stroke in Vertebral Artery Stump Syndrome: A Case Series